A Good Place to Hide
HOW ONE FRENCH COMMUNITY SAVED THOUSANDS OF LIVES DURING WORLD WAR II
PETER GROSE

A GOOD PLACE TO HIDE
Pegasus Books LLC
80 Broad Street, 5th Floor
New York, NY 10004
Copyright 2015 by Peter Grose
First Pegasus Books hardcover edition April 2015
ISBN: 978-1-60598-692-0
ISBN: 978-1-60598-751-4 (e-book)
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in whole or in part without written permission from the publisher, except by reviewers who may quote brief excerpts in connection with a review in a newspaper, magazine, or electronic publication; nor may any part of this book be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or other, without written permission from the publisher.
Distributed by W. W. Norton & Company, Inc.
CONTENTS
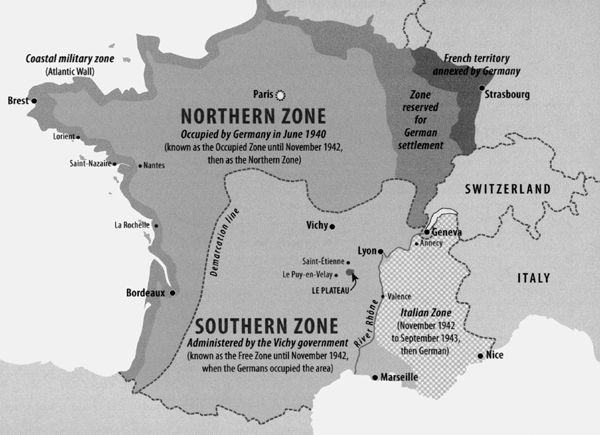
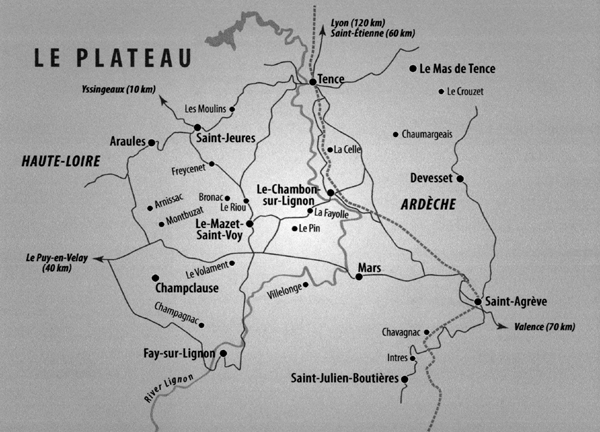
The drive to the village of Le Chambon-sur-Lignon, in the hilly Auvergne region of central-eastern France, brings back childhood memories of those never-ending car trips peppered with the question Are we there yet? The 80-kilometre journey from Saint-tienne, the nearest city of any consequence, starts on a broad national highway. The route soon narrows down to a local departmental road, the twisting and almost deserted D103, which scrambles up through hills, following the course of the River Lignon. Towards the end of this road, the trees give way to vast panoramas across green fields. These are the pastures of the plateau of Vivarais-Lignon. The joy of the drive is the scenery, which is stunningly beautiful, with towering dark forests lining the first part of the route, followed, in spring, by wild forget-me-nots along the verges, while vivid yellow Scotch broom flowers light up the fields and hillsides beyond. In winter it is a different story: the road disappears under treacherous snow, with only some slim poles to mark where the road ends and the ditch begins.
The villages of the Plateau are few, and usually far between. This is Huguenot country, and the Protestants fully live up to their French stereotype. The houses are built of grey granite supporting thick slate roofs, with none of the flashes of colour that distinguish the sunny houses of Provence or the cheerful chalets of the French skiing resorts in the mountains across the River Rhne. In the villages of the Plateau, few windows have the traditional flowerboxes with bright geraniums. These are solid, grey houses, and nothing flamboyant disturbs their serenity. They give the impression of being occupied by equally solid people, honest and hard-working, a world away from the bright lights of Paris, or the hedonistic bedlam of the Cte dAzur. This is not wine country, or even food country. (None of the modest handful of restaurants, bars and cafs in Le Chambon is ever likely to trouble the Michelin inspectors.)
At the small village of La Fayolle, about three kilometres outside Le Chambon, there is a graceful old farmhouse close to the road. At the time of writing, it was being lovingly restored by a young couple, Philippe and Aziza Mariotte, who run part of it as a bed and breakfast (chambre dhte in French) known as LAulne. In the years between 1940 and 1944, the farmhouse offered a different kind of hospitalitynot quite as comfortable, and a great deal more dangerous.
The buildings of LAulne form a U-shape. The Mariottes live in one wing and the bedrooms of the B&B occupy another. Across the courtyard from the Mariottes home, and still part of the same U-shape, is a large stone barn. At one end there is a tiny doorway, leading to a couple of equally tiny, linked storerooms, not much bigger than two large cupboards.
Today the storerooms are piled with junk: ancient bicycles, discarded furniture, a couple of window-frames, an old metal jug. The wooden panelling on the walls has come away in places. Cobwebs festoon the beams and the ceiling. The second room looks impossibly small for someone to sleep in, let alone live in. The entry room looks even more cramped, surely too small a workspace for a pair of forgers.
Yet in these two storerooms, and in scattered barns, farmhouses, spare rooms, hostels, guesthouses, hotels and school dormitories, literally thousands of human beings survived who might otherwise have been murdered. In the years between 1940 and 1944, something extraordinary happened here and in hundreds of farmhouses like it. In those dark days of World War II, human decency was in short supply. But on the Plateau, it triumphed.
Peter Grose
March 2014
Oscar Rosowskys childhood was nothing if not exotic. He came from a family of Russian Jews, originally from the town of Bobruysk, 600 kilometres southwest of Moscow, in Byelorussia. Oscars grandfather had made the family fortune, building a substantial business exporting oak wood.
There was enough money to pay for graduate studies for Oscars father, so he moved to Riga, the capital of nearby Latvia. Graduate studies were a serious privilege: higher education was not for Jews in Tsarist Russia. After the Russian revolution, Oscars father settled in Latvia and took Latvian citizenship. In 1921 he married Oscars mother in the Latvian beach resort town of Libau.
Oscars grandfather had planned carefully for his three sons. The oldest son was placed in charge of one branch of the family timber business, in the port town of Danzig, then part of Germany; the youngest son managed another branch in Edinburgh, Scotland; Ruben Rosowsky, the middle son and Oscars father, took charge in Berlin. Oscar was born in Berlin in 1923.
Oscars family kept their Latvian citizenship, but in Berlin they led a very Russian life. They spoke nothing but Russian at home, though Oscar never learned to read or write Russian. At school, he learned to write as well as speak German. The Nazi Party was on the rise, and anti-Semitism was widespread in Germany; however, the family made no attempt to conceal their Jewish identity. It was barely visible anyway: they were liberal rather than strict or Orthodox Jews. Oscar Rosowsky remembers a visit from his grandfather to Berlin when the family observed the Passover ceremony and ate the Passover meal, but in general Oscars father stayed away from the synagogue, doing no more than popping in occasionally for Yom Kippur.
These were golden days for the Rosowskys. Germanys Weimar Republic was breaking all records for financial catastrophe, and the German currency famously collapsed in 1923. Anyone with foreign currency was king, and the Rosowskys, whose business was exporting timber, had access to hard currency. They lived in a furnished six-room apartment in Berlins fashionable Charlottenburg district, rented from a Prussian Army officer down on his luck (he and his wife slept behind the kitchen). Young Oscar spent his primary school years surrounded by gilt antique furniture. His parents social life included throwing a succession of extravagant parties.
Although this was the period of Hitlers rise to power, the Rosowskys Jewishness caused no problems. As far as their German friends and neighbours were concerned, they were Latvians, and Latvians were like brothers to Germans. The familys wealth even spared Oscar some pain at school. At the strict boys primary school he attended, one of the teachers kept two canes, which he soaked in a humidifier to inflict maximum pain on boys who irritated him. But the public beatings were reserved for poor children. Oscars family was rich, and he emerged from primary school unscathed.












