Information and Computer Engineering
ISBN 9783110595383
e-ISBN (PDF) 9783110593822
e-ISBN (EPUB) 9783110592931
Bibliographic information published by the Deutsche Nationalbibliothek
The Deutsche Nationalbibliothek lists this publication in the Deutsche Nationalbibliografie; detailed bibliographic data are available on the Internet at http://dnb.dnb.de.
2020 China Science Publishing & Media Ltd. and Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston
Chapter 1 Introduction to basic knowledge of communication electronic circuits
1.1 Introduction to communication system
Communication is a process of delivering information from transmitter to receiver. All the required technical equipments and transmission medium during the process compose a communication system altogether. There are various approaches to realize information communication. The history can be traced back to the ancient times when the primitive methods were used widely such as beacons, courier stations and signal fires. The study on electromagnetism in the seventeenth century laid the theoretical foundation for modern communication. Samuel Morse invented the first telegraph device in 1837, which practically marked the beginning of modern electrical communication. Being fast, accurate, reliable and massive in global coverage, modern communication systems are playing irreplaceable roles in all aspects of life.
1.1.1 Composition of communication system
Modern communication systems are mainly in the forms of voltage signals, current signals, electromagnetic (EM) waves or light signals. In this book, communication refers to electrical communication. The general model of communication system is shown in .
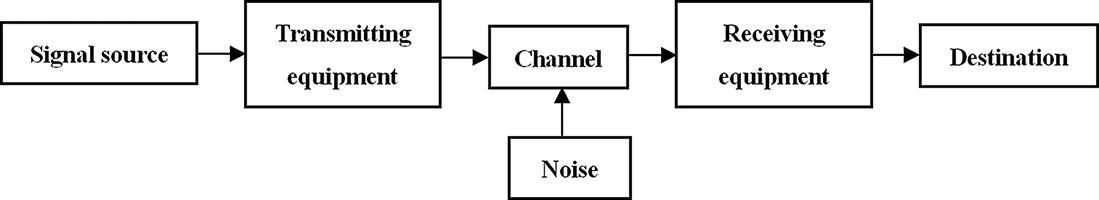
Fig. 1.1: General model of communication system.
1.1.1.1 Signal source
Signal source is the origin of information, which can be analog or digital. Analog source outputs continuous signals, such as telephone and television. Digital source outputs discrete signals, such as computer and other digital terminal equipments.
The output signal of signal source is called baseband signal or modulation signal. Baseband signal (or modulation signal) refers to the original signal with the frequency spectrum starting from zero to low frequencies. Accordingly, baseband signal can be analog or digital.
1.1.1.2 Transmitting equipment
Transmitting equipment functions to match signal source and channel. By transforming and processing baseband signals, information becomes possible for transmission in channel. The original messages are not always electrical, such as sound, text and image, and they should be converted into electrical signals by the transmitting equipment. For instance, microphone converts voice signals into continuous analog electrical signals and then transmitting equipment sends the analog electrical signals to the channel. For digital signals, transmission equipments often contain source coding and channel coding units.
1.1.1.3 Channel
Channel is the path for information transmission like a highway for automobiles. And it usually includes unwanted interferences or noises at the same time. The property of transmission material and interference are closely related to the quality of communication. Channel can be wired or wireless, both of which have many choices on transmission media. Wired channels include electrical cable, optical cable and so on. Wireless channels include the surface of earth ground, seawater and air. In space communication, channel is the free space of the universe.
1.1.1.4 Noise
Noise refers to all unwanted interferences and distortions that occur in channel or other communication units of the system.
1.1.1.5 Receiving equipment
The functions of the receiving equipment are reverse to transmitting equipment, namely, demodulation, decoding and so on. Its task is to recover the original signals based on the received signals with interferences. For example, telephones can restore transmitted electrical signals back into human sounds. Since interferences and distortions exist in every process of signal transmission and recovery, receiving equipments are expected to minimize those negative effects.
1.1.1.6 Destination
Destination is the final recipient of information.
1.1.2 Classification of communication systems
Communication systems are categorized differently based on different standards. Although the system composition and equipments are not quite the same, the operational principle is usually similar.
According to transmission channel, communication systems can be divided into wired and wireless. Wired communication utilizes transmission channels such as electric cable, optical cable and waveguide which are physical media. In contrary, wireless communication utilizes air or free space to transmit signals. Common forms of wireless communication are microwave communication, shortwave communication, mobile communication, satellite communication, scatter communication and laser communication.
According to the types of signals, communication systems can be divided into analog or digital systems.
According to modulation, communication systems can be different as baseband transmission or waveband (modulation) transmission. Baseband transmission transmits signals directly without modulation, such as local audio telephone; waveband transmission deals with modulated signals.
According to signal transmission mode, communication systems can be divided into three categories, simplex, half duplex and duplex. Simplex is a one-way transmission mode in which messages are delivered with no response needed. Radio, remote controller and television are familiar examples of simplex communication. Half duplex communication means messages can be sent and received from both sides, but the receiving and the sending action cannot take place at the same time. Intercoms and transceivers are typical half duplex communication. Duplex communication is a two-way transmission mode. In this mode, messages can be sent and received simultaneously such as telephone and mobile phone.
According to terminal movement, communication systems can be divided into mobile or fixed. Mobile communication is that at least one terminal is in motion.
According to physical characteristics of information, there are telephone, telegraph, fax communication systems, radio and television communications systems, data communication systems and so on.
According to operating frequency, communication systems can be divided into longwave, medium wave, shortwave and microwave communication systems.
Additionally, there are also other classifications. For example, according to multiple addresses mode, there are frequency division multiple access communication, time division multiple access communication and code division multiple access communication. According to users, there are public communication and private communication. According to location of the communication objects, there are ground communication, air communication, deep space communication, underwater communication and so on.
In this book, we mainly focus on wireless analog communication system and explain the circuit composition, operational principle, theoretical and practical analysis and application of each important communication units.