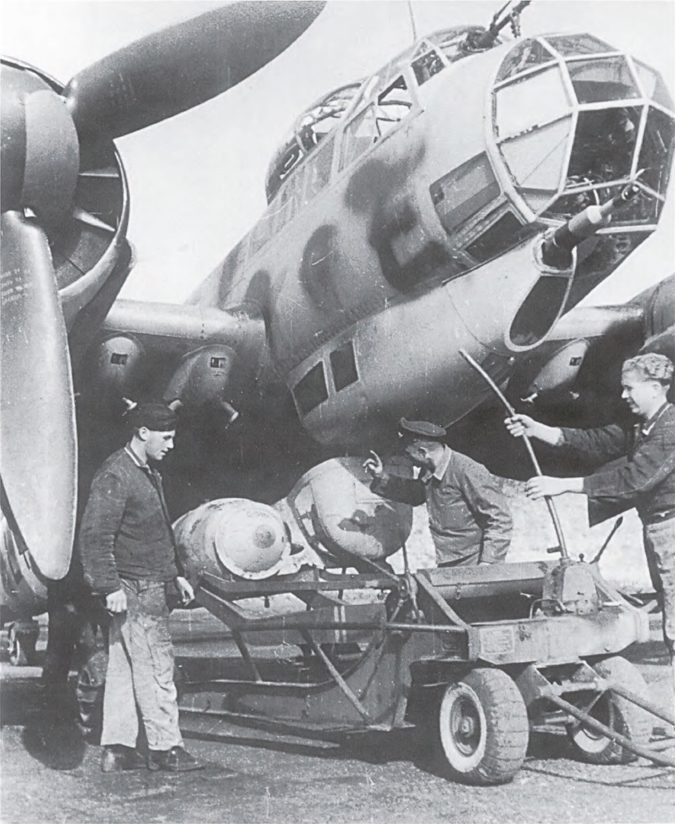
Ground crew use the outstanding hydraulic bomb trolley to load 1000 kg bombs on the external racks of an LG 1 Ju 88A-14 at Tunis in 1943. The forward-firing 20 mm cannon in the ventral blister gave the aircraft an excellent punch for the anti-shipping sorties it flew across the Mediterranean. (Simon Perry via Barry Rosch)
Jeffrey Lance Ethell. 29 September 1947 - 6 June 1997
Eagles over North Africa and the Mediterranean, 19401943

A Greenhill Book
First published in 1997 by Greenhill Books,
Lionel Leventhal Limited
www.greenhillbooks.com
This edition published in 2016 by
PEN & SWORD AVIATION
An imprint of
Pen & Sword Books Ltd
47 Church Street
Barnsley
South Yorkshire
S70 2AS
Copyright Lionel Leventhal Limited, 1997
ISBN: 978-1-84832-792-4
PDF ISBN: 978-1-47388-391-8
EPUB ISBN: 978-1-47388-390-1
PRC ISBN: 978-1-47388-389-5
The right of Jeffrey L. Ethell to be identified as Author of this work has been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise) without the prior written permission of the publisher. Any person who does any unauthorized act in relation to this publication may be liable to criminal prosecution and civil claims for damages.
CIP data records for this title are available from the British Library
Designed by DAG Publications Ltd
Design by David Gibbons
Layout by Anthony A. Evans
Printed and bound in Malta by Gutenberg Press Ltd
Pen & Sword Books Ltd incorporates the Imprints of Aviation, Atlas, Family History, Fiction, Maritime, Military, Discovery, Politics, History, Archaeology, Select, Wharncliffe Local History, Wharncliffe True Crime, Military Classics, Wharncliffe Transport, Leo Cooper, The Praetorian Press, Remember When, Seaforth Publishing and Frontline Publishing.
For a complete list of Pen & Sword titles please contact
PEN & SWORD BOOKS LIMITED
47 Church Street, Barnsley, South Yorkshire,
S70 2AS, England
E-mail:
Website: www.pen-and-sword.co.uk
Contents
LUFTWAFFE AT WAR
EAGLES OVER NORTH AFRICA AND THE MEDITERRANEAN, 19401943
Shortly after Italy had declared war on Great Britain on 10 June 1940, combat between the two countries began in the Middle East as a series of skirmishes in Egypt and Libya. Escalating into a full-blooded confrontation, this resulted in a thrashing for the Italians that lasted through the rest of the year. Consequently in February 1941 Axis partner Adolf Hitler sent Generalleutnant Erwin Rommel to Tripoli with the Afrika Korps, to help Benito Mussolini get his lost territory back. Thus began a long, hard slog in the Mediterranean theatre which would stretch the Luftwaffe to its very limits, both sides quickly discovering that aircraft operating in this harsh, hot, sandy environment were more often rendered unserviceable by the conditions than by the enemy.
Hitler had by now committed himself to multiple theatres of war without either the logistics or the equipment this called for. His most technology-dependent service, the air force, quickly began to suffer the consequences, even while Reichsmarshall Hermann Gring kept assuring his Fhrer that the Luftwaffe could still achieve the impossible. Nevertheless, the Luftwaffes pilots and ground crews proved more than capable of meeting the Allies on equal terms. Many pilots became top aces here, most notable among them being Hans-Joachim Marseille, who seemed to thrive on the hardships. When the inexperienced US Army Air Forces units arrived in this theatre in mid-1942, the Luftwaffe quickly chopped them to shreds, an early indication that the soft underbelly which Winston Churchill liked to talk about was in reality going to prove anything but.
This book traces the rough Mediterranean campaign from its beginnings in the Balkans, through the German surrender in North Africa, and on to Sicily and the first combats over Italy. Reflecting Rommels skill, not only was the Luftwaffe able to stem the Allied tide but on occasion even turned it back in the face of encroaching defeat.
Authors note: For years controversy has raged regarding what prefix should be used when describing Messerschmitt aircraft Bf or Me? Wartime German documents use both, though the Me prefix predominates. The following explanation is provided by Dr Winfried Heinemann of the Militrgeschictliches Forschungsamt, Potsdam: In 1927, Professor Willy Messerschmitt began a co-operation with the Bayerische Flugzeugwerke AG. He increased his share in the business during and after the Great Depression, until, m September 1938, the entire firm was renamed Messerschmitt AG. Any aircraft designed before that time were officially designated as Bf. This applies to the Bf 108 Taifun even those models built after the Second World War and also the Bf 109A-D series, whereas the F.-Z versions bore the designator Me. Similarly, the Bf 110A and B bore the former prefix, whereas the Me 110C-G bore the latter. I have long subscribed to this convention, and follow it here.
Malta
When the Italians found that their Regia Aeronautica (Air Force) and Navy could not stop British convoys from resupplying Egypt, Mussolini quickly called on his Axis partner to come to his aid. The Luftwaffe, with a mission in Italy since June 1940, had been flying a number of tentative sorties but a formal co-belligerent status was not formalised until January 1941. Hitlers prime interest was in assuring the security of his southern flank in the coming war against Russia, not helping Italy. In the face of strong protests from his generals, Hitler gave Mussolini his commitment.
Initially, the Luftwaffe presence was mainly in the form of transport aircraft, but combat units began to filter in steadily. The first objective was the subjugation of the island stronghold of Malta, a real thorn in the side of German sea supply lines. On 7 January 1941, Ju 87s, Ju 88s, He 111s and Italian SM 79s opened the campaign by striking a British convoy. Shortly thereafter the Axis air forces began systematic attacks on Malta, with airfields being the prime targets. The defenders were quickly worn down until just three Royal Navy Fulmars, six Royal Air Force Hurricanes and a single Gladiator biplane were left to face the almost daily raids. The Luftwaffe was able to mount between 40 and 80 sorties a day unless poor weather kept the aircraft on the ground.
All through February and March German bombers, supported by Me 110s and experienced Me 109E pilots from JG (Jagdgeschwader or Fighter Wing) 26 and JG 27 hit Maltas three airfields and Valetta harbour constantly. Each time a convoy managed to get through, Stukas would hit the harbour with a vengeance, even when under attack from experienced anti-aircraft crews and an increasing number of Hurricanes sent to bolster the air defences. In mid-March, as the island seemed to be teetering on the brink of defeat, the bombing suddenly let up. The Luftwaffe units had been called away to support the coming Balkan campaign.
Greece, Yugoslavia and Crete
Over 400 aircraft were gathered in Bulgaria to support the Italian invasion of Greece. When the pro-Nazi Yugoslavian government was overthrown, Hitler ordered another 600 aircraft flown to Bulgaria and Rumania for a double strike. With complete air superiority, the
Next page












