Springer International Publishing AG 2017
Mohammad Jawaid , Mohd Sapuan Salit and Othman Y Alothman (eds.) Green Biocomposites Green Energy and Technology 10.1007/978-3-319-49382-4_1
Green Biocomposites for Structural Applications
N. Saba 1 , Mohammad Jawaid 1, 3, 4, M. T. H. Sultan 2, 3 and Othman Y. Alothman 4
(1)
Laboratory of Biocomposite Technology, Institute of Tropical Forestry and Forest Products (INTROP), Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
(2)
Department of Aerospace Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
(3)
Faculty of Engineering, Aerospace Manufacturing Research Centre, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Level 7, Tower Block, 43400 Serdang, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
(4)
Department of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
The quest for the development of innovative materials having zero impact with high performance at affordable costs to meet the basic human and society demands results a dynamic composite materials. Green or biocomposites regarded as a high-performance or advanced fourth generation engineered composite materials that are comparatively better and attractive in terms of environmentally friendly, composability and complete degradability of end use products. The reinforcement of renewable and environment-friendly plant based lignocellulosic fibers with bio-based polymeric matrix (plastics) is the only ways to fabricate the green composites or to make them fully greener materials. Green composites offer a significant environmental key for both food and non-food market including the aerospace, automotive, decking and for others variety of structural applications over the past decades because of their relatively higher specific modulus and strength compared to metals. Developed bio-material undoubtedly delivers greater impact on the world economy by developing energy saving products for the improvement of life quality. Present study is designed to deliver an outline of the comprehensive recent research studies and works reported on sustainable green friendly biocomposites, focusing the concern on biopolymers, natural fibers, composite processing and their diverse structural applications. Currently, green composites considered as one of the emerging innovative products in materials and polymer composite science to expand the commercial application in the sectors ranging from packaging to the constructional industry.
Keywords
Natural fibers Polymer Biopolymer Green composites Applications
Introduction
Recently, higher motivation, efforts and consideration has been given by the materials scientists and politicians in the composite fields towards the utilization of renewable bio-based and biodegradable materials due to persistent discussions on the climate changes and growing regulatory demands underlining the need for cleaner and safer environment globally. Green composite materials are refers to those materials which are completely biodegradable or renewable and can address the twin issues of sustainability and zero environmental impact.
The chemical, physical and biological degradation of composite materials having time resistant polymeric matrix, poses serious concerns, when used in certain human related areas such as surgery, pharmacology, agriculture and the environment. Such biodegradable materials have become invaluable gifts to the society through the modern science and technology as they are preferred in products having single use, short-life, and easy disposability. Besides this, they have controlled-life and hence used in applications such as packaging, consumer products (disposable plastics, agricultural films) and marine disposables components (Satyanarayana ).
Bio or Green Composites
The ecological concerns and issues such as recycling and environmental care are increasingly important to handle the present situation. As a consequence of growing environmental awareness surrounding society a great interest in the research on more environmentally friendly materials that are derived from non-renewable resources are gaining attention (Garca-Garca et al..
Fig. 1
General scheme for the fabrication of green composite (Color figure online)
In green composites the reinforcing fibers possess a high tensile strength and stiffness, while the embedding or reinforcing agent (matrix) offers the shape of the composite structure and transmits the applied shear forces between the fibers and also protects them against destructive and radiation source (Nickel and Riedel ). The developed products are called green composites, principally due to their sustainable and degradable properties, without impairing the surrounding environment. As non-biodegradability results many serious environmental problems such as unsightly litter, eutrophication and polluted marine waters.
Currently, green composites material become extremely valuable not only in the scientific world but also in the commercial daily applications with their marked futures (Niaounakis ). Green composites are quite durable and hence are used to increase the life cycle of short life end products. However, the only challenge is to procured green polymers to be used as polymer matrices required during the fabrication of green composites.
Reinforcement/Filler
Reinforcement in green composites include materials from renewable source consisting of cellulose and chitin such as plant fibers (bast, leaf, core fibers), fibers from recycled wood or waste paper, regenerated cellulose fibers (viscose/rayon), by-products from food crops, bio-agricultural wastes. To the present, significant research efforts were made in developing a new class of fully biodegradable green composites by combining natural fibers with biodegradable resins (Netravali and Chabba ). In the composites, reinforced fibers provide stiffness,sufficient strength and governed the inherent properties of the final material.
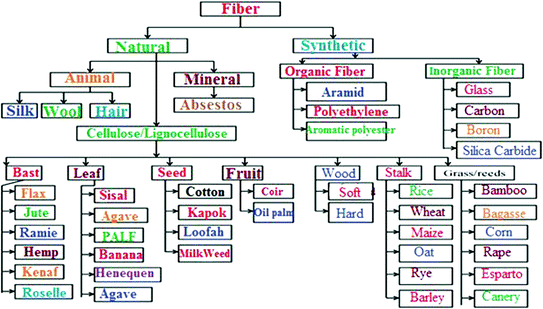
Fig. 2
Broad classifications of fibers (Saba et al. )
Different types of natural fibers and their properties have been studied which can as a potential replacement of synthetic fibers like glass and carbon fiber. Individual properties of each types fibers have significant importance to generate new applications and opportunities for biocomposite for the 21st century green materials environment (Gurunathan et al. ). However, the quest for the entrance of biocomposites into commercial markets to stimulate the increasing demand of non-food crops ensuring suitable fiber selection relative to the bio-polymer would led to future novel innovations.
Fig. 3
Different types of natural fibers used as reinforcement in polymer composites
Bio-Based Polymeric Matrix
The growing desire to mitigate climate change due to greenhouse gas emissions, biodegradable resins or bio-resins are explored as the best potential alternatives of petroleum/fossil based traditional polymers for composites in a wide range of applications (Rwawiire et al..