
Published in 2015 by The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010
2015 Brown Bear Books Ltd
First Edition
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, without the prior written consent in writing from the publisher.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Johnson, Rose, 1981-author.
Discoveries in medicine that changed the world / Rose Johnson. -- First edition.
pages cm. -- (Scientific breakthroughs)
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN 978-1-4777-8611-6 (library bound)
1. Medicine--History--Juvenile literature. 2. Discoveries in science--Juvenile literature. I. Title.
R133.5.J64 2015
610.9--dc23
2014027728
Editor and Text: Rose Johnson
Editorial Director: Lindsey Lowe
Childrens Publisher: Anne ODaly
Design Manager: Keith Davis
Designers: Lynne Lennon
Picture Researcher: Clare Newman
Picture Manager: Sophie Mortimer
Brown Bear Books has made every attempt to contact the copyright holder. If anyone has any information please contact:
All artwork: Brown Bear Books
Manufactured in the United States of America
Picture Credits
t=top, c=center, b=bottom, l=left, r=right.
FC, Digital Storm/Shutterstock; b, Design Pics/ Thinkstock
Contents
Introduction
The practice of medicine is as old as civilization. Ever since the dawn of history, doctors have been looking for ways to cure disease and extend life.
I t is not just humans that take medicine. Chimpanzees living in the forests of Africa eat the leaves of a particular plant when they have upset stomachs. It is likely that primitive humans used herbal medicines in the same way. Experts in these remedies would have been highly respected like doctors are today. The first doctors we know about were from 5,000 years ago in Mesopotamia (now Iraq). As well as being doctors, these people were also priests, who believed that illness was caused by evil spirits in the body.
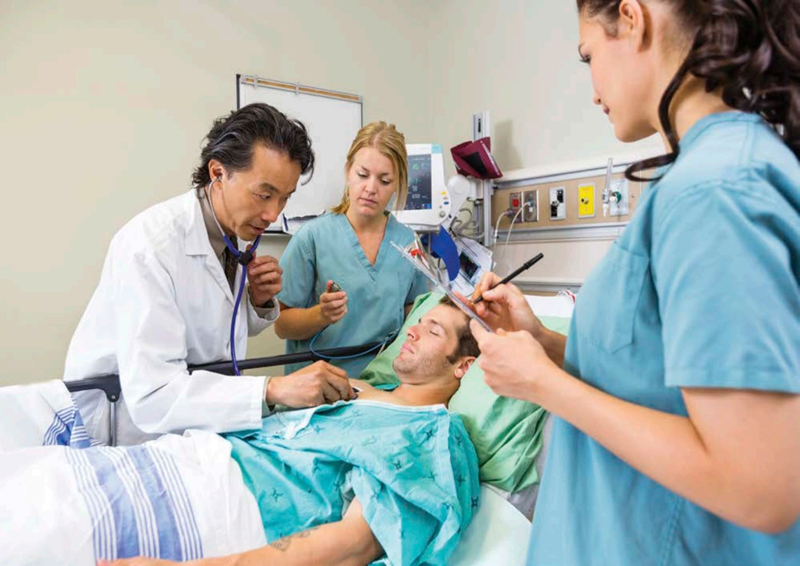
Healthcare is provided by a team of doctors, nurses, and technicians.

Eating the right foods is important for maintaining a healthy body.

Sports and exercise are a good way of staying healthy and avoiding disease.
Ancient links
All doctors working today take the Hippocratic Oath. This is a promise that they will do nothing that could make a person more illonly try to make them better. This idea stems from a Greek doctor called Hippocrates, who lived 2,400 years ago. Hippocrates was one of the first to say that illness was caused by problems with the body, not supernatural spirits.
Understanding the body
The history of medicine relates how doctors figured out how the body works in ever greater detail, so they could identify what was causing disease. Today, there are cures for many common diseases that would have killed people in the past. Modern medicine offers the prospect of a long life, but it also shows that we have to look after our bodies to avoid developing diseases.
Surgery
Today, surgery is at the cutting edge of modern medicine, with doctors slicing into the body to fix problems. However, surgery is an ancient practice.
I t may come as a surprise to hear that the earliest operations were brain surgery. Human skulls dating back to the dawn of civilization, some suggest even 14,000 years ago, have been found with a hole cut in them. This is trepanation, in which the skull was operated on to cure seizures, headaches, and mental problems. Evidence from other ancient human remains shows that people performed surgery on teeth and were able to set broken bones. Ancient writings show pictures of doctors working with knives. These were the first surgeons.
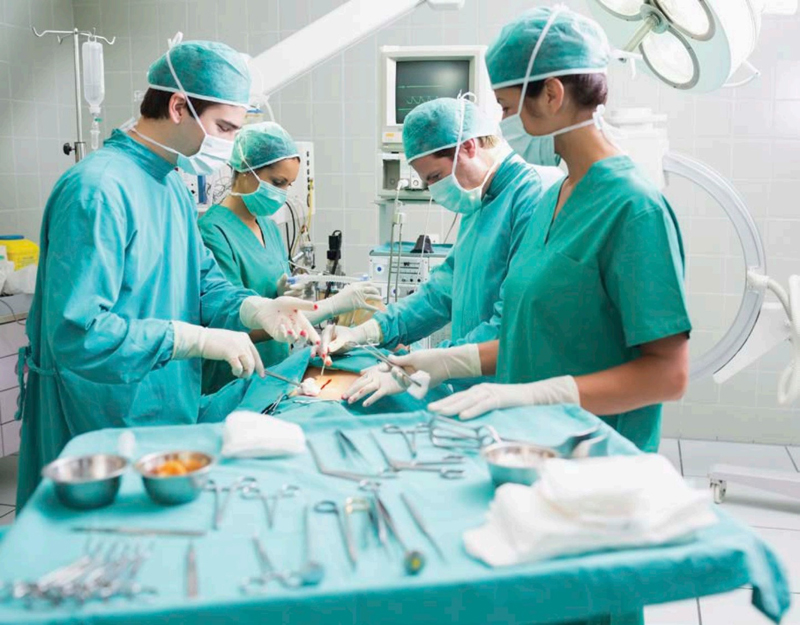
Modern surgery can last many hours. The blue-green clothes worn by surgical teams helps the surgeon to concentrate on the red colored body parts without getting tired eyes.
Surgical manual
The earliest book about surgery we know about was written by Sushruta, an Indian doctor who lived about 2,600 years ago. His writing gives instructions on how to cut open parts of the body, how to feel around inside the body, and then how to close up the cut safely using stitches or other techniques.
Modern surgery
Todays surgeons are very skilled at what they do, but about 200 years ago they were not seen as proper doctors. In many cases, people went to see the barber if they needed an operation. Barbers did everything from cutting hair to chopping off legs!
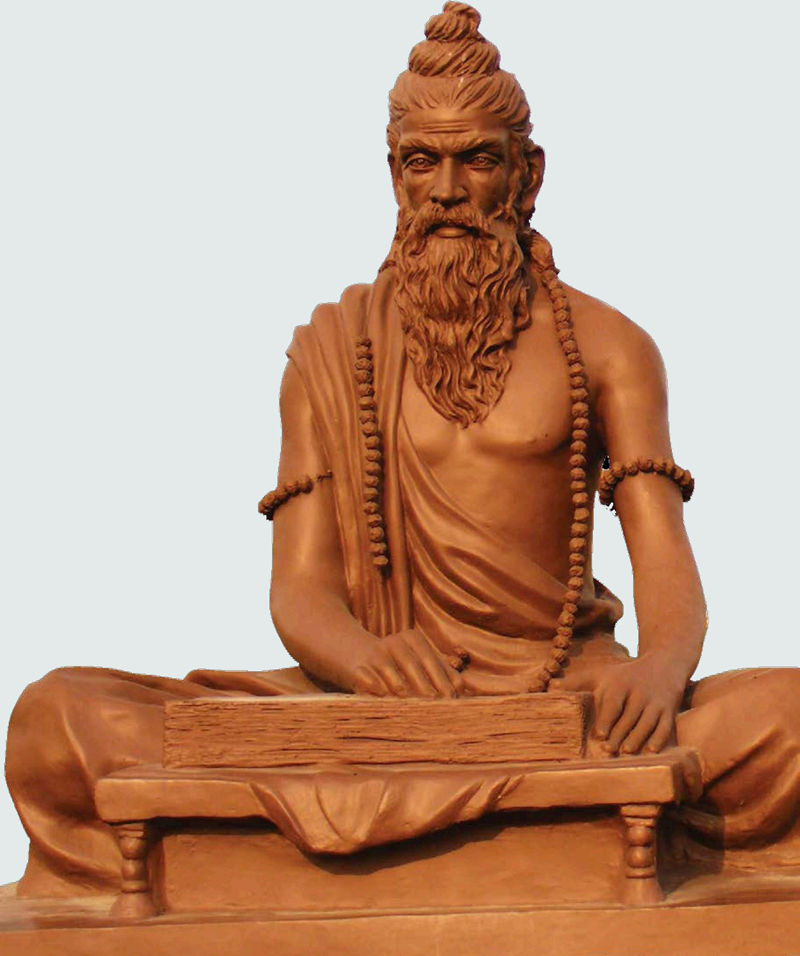

A statue of Sushruta in India honors the ancient figure as one of the founding fathers of medical science.
SUSHRUTA
No one is sure when this Indian doctor lived. He may have worked as far back as 3,000 years ago but the best guess is he lived in Varanasi in northern India around 600 BCE. He is thought to be the inventor of plastic surgery, where he used tissue taken from one part of the body to fix damage somewhere else.
Blood Circulation
Blood carries oxygen and nutrients around the body and carries away the waste. The way blood circulates was not figured out until 1628.
W illiam Harvey discovered how blood moved around the body in the early 17 th century. Before that time doctors were taught blood was made inside the heart and liver and drawn into the body where it was used upand replaced by new blood. Harvey figured out that if this were true a person would be making 550 lb (250 kg) of blood a day!
BLOOD VESSELS
William Harvey found that there are two types of blood vessel. Arteries carry blood away from the heart; veins bring it back. Valves inside the veins stop blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
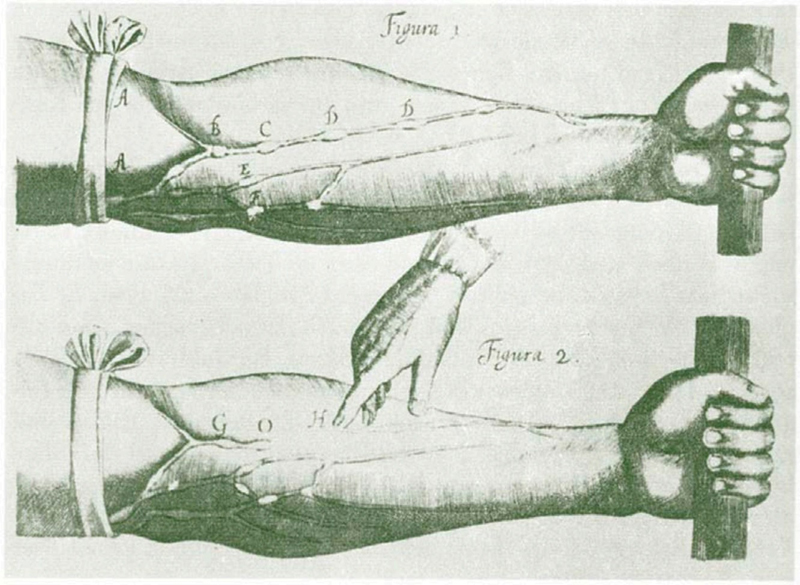
William Harvey made drawings of the valves that he found in the veins of the forearm.
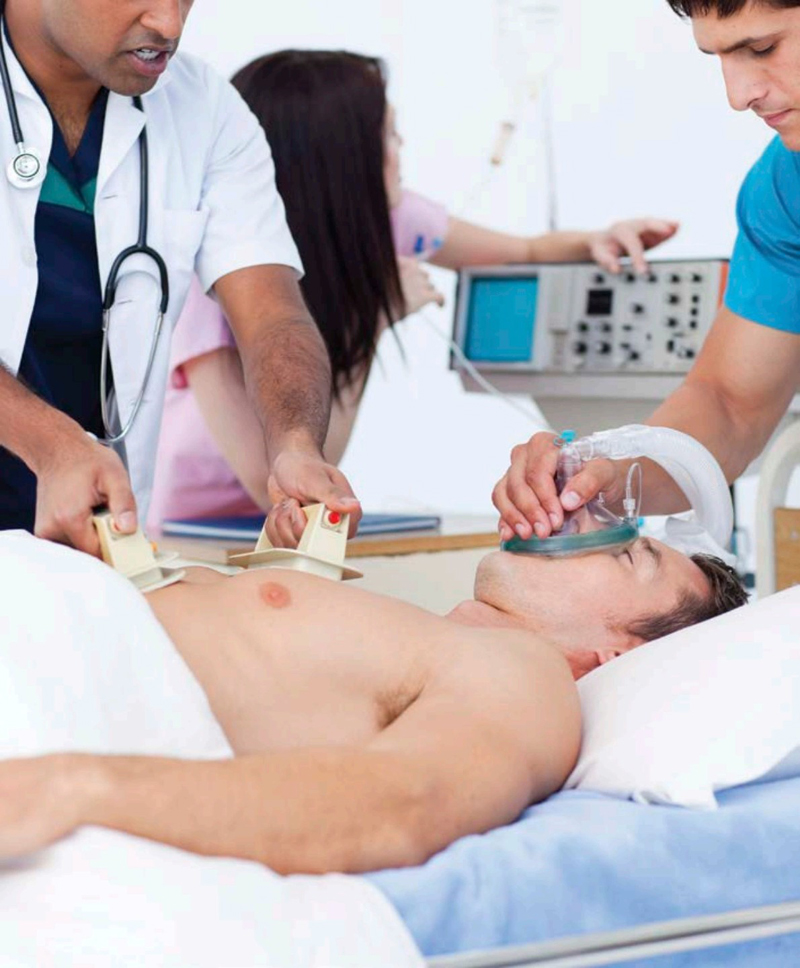
A defibrillator restarts the electrical control system that makes the hearts muscles pump in the correct sequence.
IMPLICATIONS
When a sick person arrives in an ER, the first thing a doctor does is check if a persons heart is beating. The body cannot survive if the heart stops. If the heart has stopped, the medics try to get it going again. To do this, they give it a powerful electric shock with a machine called a defibrillator.
Body pump
Harvey reasoned that the amount of blood stayed the same and was pumped around by the heart. He performed experiments to find out how the heart worked, which by todays standards would be unethical. He sliced open living animals and observed their hearts until the subjects died.
Next page

















