1.1 Definition of Andrology
Andrology is defined as the branches of science and medicine dealing with reproductive functions of the male under physiological and pathological conditions (Statutes of the European Academy of Andrology).
If this definition were to be interpreted in the context of sociobiology, considering reproduction the central task of life to which the entire organism is devoted (e.g., Dawkins ), andrology would be a broad field. Generally and also for the purpose of this book, andrology is considered the science and practice of dealing with male reproductive functions and their disturbances in the strict sense. Following the definitions of the WHO, male reproductive health is the subject of andrology.
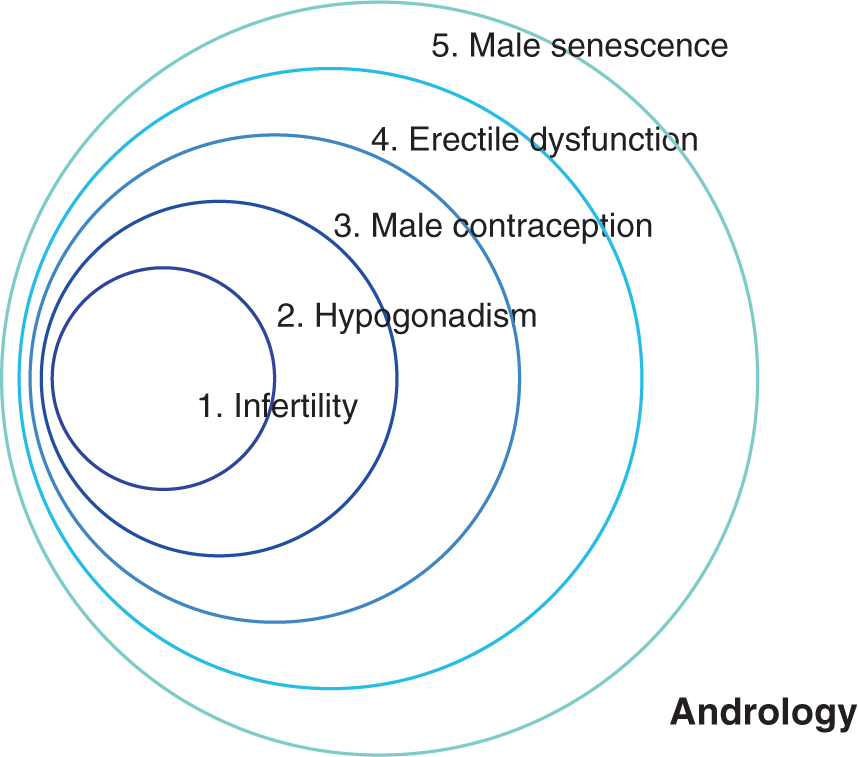
The central topics of andrology are: (1) Infertility, (2) hypogonadism, (3) male contraception, (4) erectile dysfunction, and (5) male senescence (Fig. ).
Fig. 1.1
Symbolic representation of development and scope of andrology
1.2 Andrology, Gynecology, Reproductive Medicine: Reproductive Health
Every layman knows that a man and a woman are necessary to produce offspring. However, a barren couple does not necessarily know whether the affliction lies on the male or the female or both sides. Therefore, it would be sensible for the couples to turn to a physician in a discipline dealing holistically with problems of infertility.
No matter how logical this concept may appear to the patients, medicine has barely offered appropriate solutions. Most often the individual partners of a barren couple continue to consult physicians of different disciplines in order to be diagnosed and treated. For the woman it is relatively easy to find a competent physician, since gynecology is a traditional field of medicine and amply represented.
It is much more difficult for the afflicted male. If he suspects problems of infertility on his part, he does not know immediately to whom he should turn. One third first consults the primary health care physician or family practitioner, one quarter turns to (his wife's) gynecologist and the remaining patients consult urologists (Bruckert ) and perhaps endocri-nologists. As a firm discipline of medicine andrology is established in very few countries. It is a recognized field only in Poland and Estonia; in Italy it is a speciality, practiced, however, within the frame of endocrinology. In addition, andrology is a speciality in Egypt and Indonesia. Finally, in Germany, in 2003 the Federal Medical Board published guidelines for specialization including andrology and by 2005 andrology was established in all 16 State Medical Boards as a subspeciality of urology, endocrinology/ internal medicine, and dermatology, the qualifications for which can be acquired after an 18-month postgraduate course which can be reduced to 12 months if andrological training had been included in the basic courses.
The European Academy of Andrology (EAA), founded in 1992, has established over 20 training centers in Europe.
These centers offer a 2-year course in which quali-fied physicians can acquire the specialty training required for the EAA examination. It is the hope of the EAA that this will gradually lead to official recognition of the field throughout Europe. Recent acceptance of the EAA training objectives by the German Federal Medical Board is an acknowledgement of this goal.
From the point of view of the afflicted couple, a specialized interdisciplinary field of reproductive medicine would seem to offer a solution. A few such services are in fact available at universities or in individual practices. It is, however, seldom that both partners of an infertile couple are cared for by one person; usually an interdisciplinary team consisting of an andrologist and a gynecologist working together represent reproductive medicine. At the same time there is a tendency to recognize that, because reproductive medicine has become so complex and comprehensive over recent decades, a discipline encompassing both sexes is imaginable. Especially those gynecologists working in this field have distanced themselves so far from oncology and obstetrics that they can conceive of an independent specialty of reproductive medicine including andrology .
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers the couple as a single entity in its definition of reproductive health , which it defines as freedom from disease and disturbances of reproductive functions, both in the male and in the female. As part of its concept of reproductive health the WHO postulates that reproduction should take place in an environment of physical, mental and social well-being. In addition, in its demand for self-determination of the number of children by the couple, it assumes that both partners have free access to reliable contraceptive methods. In its research program on human reproduction the WHO devotes itself to problems both in the female and in the male. Whereas in previous years the investigation of female reproductive functions stood in the foreground, more recently studies on male fertility have been given equal weight.
As desirable as care for the infertile couple by only one attending physician may appear, it should not be overlooked that, apart from the initial consultation and those eventually occurring during the course of treatment, the actual investigations of husband and wife do not necessarily proceed in synchrony. Only when techniques of assisted fertilization, which, however, are still only appropriate for selected couples, are applied is closest cooperation mandatory. Moreover, andrology covers certain aspects of male reproductive functions which can be treated largely without recourse to the partner, e.g., replacement therapy in hypogonadism, delayed pubertal development, erectile dysfunction, contraception and male senescence. For this reason, in addition to gynecology , the part of reproductive medicine dealing with the male, i.e., andrology , is indispensable. Moreover, the field of reproductive gynecology is so comprehensive that it cannot adequately deal with problems of the male as well. While not losing sight of the goal of an integrated field of reproductive medicine, at present, the development of gynecology and andrology as separate fields seems to offer the most advantages, not forgetting, however, that both fields should cooperate most closely in the care of the infertile couple, e.g., within the framework of a center for reproductive medicine . When treatment consists of assisted reproduction, German guidelines (Bundesrztekammer ) require that one of a minimum of three physicians must be an andrologist. For practical purposes this means that an andrologist must be part of every center of reproductive medicine.