Glossary
(DEL-tuh) the triangle-shaped area where a river deposits mud, sand, and pebbles (di-SEN-duhnts) all the relatives who trace their family roots back toone person (FUHR-tuhl) good for growing crops; fertile soil has many nutrients (FUHR-til-uh-tee) the ability to support the growth of many plants (HYE-ruh-glif) a picture or symbol used in the ancient Egyptian systemof writing (IHR-uh-gate) to supply water to dry soil through methods such as pipesand channels (mon-SOON) very heavy rainfall (muh-mi-fuh-KAY-shun) the process of preserving a dead body with specialsalts and cloth to make it last for a very long time (puh-PYE-ruhss) a type of paper made from a tall grasslike plant in ancienttimes (FAIR-oh) a ruler of ancient Egypt (RICH-oo-uhl) an action that is always performed in the same way, usuallyas part of a religious or social ceremony (SIM-buh-lize) to stand for or represent something else (TOOM) a room or building that holds a dead body and any items that were buriedwith that person (yoo-NITE) to join together to make a whole
Read More
- Conklin, Wendy, and Blane Conklin. You Are There! Ancient Egypt 1336 BC. HuntingtonBeach, Calif.: Teacher Created Materials, 2017.
- Napoli, Donna Jo. Treasury of Egyptian Mythology: Classic Stories of Gods, Goddesses,Monsters & Mortals. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic, 2013.
- Owings, Lisa. What We Get from Egyptian Mythology. Mythology and Culture. Ann Arbor,Mich.: Cherry Lake Publishing, 2015.
Critical Thinking Questions
- The Greek gods were often jealous, angry, and cruel. Why do you think they actedthis way? Use details from the text in your answer.
- What lessons do you think the story Isis and the Seven Scorpions (page 24) taughtEgyptians? Are those lessons still important today? Why or why not?
- Maat, the goddess of truth, justice, and order, was also the most important conceptto ancient Egyptians. What do you think is the most important concept in your community?Create a god or goddess to represent it.
Chapter 1
The Culture of Ancient Egypt
Imagine what it was like living in ancient Egypt. Cattle pulled carts in the streetsand kicked up dust as they dragged plows in the fields. Because of the scorchingsun, growing crops was difficult in some areas.
The Sahara Desert is one of the hottest and driest places on Earth. Summer temperaturesin the Sahara are often well over 100 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius).
As much as possible, ancient Egyptians tried to avoid the Sahara Desert or red land. With the blazing heat, lack of water, and dangerous creatures, such as snakesand scorpions, this region could be deadly.
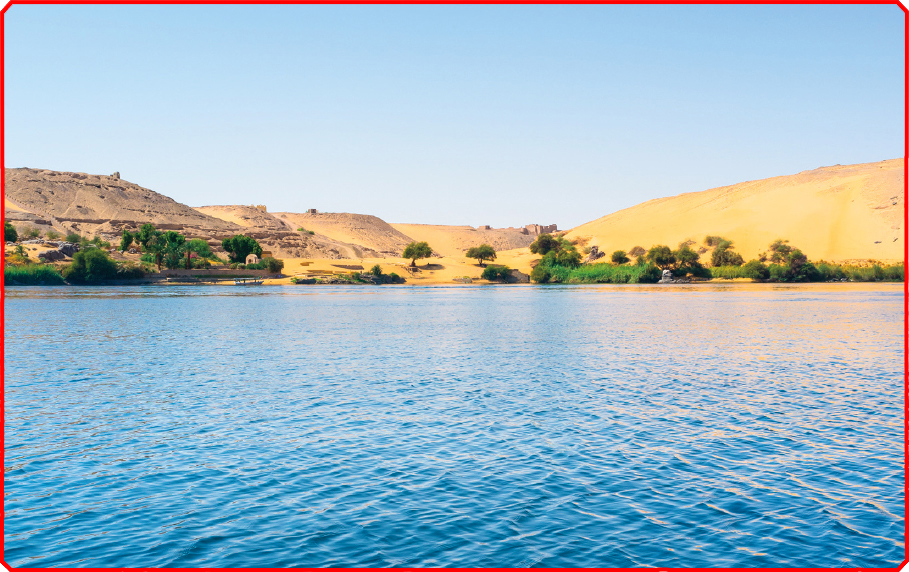
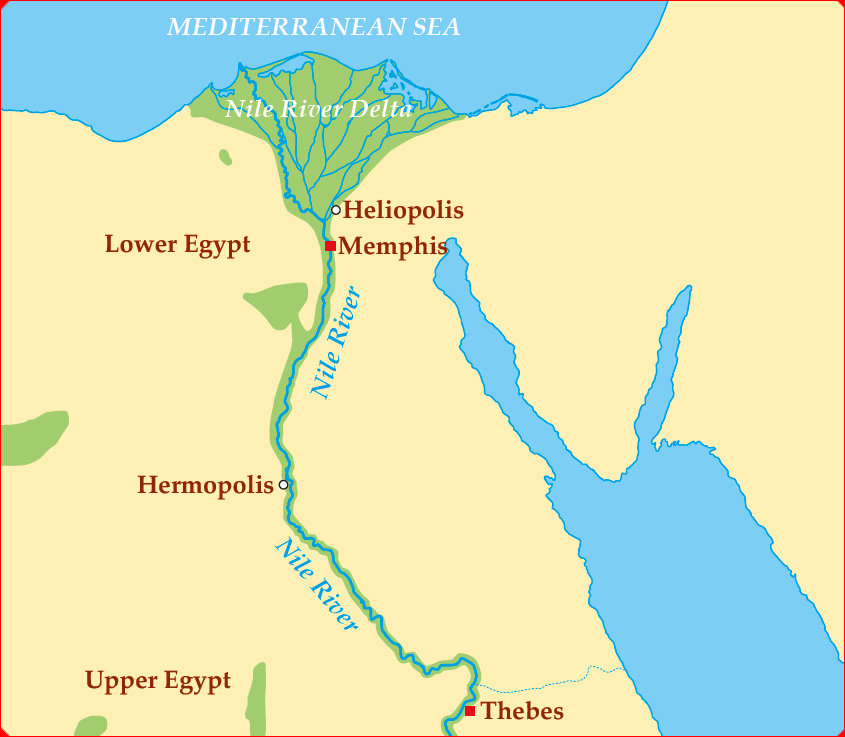
The Nile River cuts through the Sahara. Because the Nile was the major source ofwater in Egypt, most people lived near it in ancient times. The land along the riverwas also very , which made growing crops easier. But life along the Nilehad its dangers too, as the river was home to crocodiles and hippos.
The Nile is the longest river in the world. It is more than 4,130 miles (6,647 kilometers) long.
Cycle of Flooding
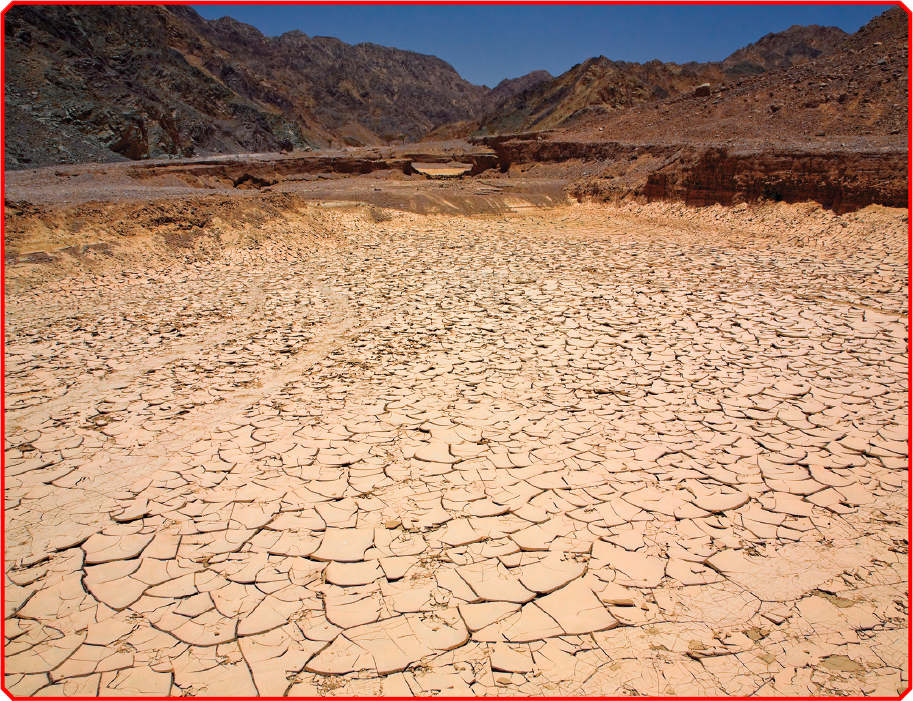
Life for the ancient Egyptians centered around the Nile River. Each year by latespring, the Nile was at its lowest level. The land surrounding it was so dry thatthe earth would crack. But then summertime fed the river, causing it toflood the area nearby. All summer the land was swampy and difficult to live in.When the floodwaters went back down, the soil left behind was perfect for growingcrops.
When the Nile River reached its lowest levels, the land around it became extremelydry.
The ancient Egyptians could not always depend on the floods, though. Some yearsthe floods didnt come at all. Other times the floods were too small. When therewasnt enough water for the crops to grow, many people died from lack of food.
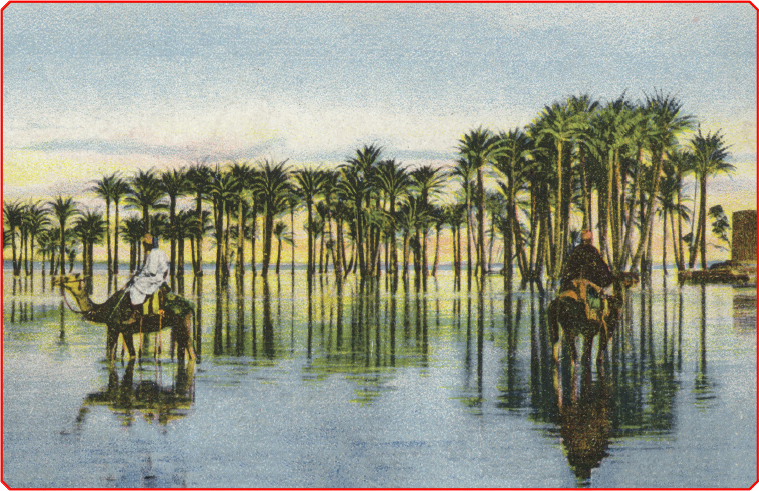
Some years the floods were too big and destructive. Even so, to the people of ancientEgypt, the floods were a gift from the heavens. They believed the floods .
Men ride camels across the water-soaked land following the flooding of the Nile.
Kingdoms, Pharaohs, and Priests
By about 3400 BC, two kingdoms had been established in ancient Egypt. Lower Egypt,where the Nile the two kingdoms.
With the kingdoms united, Menes wanted to form one national religion. The ancientEgyptians believed in many gods and goddessessome even had the same characteristicsand duties. Some of them were national and official gods that were worshipped inhuge temples. Others were local gods that were only worshipped in certain towns.
In ancient Egypt . For example, they put perfume or food on thestatues of the gods inside the temples.
Ancient Egypt
Upper and Lower Egypt were named because the Nile flows from south to north. Therefore,the upper part of the river is in the south and the lower part is in the north.
Did You Know?
The word pharaoh comes from the ancient Egyptian word per-aa, which means greathouse. Today we use the word pharaoh to mean a king or ruler in ancient Egypt.
Ancient Egyptian Way of Lifeand Death
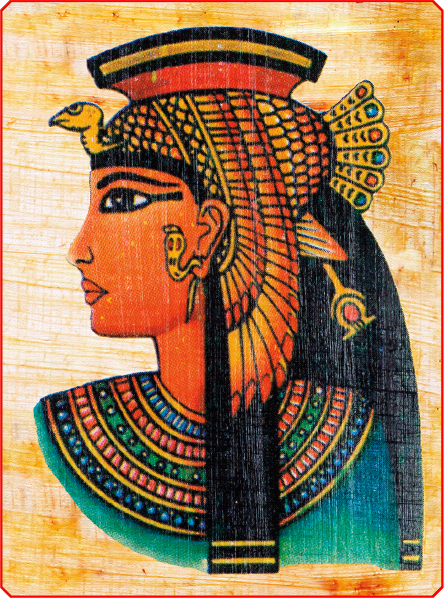
Women in Egypt had the same legal rights as men. They could run businesses and buyand sell property. There were even female rulers, such as Hatshepsut and Cleopatra,who shaped the politics and religion of the country.
Ancient Egyptians were responsible for many of the worlds earliest technical advances. They invented a type of thick paper called crops on a large scale.
The ancient Egyptians also made important developments in medicine. For example,they recognized the importance of washing regularly to avoid diseases.
Cleopatra ruled Egypt in the 1st century BC.
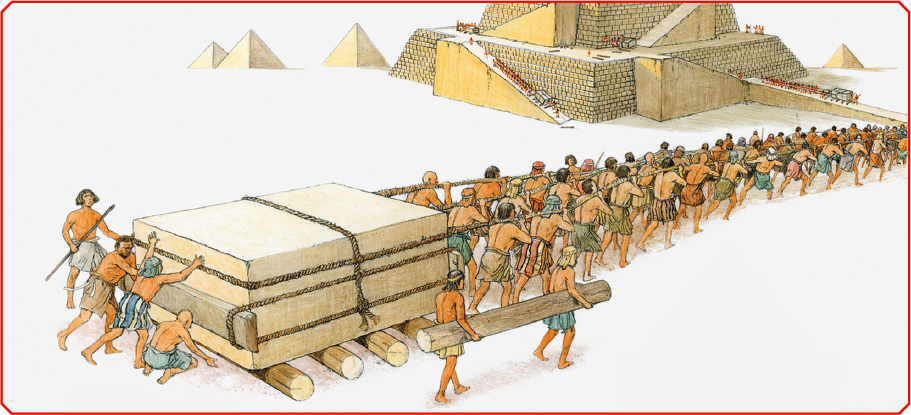
The ancient Egyptians were also expert shipbuilders, and their art and architecturewas known for its details and beauty. Much of their art had to do with the ideaof death. To them, life on Earth was only a small part of an endless journey. Forthat reason, pharaohs were buried with weapons, furniture, food, and other itemsanythingthey might need in the afterlife.