HOMES OF THE NATIVE AMERICANS
Colleen madonna flood williams
NATIVE AMERICAN LIFE
E UROPEANS AND N ATIVE A MERICANS
H OMES OF THE N ATIVE A MERICANS
H UNTING WITH THE N ATIVE A MERICANS
N ATIVE A MERICAN C ONFEDERACIES
N ATIVE A MERICAN C OOKING
N ATIVE A MERICAN F AMILY L IFE
N ATIVE A MERICAN F ESTIVALS AND C EREMONIES
N ATIVE A MERICAN H ORSEMANSHIP
N ATIVE A MERICAN L ANGUAGES
N ATIVE A MERICAN M EDICINE
N ATIVE A MERICAN R ELIGIONS
N ATIVE A MERICAN R IVALRIES
N ATIVE A MERICAN S PORTS AND G AMES
N ATIVE A MERICAN T OOLS AND W EAPONS
W HAT THE N ATIVE A MERICANS W ORE
HOMES OF THE NATIVE AMERICANS
Colleen madonna flood williams

SENIOR CONSULTING EDITOR DR. TROY JOHNSON
PROFESSOR OF HISTORY AND AMERICAN INDIAN STUDIES
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY
As always, to Paul R. Williams and Dillon J. Meehan with all my love.
For Big D, Noreen, Patrick Jr., Dennis, and Daniel Flood with love.
 | Mason Crest
450 Parkway Drive, Suite D
Broomall, PA 19008
www.masoncrest.com |
2014 by Mason Crest, an imprint of National Highlights, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission from the publisher.
Printed and bound in the United States of America.
CPSIA Compliance Information: Batch #NAR2013. For further information, contact Mason Crest at 1-866-MCP-Book
First printing
1 3 5 7 9 8 6 4 2
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Williams, Colleen Madonna Flood.
Homes of the native Americans / Colleen Madonna Flood Williams.
pages cm.(Native American life)
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN 978-1-4222-2965-1 (hc)
ISBN 978-1-4222-8852-8 (ebook)
1. Indians of North AmericaDwellingsJuvenile literature. I. Title.
E98.D9W54 2013
392.360899708dc23
2013007477
Native American Life series ISBN: 978-1-4222-2963-7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
For hundreds of years the dominant image of the Native American has been that of a stoic warrior, often wearing a full-length eagle feather headdress, riding a horse in pursuit of the buffalo, or perhaps surrounding some unfortunate wagon train filled with innocent west-bound American settlers. Unfortunately there has been little written or made available to the general public to dispel this erroneous generalization. This misrepresentation has resulted in an image of native people that has been translated into books, movies, and television programs that have done little to look deeply into the native worldview, cosmology, and daily life. Not until the 1990 movie Dances with Wolves were native people portrayed as having a human persona. For the first time, native people could express humor, sorrow, love, hate, peace, and warfare. For the first time native people could express themselves in words other than ugh or Yes, Kemo Sabe. This series has been written to provide a more accurate and encompassing journey into the world of the Native Americans.
When studying the native world of the Americas, it is extremely important to understand that there are few universals that apply across tribal boundaries. With over 500 nations and 300 language groups the worlds of the Native Americans were diverse. The traditions of one group may or may not have been shared by neighboring groups. Sports, games, dance, subsistence patterns, clothing, and religion differedgreatly in some instances. And although nearly all native groups observed festivals and ceremonies necessary to insure the renewal of their worlds, these too varied greatly.
Of equal importance to the breaking down of old myopic and stereotypic images is that the authors in this series credit Native Americans with a sense of agency. Contrary to the views held by the Europeans who came to North and South America and established the United States, Canada, Mexico, and other nations, some Native American tribes had sophisticated political and governing structuresthat of the member nations of the Iroquois League, for example. Europeans at first denied that native people had religions but rather worshiped the devil, and demanded that Native Americans abandon their religions for the Christian worldview. The readers of this series will learn that native people had well-established religions, led by both men and women, long before the European invasion began in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Gender roles also come under scrutiny in this series. European settlers in the northeastern area of the present-day United States found it appalling that native women were treated as drudges and forced to do the mens work in the agricultural fields. They failed to understand, as the reader will see, that among this group the women owned the fields and scheduled the harvests. Europeans also failed to understand that Iroquois men were diplomats and controlled over one million square miles of fur-trapping area. While Iroquois men sat at the governing council, Iroquois clan matrons caucused with tribal members and told the men how to vote.
These are small examples of the material contained in this important series. The reader is encouraged to use the extended bibliographies provided with each book to expand his or her area of specific interest.
Dr. Troy Johnson
Professor of History and American Indian Studies
California State University
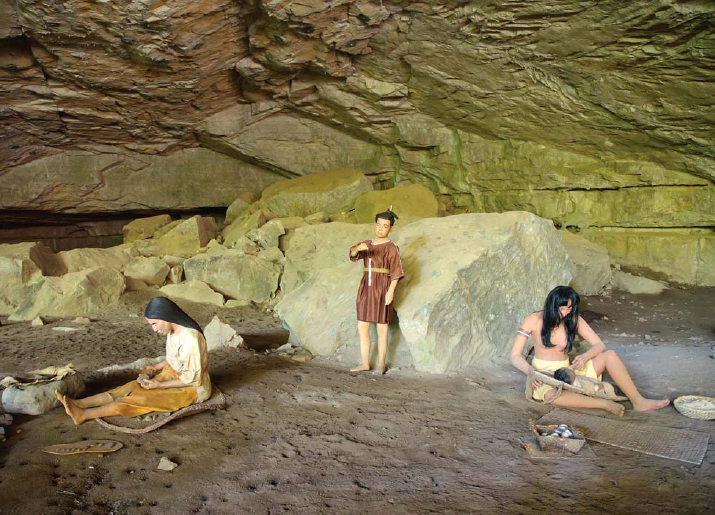

Representation of a Native American family at Russell Cave National Monument, a site in present-day Alabama that was apparently inhabited by Paleo-Indians some 10,000 years ago. Archaeologists believe that it was around this time that Native Americans began constructing their own dwellings and forming communities
Where did the first Americans build their homes? Did they live in open camps, caves, or timber-and-earthen houses? are still trying to answer these important questions.
For many years, experts believed that migrated to America from northeast Asia approximately 10,000 to 12,000 years ago. Scientists believed that they walked into present-day Alaska at a time when sea levels were lower, and the Bering Strait was not covered by water. They speculated that the Paleo-Indians made this journey in pursuit of the animals that they depended upon for food. These people, known as the Clovis Culture, were believed to be the ancestors of all Native American tribal groups.
This theory began to be challenged during the 1980s with the excavation of an ancient human settlement in Monte Verde, Chile. tests performed on pieces of the relics and ruins found at the site indicated that Paleo-Indians had lived there more than 13,000 years ago.
The Paleo-Indian Clovis Culture has been traced back to between 10,000 and 8,000 B.C . Archaeologists believe that these people lived beneath rock shelters, inside caves, and in outdoor camps
Next page