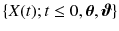1.1 Introduction
Prognosis and health management (PHM) has drawn increasing attention and gained deepening recognition and widening applications during the past decades [], as well as commercial companies such as Boeing have launched a great deal of theoretical and applied research works about PHM technology. The PHM conference has been successfully organized and held by IEEE Reliability Society in Shenzhen, Macau, Beijing, Rome, and Zhangjiajie respectively, Beijing in six consecutive years since 2010.
Remaining useful life (RUL) estimation, offering guidance for sequential management involving inspection schedule, maintenance, replacement and spare parts ordering, has been considered as the kernel technology of PHM, and the focus of current research in the field of reliability also. According to Petchs classical monograph about PHM technology []. While being satisfactory for RUL estimation under each specific applying condition, these methods exhibit some limits in cases with heterogeneity from the inner states or the external operating conditions of systems.
Heterogeneity is widespread in the inner states of the system and the related working environments. Examples involve that a weapon system may experience various operating conditions, saying storage, inspection, transport, and maintenance during its life cycle due to different tasks; that a manufacture system produces different products under different workloads; and that even systems from the same category may exhibit various degrading paths in the same environment. The performance degradation of a system is a result of interactions of both inner deterioration and working environment of the system, indicating a need for incorporating the heterogeneity into degradation modeling, to achieve a more accurate RUL estimation. For particular heterogeneity, such as the unit-to-unit variability, changing working conditions and periodic tasks, many recent advances in RUL estimation have appeared. However, to the best of the authors knowledge, there is still no review regarding degradation modeling and RUL estimation for systems with heterogeneity. Therefore, this chapter tries the best to fill this gap.
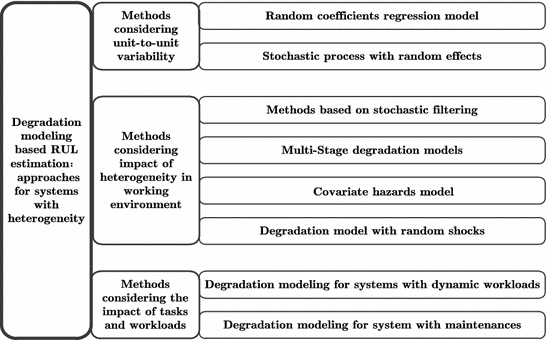
Toward the end of this chapter, three kinds of heterogeneity are considered consecutively: the unit-to-unit variability for systems from the same category, the variability in time-varying operating conditions, and the diversity of tasks and workloads of system during their life cycles. The first kind of variability describes the differences in degradation processes of units from the same category, while the second represents noninform working conditions related to the degradation, such as the time-varying, multi-state and stochastic working environments or random shocks. The third kind of heterogeneity captures the influence of changes in tasks and management activities involving inspection, maintenance, etc. Accordingly, this chapter classifies methods addressing degradation modeling and RUL estimation with heterogeneity into three kinds, each of which considers one kind of heterogeneity introduced above and consists of some subclassifications. The taxonomy of RUL estimation approaches for systems with heterogeneity is illustrated in Fig..
Fig. 1.1
Taxonomy of RUL estimation approaches for system under heterogeneity
The remainder of the chapter is structured as follows: Section concludes the chapter and provides several possible directions for future studies.
1.2 Methods Considering Unit-to-Unit Variability
A large number of experiments and engineering phenomena show that systems of the same category, even from one batch degrade differently from one another in performance. This kind of difference in degradation is usually defined as the unit-to-unit variability, due to the variability in inner structures of the considered systems, as well as the diversity in their working environment. Commonly, models with random effects are employed to capture the unit-to-unit variability, when we model the degradation process and estimate the RUL. The most typical way to do so is to specify some parameters of the model as random variables governed by distributions with computing convenience, presenting the individuality in degradation processes from different units and leave the rest of parameters as constants describing the universality in degradation of systems from the same category or batch. In the following, random coefficients regression models and stochastic process models with random coefficients of this kind are discussed, respectively.
1.2.1 Random Coefficients Regression Models
Random effects first appeared in random coefficients regression models. In the most frequently cited paper about degradation modeling and RUL estimate [], Lu and Meeker described the random coefficients regression model in a general form as
where
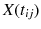
is the amount of the degradation of the i th device in the j th inspecting time
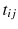
, the fixed coefficients
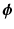
and the random coefficients
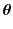
are, respectively, used to characterize the universality and individuality in degradation of different systems, and is the random noise.
Random coefficients regression models have been extended, developed and applied widely in many areas, in which a series of extended works presented by Gebraeel et al. are included []. A procedure deciding the minimum sample size and the minimum times of systematic sampling for each item to achieve an anticipant accuracy of estimation (large sample approximate variance) has been provided in their works.
However, according to Wangs analysis in [], the assumptions of random coefficient regression models result in several limitations, involving the need for more historical degradation data from different systems of the same category, the difficulty in capturing the time-varying dynamics of systems and the independency between random noise with time.
1.2.2 Stochastic Process Models with Random Coefficients
Incorporating random coefficients into stochastic degradation process-based models enables both considerations of time-varying dynamics of an individual system, and description of unit-to-unit variability, and thus has been favored by many researchers. Suppose that the degradation of a system is modeled by a stochastic process











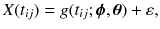
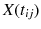 is the amount of the degradation of the i th device in the j th inspecting time
is the amount of the degradation of the i th device in the j th inspecting time 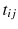 , the fixed coefficients
, the fixed coefficients 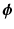 and the random coefficients
and the random coefficients 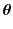 are, respectively, used to characterize the universality and individuality in degradation of different systems, and is the random noise.
are, respectively, used to characterize the universality and individuality in degradation of different systems, and is the random noise.