A sketch is a free-hand drawing of a map or picture of an area or route of travel. It shows enough detail and has enough accuracy to satisfy special tactical or administrative requirements.
A-1.2 PURPOSE
Sketches are useful when maps are not available or the existing maps are not adequate, or to illustrate a reconnaissance or patrol report. Sketches may vary from hasty to complete and detailed, depending upon their purpose and the degree of accuracy required. For example, a sketch of a large minefield will require more accuracy than a hasty sketch of a small unit's defensive position.
A-2. MILITARY SKETCHES
The scale of a sketch is determined by the object in view and the amount of detail required to be shown. The sketch of a defensive position for a platoon or company will normally call for a sketch of larger scale than a sketch for the same purpose for a division. A field sketch () must show the north arrow, scale, legend, and the following features:
- Power lines.
- Rivers.
- Main roads.
- Towns and villages.
- Forests.
- Rail lines.
- Major terrain features.
Military sketches include road and area sketches.
a. Road sketches show the natural and military features on and in the immediate vicinity of the road. In general, the width of terrain sketches will not exceed 365 meters on each side of the road. Road sketches may be used to illustrate a road when the existing map does not show sufficient detail.
b. Area sketches include those of positions, OPs, or particular places.
(1) Position sketch. A position sketch is one of a military position, campsite, or other area of ground, To effectively complete a position sketch, the sketcher must have access to all parts of the area being sketched.
(2) Observation post sketch. An OP sketch shows the military features of ground along a friendly OP line as far toward the enemy position as possible.
(3) Place sketch. A place sketch is one of an area made by a sketcher from a single point of observation. Such a sketch may cover ground in front of an OP line, or it may serve to extend a position or road sketch toward the enemy.
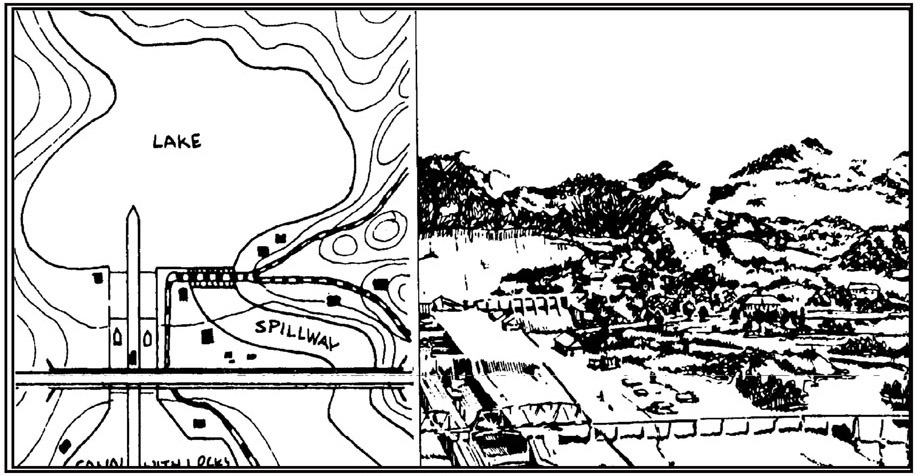
Figure A-1. Sketch map.
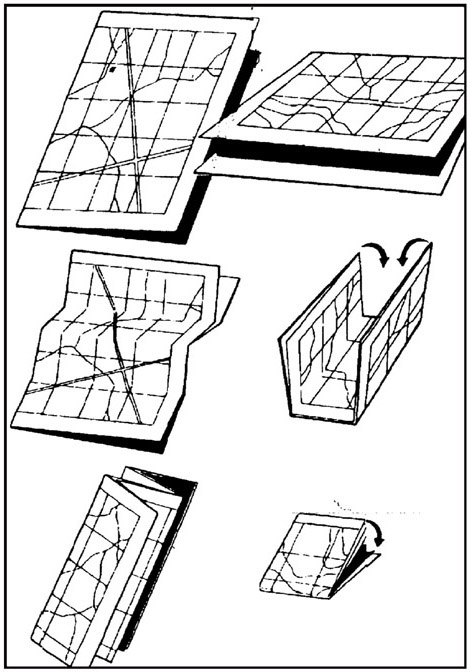
One of the first considerations in the care of maps is its proper folding.
B-1. FOLDING METHODS
show ways of folding maps to make them small enough to be carried easily and still be available for use without having to unfold them entirely.
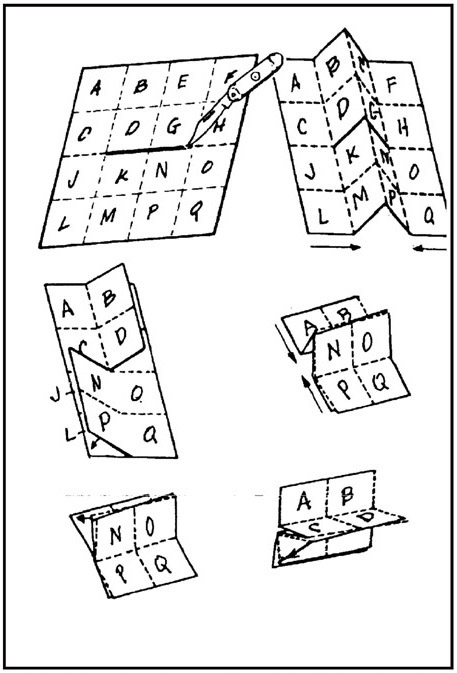
B-2. PROTECTION METHOD
After a map has been folded, it should be pasted in a folder for protection. Apply adhesive to the back of the segments corresponding to A, F, L, and Q ().
B-3. PRACTICE CUT
It is suggested that before attempting to cut and fold a map in the manner illustrated in , make a practice cut and fold with a piece of paper.
Figure B-1. Two methods of folding a map.
Figure B-2. How to slit and fold a map for special use.
| ENGLISH SYSTEM OF LINEAR MEASURE |
| 12 inches | = | 1 foot |
| 36 inches | = | 1 yard |
| 3 feet | = | 1 yard |
| 1,760 yards | = | 1 mile statute |
| 2,026.8 yards | = | 1 mile nautical |
| 5,280 feet | = | 1 mile statute |
| 6,080.4 feet | = | 1 mile nautical |
| 63,360 inches | = | 1 mile statute |
| 72,963 inches | = | 1 mile nautical |
METRIC SYSTEM OF LINEAR MEASURE |
| 1 millimeter | = | 0.1 centimeter | = | 0.0393 inch |
| 10 millimeters | = | 1.0 centimeter | = | 0.3937 inch |
| 10 centimeters | = | 1.0 decimeter | = | 3.937 inches |
| 10 decimeters | = | 1.0 meter | = | 39.37 inches |
| 10 meters | = | 1.0 decameter | = | 32.81 feet |
| 10 decameters | = | 1.0 hectometer | = | 328.1 feet |
| 10 hectometers | = | 1.0 kilometer | = | 0.62 mile |
| 10 kilometers | = | 1.0 myriameter | = | 6.21 miles |
EQUIVALENT UNITS OF ANGULAR MEASURE |
| 1 mil | = | 1/6400 circle | = | 0.05625 | = | 0.0625 grad |
| 1 grad | = | 1/400 circle | = | 16.0 mils | = | 054' = 0.9 |
| 1 degree | = | 1/360 circle | = | about 17.8mils | = | about 1.1 grad |
CONVERSION FACTORS |
One | Inches | Feet | Yards | Statute Miles | Nautical Miles | mm |
| Inch | 1 | 0.0833 | 0.0277 | 25.40 |
| Foot | 12 | 1 | 0.333 | 304.8 |
| Yard | 36 | 3 | 1 | 0.00056 | 914.4 |
| Statute Mile | 63,360 | 5,280 | 1,760 | 1 | 0.8684 |
| Nautical Mile | 72,963 | 6,080 | 2,026 | 1.1516 | 1 |
| Millimeter | 0.0394 | 0.0033 | 0.0011 | 1 |
| Centimeter | 0.3937 | 0.0328 | 0.0109 | 10 |
| Decimeter | 3.937 | 0.328 | 0.1093 | 1,00 |
| Meter | 39.37 | 3.2808 | 1.0936 | 0.0006 | 0.0005 | 1,000 |
| Decameter | 393.7 | 32.81 | 10.94 | 0.0062 | 0.0054 | 10,000 |
| Hactometer | 3,937 | 328.1 | 109.4 | 0.0621 | 0.0539 | 100,000 |
| Kilometer | 39,370 | 3,281 | 1,094 | 0.6214 | 0.5396 | 1,000,000 |
| Myriameter | 393,700 | 32,808 | 10,936 | 6.2137 | 5.3959 | 10,000,000 |
One | cm | dm | m | dkm | hm | km | mym |
| Inch | 2.540 | 0.2540 | 0.0254 | 0.0025 | 0.0003 |
| Foot | 30.48 | 3.048 | 0.3048 | 0.0305 | 0.0030 | 0.0003 |
| Yard | 91.44 | 9.144 | 0.9144 | 0.0914 | 0.0091 | 0.0009 |
| Statute Mile | 160,930 | 16,093 | 1,609 | 160.9 | 16.09 | 1.6093 | 0.1609 |
| Nautical Mile | 185,325 | 18,532 | 1,853 | 185.3 | 18.53 | 1.8532 |