Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016
Christian Heumann , Michael Schomaker and Shalabh Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis 10.1007/978-3-319-46162-5_1
1. Introduction and Framework
Statistics is a collection of methods which help us to describe, summarize, interpret, and analyse data. Drawing conclusions from data is vital in research, administration, and business. Researchers are interested in understanding whether a medical intervention helps in reducing the burden of a disease, how personality relates to decision-making, whether a new fertilizer increases the yield of crops, how a political system affects trade policy, who is going to vote for a political party in the next election, what are the long-term changes in the population of a fish species, and many more questions. Governments and organizations may be interested in the life expectancy of a population, the risk factors for infant mortality, geographical differences in energy usage, migration patterns, or reasons for unemployment. In business, identifying people who may be interested in a certain product, optimizing prices, and evaluating the satisfaction of customers are possible areas of interest.
No matter what the question of interest is, it is important to collect data in a way which allows its analysis. The representation of collected data in a data set or data matrix allows the application of a variety of statistical methods. In the first part of the book, we are going to introduce methods which help us in describing data, and the second and third parts of the book focus on inferential statistics, which means drawing conclusions from data. In this chapter, we are going to introduce the framework of statistics which is needed to properly collect, administer, evaluate, and analyse data.
1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations
Let us first introduce some terminology and related notations used in this book. The units on which we measure datasuch as persons, cars, animals, or plantsare called observations . These units/observations are represented by the Greek symbol
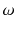
. The collection of all units is called population and is represented by
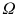
. When we refer to
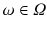
, we mean a single unit out of all units, e.g. one person out of all persons of interest. If we consider a selection of observations
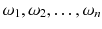
, then these observations are called sample . A sample is always a subset of the population,
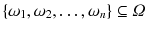
.
Example 1.1.1
If we are interested in the social conditions under which Indian people live, then we would define all inhabitants of India as
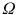
and each of its inhabitants as
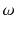
. If we want to collect data from a few inhabitants, then those would represent a sample from the total population.
Investigating the economic power of Africas platinum industry would require to treat each platinum-related company as
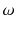
, whereas all platinum-related companies would be collected in
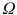
. A few companies
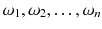
comprise a sample of all companies.
We may be interested in collecting information about those participating in a statistics course. All participants in the course constitute the population
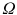
, and each participant refers to a unit or observation
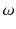
.
Remark 1.1.1
Sometimes, the concept of a population is not applicable or difficult to imagine. As an example, imagine that we measure the temperature in New Delhi every hour. A sample would then be the time series of temperatures in a specific time window, for example from January to March 2016. A population in the sense of observational units does not exist here. But now assume that we measure temperatures in several different cities; then, all the cities form the population, and a sample is any subset of the cities.
1.2 Variables
If we have specified the population of interest for a specific research question, we can think of what is of interest about our observations. A particular feature of these observations can be collected in a statistical variable X . Any information we are interested in may be captured in such a variable. For example, if our observations refer to human beings, X may describe marital status, gender, age, or anything else which may relate to a person. Of course, we can be interested in many different features, each of them collected in a different variable
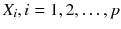
. Each observation
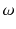
takes a particular value for X . If X refers to gender, each observation, i.e. each person, has a particular value x which refers to either male or female.
The formal definition of a variable is
This definition states that a variable X takes a value x for each observation
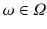
, whereby the number of possible values is contained in the set S .
Example 1.2.1
If X refers to gender, possible x -values are contained in
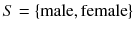
. Each observation
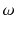
is either male or female, and this information is summarized in X .
Let X be the country of origin for a car. Possible values to be taken by an observation
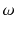












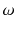 . The collection of all units is called population and is represented by
. The collection of all units is called population and is represented by 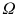 . When we refer to
. When we refer to 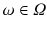 , we mean a single unit out of all units, e.g. one person out of all persons of interest. If we consider a selection of observations
, we mean a single unit out of all units, e.g. one person out of all persons of interest. If we consider a selection of observations 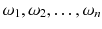 , then these observations are called sample . A sample is always a subset of the population,
, then these observations are called sample . A sample is always a subset of the population, 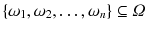 .
.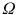 and each of its inhabitants as
and each of its inhabitants as 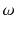 . If we want to collect data from a few inhabitants, then those would represent a sample from the total population.
. If we want to collect data from a few inhabitants, then those would represent a sample from the total population.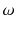 , whereas all platinum-related companies would be collected in
, whereas all platinum-related companies would be collected in 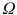 . A few companies
. A few companies 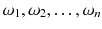 comprise a sample of all companies.
comprise a sample of all companies.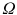 , and each participant refers to a unit or observation
, and each participant refers to a unit or observation 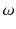 .
.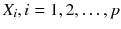 . Each observation
. Each observation 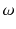 takes a particular value for X . If X refers to gender, each observation, i.e. each person, has a particular value x which refers to either male or female.
takes a particular value for X . If X refers to gender, each observation, i.e. each person, has a particular value x which refers to either male or female.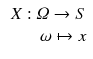
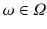 , whereby the number of possible values is contained in the set S .
, whereby the number of possible values is contained in the set S .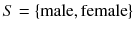 . Each observation
. Each observation 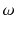 is either male or female, and this information is summarized in X .
is either male or female, and this information is summarized in X .