
First published in Great Britain in 2005 by
Pen & Sword Military
an imprint of
Pen & Sword Books Ltd
47 Church Street
Barnsley
South Yorkshire
S70 2AS
Copyright Geoffrey Brooks, 2005
ISBN: 9781844153176
Digital Edition ISBN: 9781848846937
The right of Geoffrey Brooks to be identified as Author of this Work has been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
A CIP catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical including photocopying, recording or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission from the Publisher in writing.
Typeset by Kirsten Barber,
Leeds, West Yorkshire
Printed and bound in England by
CPI UK
For a complete list of Pen & Sword titles please contact
PEN & SWORD BOOKS LIMITED
47 Church Street, Barnsley, South Yorkshire, S70 2AS, England
E-mail:
Website: www.pen-and-sword.co.uk
I dedicate this book to my daughter,
Angie Valeria Brooks-Canepa
Contents
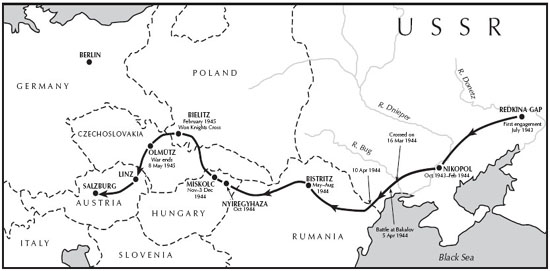
The route followed by Josef Sepp Allerberger from the battle of Redkina Gap near Voroshilovsk, July 1943
Introduction
This book relates the wartime career of Wehrmacht sniper Josef Sepp Allerberger, an Austrian conscript who served on the Eastern Front from July 1943 until May 1945. Although never rising above the rank of private, he was awarded the Knights Cross and is listed as the second highest scoring Wehrmacht marksman in the field with 257 confirmed kills.
Austrians such as Allerberger who served in the Wehrmacht had German nationality. On 12 March 1938, German forces entered Austria for the purpose of annexing the country into the German Reich. On 18 March 1938, the Reichstag passed the Law for the Reincorporation of Austria into the Reich (Reichsgesetzblatt I , p. 262, and BliV 1938 No. 12). This enabled frontier and customs posts to be dismantled, and to all intents and purposes, Austrian citizens obtained a status of nationality which rendered them liable, amongst other things, to conscription into the Wehrmacht .
This book is based largely on interviews given by Allerberger to Albrecht Wacker and others for the book Im Auge des Jgers (VS-Books, Herne, 2000), and on earlier question and answer sessions he gave, as for example in the official Austrian military publication Truppendienst (Hauptmann Hans Widhofner, 1967). The principal background source used has been General Paul Klatts Die 3. Gebirgsdivision .
I have preferred the autobiographical form for this book since in my opinion the narrative is best cast in the first person if the manner in which information was collated enables the material to be written as a personal memoir. The biographical approach can be appropriated as a vehicle for the expression of the political opinions of authors, particularly modern German liberal authors, which are not, and never were, held by the subject, but appear to be attributed to him to satisfy the requirements of political correctness. In the original German volume, as an aid to concealing Allerbergers identity, a pseudonym was employed, all sensitive family photographs masked, his country of origin stated as Germany instead of Austria and certain dates doctored on the grounds that German snipers, even in their own country, are reviled as ruthless murderers, and for this reason it is essential to protect the subject with anonymity. Within a day or so of receiving Wackers book I identified the subject Allerberger by briefly surfing the Internet for information on Wehrmacht snipers and accordingly I have no confidence that Wackers precautions would be likely to baffle for long a really determined revenge-seeker.
In the Epilogue to the Wacker book, Allerberger asks the critical question, Was it right, what we did? Was there an alternative under the given circumstances? One has to consider very carefully this question, for Allerberger has had the benefit of sixty years exposure to Western propaganda that it was not right, and yet he is still a dont know. This uncertainty has its roots in the hypocrisy of condemning one political regime for its excesses and aggression, and not the other.
The 1924 Soviet Constitution had as its aim one worldwide socialist Soviet Republic. Lenin and Stalin made no secret of their desire for a second European war to establish a communist Europe. The Soviet build-up towards this end began long before they embarked upon the road in 1939 with the occupation of eastern Poland, and in 1940 the Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. In his recent book, The Icebreaker , Viktor Suvorov (the former military spy Vladimir Bogdanovich Resun) makes the case that Soviet military theory was based on offence and the conquest of territory for the world revolution. Operation Groza (Thunderstorm), the invasion of Europe to the Atlantic, was scheduled to begin on 6 July 1941. The statement of General S.P. Ivanov, Chief of the General Staff Academy of the USSR armed forces in 1974 that the Nazi High Command succeeded in forestalling our troops literally two weeks before the war began seems eloquent enough proof of this allegation, and more recently Russian academic historians Vladimir Nevezhin and Mikhail Meltiujov have found archive material that supports Suvorovs allegation.
From the earliest beginnings of the National Sozialistische Deutsche Arbeiter Party or NSDAP (The Nazi Party), the primary aim had been the destruction of Bolshevism. This was for religious reasons as well as political. The hidden religious basis of National Socialism was reincarnation without a heaven (Hitlers table talk, 13 December 1941). Judeo-Christianity was nothing but communism (Hitlers table talk, 30 November 1944) and modern Bolshevism was nothing but Christianity without the metaphysical trappings (Hitlers table talk, 14 December 1941). Hitler saw himself as the Grail knight, Parsifal, the prophet of mans rebirth in a new form, his task being to elevate mankind for the global struggle to eventually escape the cycle of reincarnation. The secret name of his Berghof residence, Gralsburg fortress of the Grail seems to confirm this (Hitlers table talk, 2 February 1942). Hitlers dedication to a Buddhist philosophy is obvious from the fact that throughout the Great War he carried the five works of the philosopher Schopenhauer in his gas mask case (Hitlers table talk, 19 May 1944) and knew large tracts of them by heart. He thought as a pantheist and a mystic, since he perceived God as being the sum total of all that is (Hitlers table talk, 24 October 1941), and for the raising of humanity he aimed to make the whole world vegetarian (Hitlers table talk, 11 November 1941), and believed that the advancement of science lay in its extension to include the spiritual sciences where philosophy was firmly in the foreground: he considered that the borders between the disciplines were nowhere near so clear cut as one might think (Hitlers table talk, 19 May 1944). It may well have been the intention from the very outset of Nazism to overthrow the communist system in Russia, but Hitlers plans to attack the Soviet Union were certainly firm from 1940. He appears to have had definite intelligence that the Soviet Union intended attacking all Europe in the latter part of 1941, and this was the motivation for Operation Barbarossa that year (Hitlers table talk, 17 September 1941).
Next page










