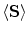1. Introduction: Problems
Abstract
Electromagnetic (EM) waves and their transmission through space are possible due to several relatively simple but fundamental physical phenomena. In modern theoretical physics, EM wave is an abstract concept that epitomizes transfer of energy through the space, which is equivalent to say that information is transferred through the space. At the same time, the information itself is embedded into the wave in the form of the energy variation in time.
Electromagnetic (EM) waves and their transmission through space are possible due to several relatively simple but fundamental physical phenomena. In modern theoretical physics, EM wave is an abstract concept that epitomizes transfer of energy through the space, which is equivalent to say that information is transferred through the space. At the same time, the information itself is embedded into the wave in the form of the energy variation in time. In this chapter we review some of the fundamental concepts from physics related to energy, matter, EM waves, EM fields, propagation of energy through matter and space, and basic interaction between two waveforms.
Problems :
1.1. An average sized snowflake consists of approximately
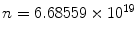
molecules. Assuming the complete matter of the snowflake is converted into energy, estimate for how long a laptop computer whose average power consumption is
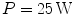
could be powered?
1.2. Our Sun produces energy in form of light by continuous nuclear fusion reaction in its core where hydrogen (H) atoms are fused together to form atoms of helium (He). Activity of the Sun is monitored by satellites positioned around Earth that measure the solar constant

, i.e. average radiated power per square metre at the distance of one astronomical unit (

) from the Sun. Estimated average value of the solar constant is
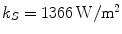
.
Knowing the average radius of the Earth
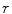
, the average distance between the Earth and the Sun

, and estimated mass of the Sun
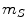
, estimate:
what is the total mass (
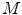
) of matter at rest that the Sun converts into energy per second?
what percentage of the total converted mass
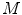
at rest is used to supply energy to the Earth?
what is the total mass (
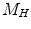
) at rest of hydrogen (H) used in the fusion process per second?
ignoring all other causes, and assuming that the Sun will collapse after converting 10 % of its current mass at rest, estimate how long the Sun will last?
what is the total power radiated by the Sun and how much is received at the Earth?
1.3. Sketch an EM sinusoidal wave that propagates in xdirection with clearly marked all three axes, as well as the other relevant wave vectors.
1.4. Sketch a rough drawing of EM wave as being generated by a dipole antenna.
1.5. Show that expression
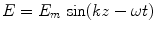
describes a wave moving in the positive
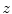
direction. In addition, express
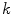
and
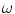
parameters in terms of the corresponding wavelength
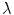
, the frequency
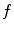
, then find relationship to the wave velocity
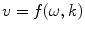
, i.e. as function of angular frequency
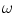
and wave number
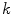
.
1.6. Starting with classical approximation of the wave equation of a sinusoidal EM wave
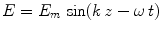
derive expression and then calculate the speed of light in vacuum with no electric charges.
1.7. Find the ratio of electric and magnetic field amplitudes of a sinusoidal EM wave whose components are
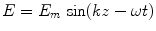
and
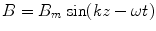
.
1.8. We note that vector product of electric and magnetic fields
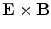
points in the same direction as the wave velocity vector. Find expression for magnitude of a vector
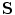
that is defined as
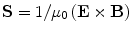
and determine its measurement unit. Comment on the nature of these results.
1.9. Estimate peak values of electric
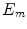
and magnetic
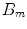
components of EM wave generated by the Sun, as measured close to the Earth.
1.10. After learning that Poynting vector represents flow of energy per unit area, and recognizing that energy is related to work, that work is related to force, and the force is related to pressure, we realize that EM wave hitting a perfectly reflective surface must exert radiation pressure on the surface. Derive expression for average Poynting vector
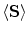












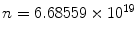 molecules. Assuming the complete matter of the snowflake is converted into energy, estimate for how long a laptop computer whose average power consumption is
molecules. Assuming the complete matter of the snowflake is converted into energy, estimate for how long a laptop computer whose average power consumption is 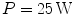 could be powered?
could be powered? , i.e. average radiated power per square metre at the distance of one astronomical unit (
, i.e. average radiated power per square metre at the distance of one astronomical unit (  ) from the Sun. Estimated average value of the solar constant is
) from the Sun. Estimated average value of the solar constant is 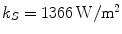 .
.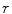 , the average distance between the Earth and the Sun
, the average distance between the Earth and the Sun  , and estimated mass of the Sun
, and estimated mass of the Sun 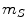 , estimate:
, estimate: 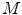 ) of matter at rest that the Sun converts into energy per second?
) of matter at rest that the Sun converts into energy per second?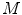 at rest is used to supply energy to the Earth?
at rest is used to supply energy to the Earth?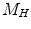 ) at rest of hydrogen (H) used in the fusion process per second?
) at rest of hydrogen (H) used in the fusion process per second?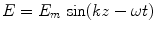 describes a wave moving in the positive
describes a wave moving in the positive 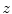 direction. In addition, express
direction. In addition, express 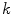 and
and 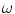 parameters in terms of the corresponding wavelength
parameters in terms of the corresponding wavelength 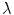 , the frequency
, the frequency 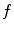 , then find relationship to the wave velocity
, then find relationship to the wave velocity 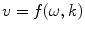 , i.e. as function of angular frequency
, i.e. as function of angular frequency 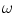 and wave number
and wave number 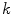 .
.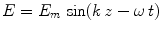 derive expression and then calculate the speed of light in vacuum with no electric charges.
derive expression and then calculate the speed of light in vacuum with no electric charges.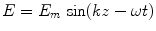 and
and 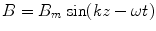 .
.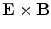 points in the same direction as the wave velocity vector. Find expression for magnitude of a vector
points in the same direction as the wave velocity vector. Find expression for magnitude of a vector 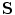 that is defined as
that is defined as 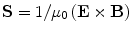 and determine its measurement unit. Comment on the nature of these results.
and determine its measurement unit. Comment on the nature of these results.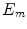 and magnetic
and magnetic 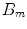 components of EM wave generated by the Sun, as measured close to the Earth.
components of EM wave generated by the Sun, as measured close to the Earth.