MAGINOT LINE GUN TURRETS
AND FRENCH GUN TURRET DEVELOPMENT 18801940
INTRODUCTION
In any discussion of the Maginot Line, the key question is always asked: was the Maginot Line a success or failure during the Battle of France in 1940? The answer depends on perception of the role the line was intended to play. If one believes the Maginot Line was built for the primary purpose of stopping a German invasion of France, most will consider it a massive failure and a waste of money, because it did not achieve this. In reality, the line was not built to be the ultimate saviour of France, although too many Frenchmen at the time believed it to be so, thus giving them a very false sense of security and resulting in subordination of the offensive spirit of 1914. Rather, it was assigned a series of minor yet crucial roles, all of which were fulfilled. The problem with the Maginot Line is that it was not used as it should have been by the French army. Nevertheless, theory aside, its engineering was outstanding. Based on its proven performance, in particular its armoured gun turrets, one can only conclude that the Maginot Line was a remarkable weapon, and that is what we will discuss here.
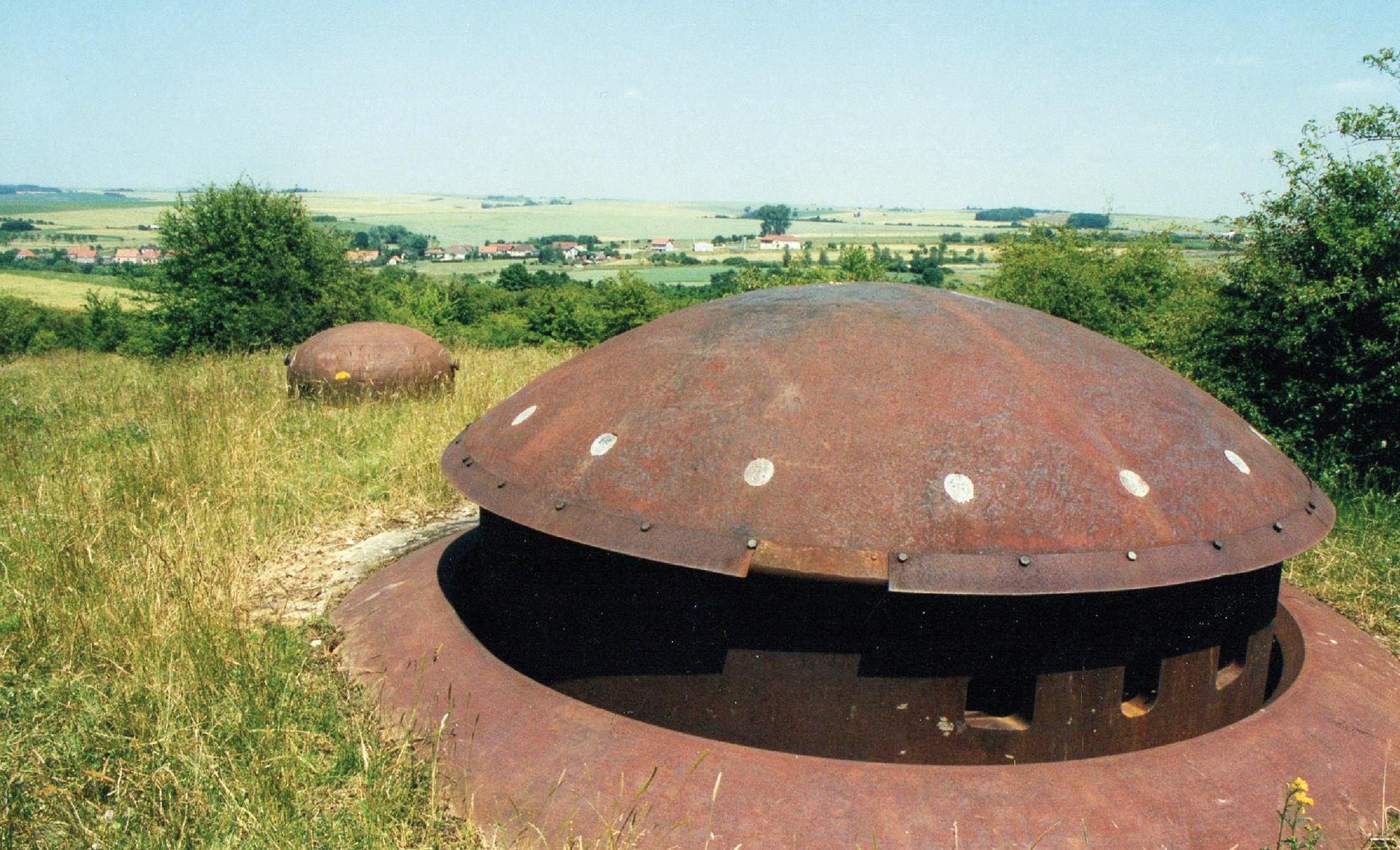

The mixed-arms turret of Ouvrage du Welschoff, Fortified Sector Rohrbach. The cloche GFM Type B is in the background. (Authors collection)
The armoured gun turret a revolving compartment driven by a motor that fits into a circular well has been around for a long time and it still exists in several forms today, primarily mounted on tanks and ships. The turret was first developed to protect guns and gunners as artillery became more accurate and powerful. A typical model revolved 360 degrees with its guns adjustable to fire at various angles. The first French armoured gun turrets were built primarily for land-based fortifications, because, from 1870 to 1940, the French were fighting for their lives and their territory against a powerful and aggressive German empire. The French were constantly building and being forced to modernize what they had just built.
Bloc 5 of Ouvrage du Monte-Grosso in the Alpes-Maritimes in 1983. The turret was restored by the French liberation forces and took part in combat against the Germans on the Plateau dAuthion in October 1944.
(Wikimaginot.eu Collection)
The first French gun turrets began as revolving turrets, but they evolved into a retractable model, a feature that made them different from those of other European countries. The original designs were tough, made of cast iron and steel that stood the test of fire, but the only way to protect the gun embrasures was to turn the guns away from the direction of enemy fire. Colonel Bussire, a French engineer, turned them from simple to sophisticated. Bussire designed the first retractable turret, the tourelle clipse, that enabled the turret to drop below the surface of its concrete housing to mask the embrasures. His idea evolved into the excellent designs found in the French forts of World War I and later the Maginot Line.
Despite a rough start in 1914, after which they were virtually emptied of their garrisons and stripped of flanking weapons, the French forts redeemed their value during the battle of Verdun. The earlier turrets performed well despite being hit by a massive number of heavy-calibre German shells, up to and including 420mm. Their engineering concepts also proved to be very reliable and durable. The engineers of the Maginot Line adopted and further perfected these designs, creating magnificent weapons that proved their worth during the German onslaught in 1940.
The guns were operated by professional, highly trained teams quipes who followed very tight procedures similar to those used in French naval vessels. As turrets had their origins on naval vessels it is no surprise that the forts of the Maginot Line were compared to land-based ships. They were swift to intercede and very accurate, and remained a thorn in the German side throughout the campaign.
DEVELOPMENT OF FRENCH ARMOURED TURRETS: 18701940
Pre-Maginot Era (18701914)
Since ancient times the science of fortification engineering has been a constant seesaw battle between attack and defence. For France, the Maginot Line gun turrets were the culmination of this battle the ultimate armoured protection of both gun and gunner from increasingly powerful enemy artillery shells, with the ability to strike the enemy quickly, powerfully and accurately. The final product, the armoured gun turret a revolving cylindrical compartment for one or two guns of various sizes and missions was an offshoot of the concept of using armoured masking to protect guns in land and coastal defences. The British coastal defences in particular incorporated armour into their coastal gun ports. In 1855 the British navys Captain Cowper Coles proposed the development of the first rotating armoured turret for the protection of naval guns. The proposal was rejected by the Admiralty but in 1860 the Swedish inventor John Ericsson developed an armoured turret for the American Union navys ironclad gunboat Monitor.
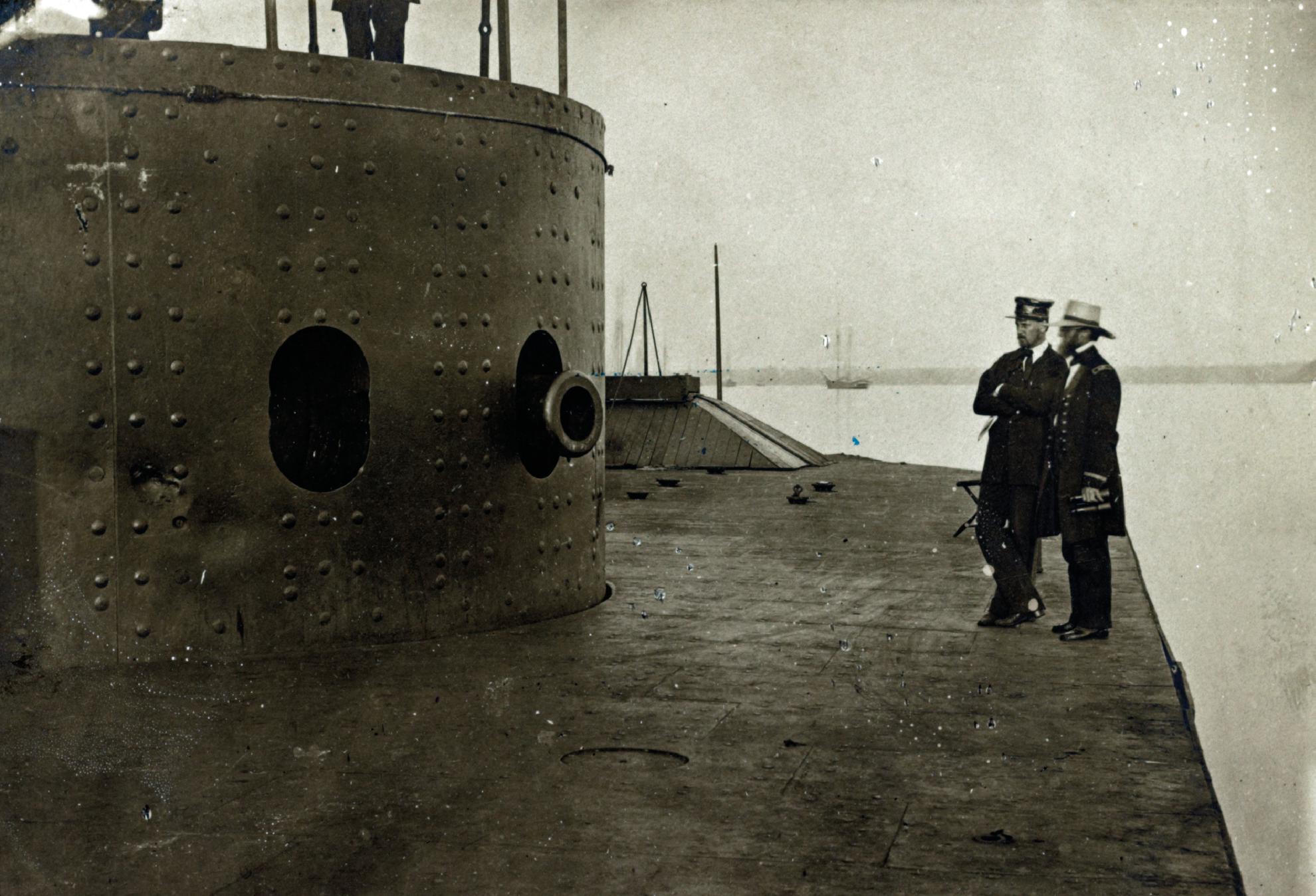

The Ericsson turret on the Union Navy ironclad USS Monitor. The turret was based on the design by British Navy engineer, Captain Cowper Coles. (Authors collection from US Library of Congress)
From 1852 to 1865, Belgian General Henri Alexis Brialmont, one of Europes greatest military engineers, conducted tests at Antwerp on various types of armour plating. In 1863, the first revolving turret, armed with two 240mm cannons based on the plan of Captain Coles, was installed at Antwerps Fort No. 3. In 1865, Captain Schumann, a Prussian army engineer, went to Antwerp, observed the Coles turret and began a series of experiments in Mainz and Berlin that culminated in 1870 with the presentation of his own design. The Schumann turret was manufactured by the armaments division of Grson (later acquired by Krupp). Built to house a 150mm cannon, the turret rotated on a circular crown of 16 cast-iron wheels. The armour was composed of a wall of rolled sheet iron topped by a spherical cap made of iron plates.
After the 1870 war between France and Germany the French created the Commission des Cuirassements (Armour Commission) to develop armoured protection for a system of forts being built along their redrawn Alsace/Lorraine border. The secretary of the commission was Commandant du Gnie Henri-Philippe Mougin. He developed the Casemate Mougin en fer lamin, a small metal compartment fronted with rolled steel plates 15cm thick, 40cm wide and 34cm high, mounted to a concrete base.
From 1876 to 1878 the French and Germans continued to test new forms of metal. The current alloy of steel stood up well to the penetration of a shell, but shattered under repeated shock. Rolled steel was tested against cast iron. Molten iron was produced under the same conditions as steel but with a 3 per cent carbon content added. It was then poured into a thick metal mould. When it cooled it formed a very strong substance called chilled cast iron. After additional testing the French armoured commission decided to use cast-iron armour rather than rolled steel sheets. Cast iron could be produced in greater thicknesses, was cheaper than rolled steel and could be moulded into more functional shapes.














