Around 1100 BCE, Phoenician traders from the area now known as Lebanon began settlingthe Tunisian coast. The Berber people, both farmers and nomads , had already livedthere for hundreds of years.
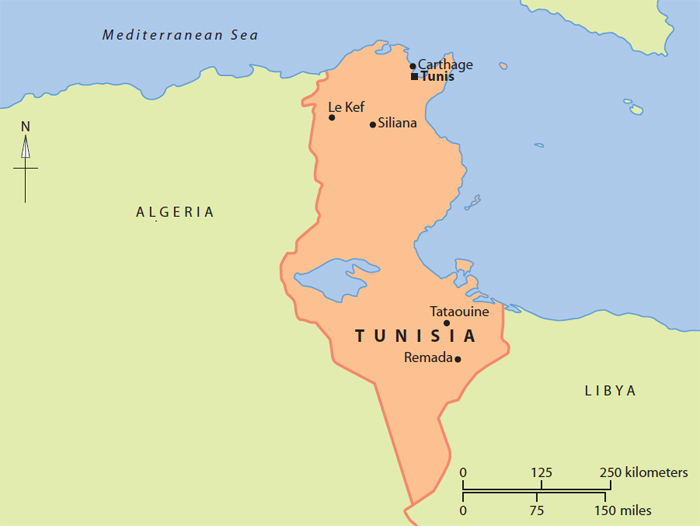
The Phoenicians came to Tunisia at the same time a climate change increased the sizeof the Sahara Desert. Travel to the area became more difficult. The city of Carthage,on the eastern side of Lake Tunis and across from the city of Tunis, was foundedin 814 BCE. Carthage and Tunis broke away from the rest of the Phoenician empire and formed their own empire.
In 241 BCE, Carthage lost its first war with Rome. Later Rome destroyed Carthage.The city remained deserted for 100 years. Roman control of Tunisia finally endedin 439 CE when the Vandals , a Germanic tribe, invaded.
Tunisias location near the Mediterranean Sea has made it a cultural and trade centerfor centuries.
Archeologists believe the remains of 20,000 children, buried between 730 and 146BCE, are located here.
YOUNG PEOPLE
Were children sacrificed to the gods in ancient Tunisia? The ancient historian Plutarch(46120 CE) said they were. But when Rome destroyed the city in 146 BCE, they destroyedalmost all of the citys records. There is very little firsthand evidence of theculture. Between 1920 and 1970, archaeologists uncovered a cemetery filled with theremains of children, many of whom were cremated . Some took this discovery as proofthat the ancient rumors of child sacrifice were true. Yet others believed it wassimply a special cemetery for children.
The Byzantine Empire
In the 500s, Tunisia became part of the Byzantine Empire , a military power. Fromabout 306 to 1453, it ruled various parts of the ancient world. It eventually fellto the Ottoman Empire . The Byzantine Empire was centered in ConstantinopletodaysIstanbul, Turkey. Constantinoples great distance from Tunis may have led to Tunisiasdecline during this period. The native Berber tribes gained power, as Tunisias citiesgrew smaller.
Arabs, Islam, and Berbers
In the 600s, many Arabs converted to Islam as Muslim armies arrived. The Berbers,often Christian, first did not convert to Islam. Over time more Berbers did convert.Today the blending of Berber and Arab-Muslim cultures has made for a unique Tunisianculture.
The Ottoman Empire
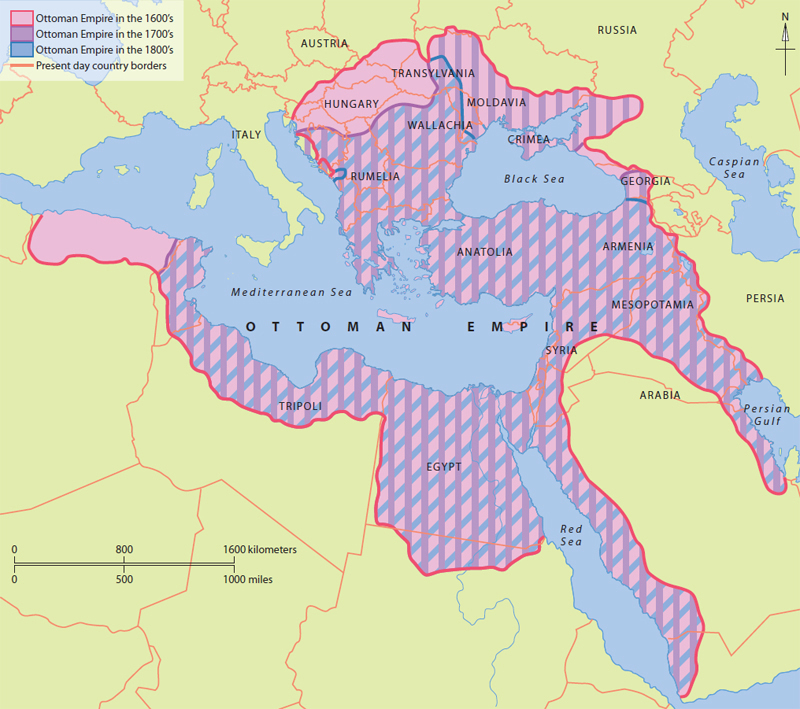
In 1574 Tunisia became part of the Ottoman Empire. It remained under Ottoman controluntil the 1700s. In the 1800s, Tunisia was in the uncomfortable position of beingin between, geographically, the Ottoman Empire and the French. The French had invadedits western neighbor, Algeria Tunisia came under French control in 1881.
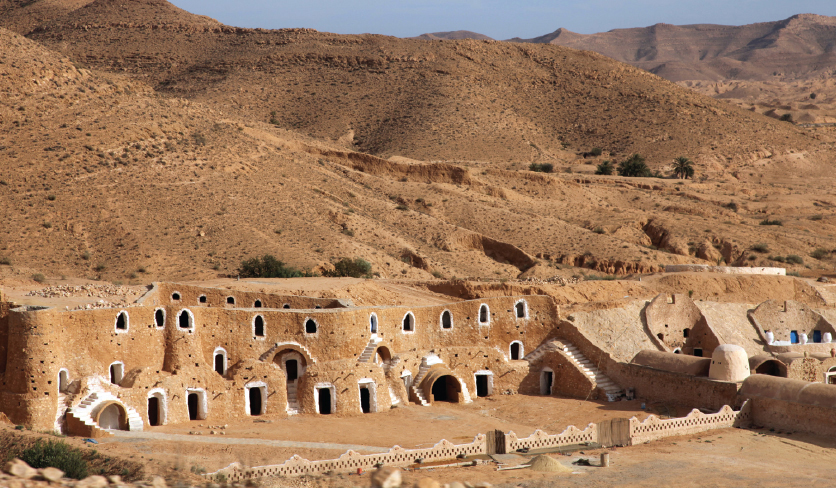
Berber villages in the south of Tunisia are popular tourist sites. Most Tunisians have Berber heritage.
How to say...
Under the control of the Ottoman Empire, local Tunisian rulers were known as beys . Bey is a Turkish word for leader or lord. Today, the word is used as a title formen. In the 1800s, a Tunisian bey was the first ruler in the Muslim world to introducea constitution to the country.
This map shows how far the Ottoman Empire reached in the 1700s. The Ottoman Empire lasted from 1299 until 1923.
From protectorate to independence
Tunisia was officially a protectorate of France. A protectorate is a country underthe economic control and military protection of another country. In contrast, manyother African countries were colonies of European powers. Colonies have less controlover themselves than protectorates do.
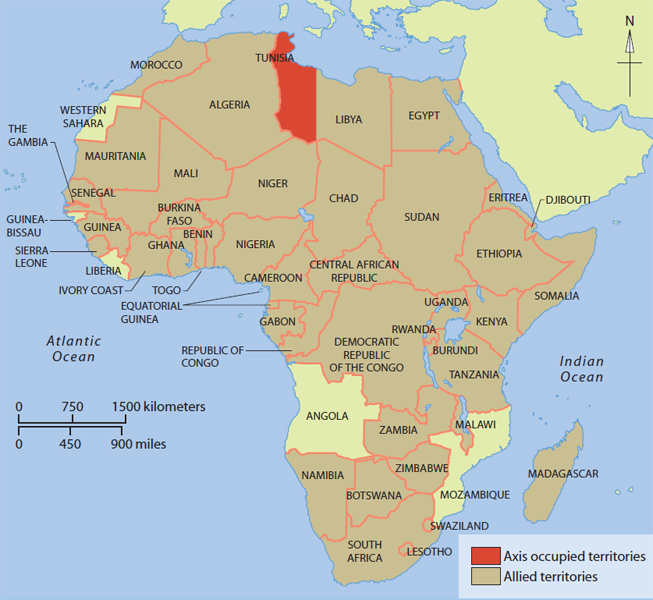
Few French actually lived in Tunisia, so it retained much of its own culture. Therelationship continued for many years with different degrees of resistance from Tunisians.In 1942, during World War II, Germany invaded Tunisia. At the end of World War II,Tunisians were unwilling to go peacefully back to French rule. In 1956 Tunisia finallyachieved independence. Tunisias independence was much less violent than that ofmany other African countries.
This map shows how Africa was divided during part of World War II.
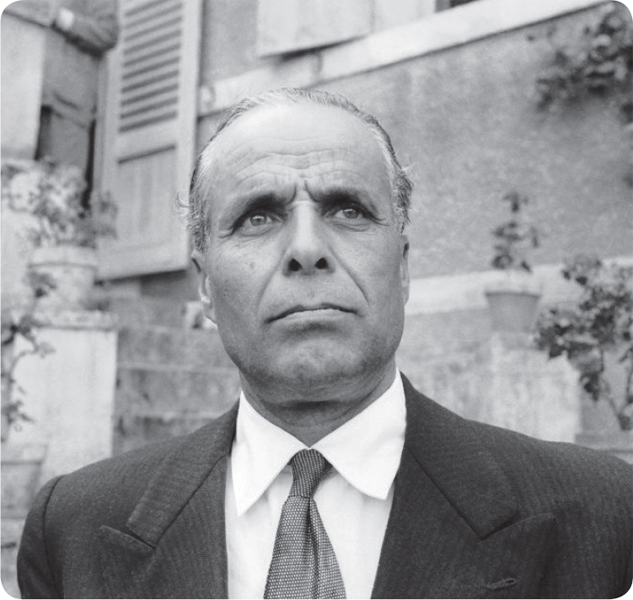
Bourguiba helped Tunisia achieve independence in the 1950s. He ruled the country for several decades.
HABIB BOURGUIBA (1903-2000)
Once jailed by the French for treason, Habib Bourguibawent on to become President of Tunisia for 30 years, from 1957 to 1987. Tunisiasconstitution gave Bourguiba dictatorial powers, but he was generally seen as a fairruler who responded to public opinion. Bourguiba worked to modernize the countrys economy and social structure. A Muslim himself, Bourguiba abolished religious lawand courts, and gave women more rights than they had in other Arab countries. In1987 the elderly Bourguiba was removed from power in a bloodless takeover, or coup .He lived the rest of his life in his hometown, 100 miles south of Tunis.