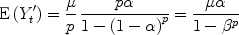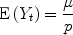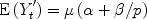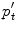Nezih Altay - Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control
Here you can read online Nezih Altay - Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. City: London, year: 2014, publisher: Springer London Ltd, genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer London Ltd
- Genre:
- Year:2014
- City:London
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Nezih Altay: author's other books
Who wrote Service Parts Management: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Control? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.









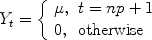
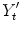 , the forecast of demand made in period t , is given by:
, the forecast of demand made in period t , is given by: 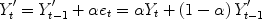
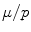 , i.e. the population expected value, but rather:
, i.e. the population expected value, but rather: