SUGGESTED READING
Marsh, Reginald. Anatomy for Artists. New York: Dover Publications reprint, 1970.
Peck, Stephen Rogers. Atlas of Human Anatomy for the Artist. New York: Oxford University Press, 1951.
Richer, Paul. Artistic Anatomy. Translated and edited by Robert Beverly Hale. New York: Watson-Guptill, 1971. London: Pitman, 1973.
de C. M. Saunders, J. B. and OMalley, Charles D. The Illustrations from the Works of Andreas Vesalius. Cleveland, Ohio: The World Publishing Company, 1950.
Sheppard, Joseph. Anatomy: A Complete Guide for Artists. New York: Watson-Guptill, 1975. London: Pitman, 1975.
Sheppard, Joseph. Drawing the Female Figure. New York: Watson-Guptill, 1975. London: Pitman, 1975.
Sheppard, Joseph. Drawing the Male Figure. New York: Watson-Guptill, 1976. London: Pitman, 1976.
Chapter One
REVIEW of ANATOMY

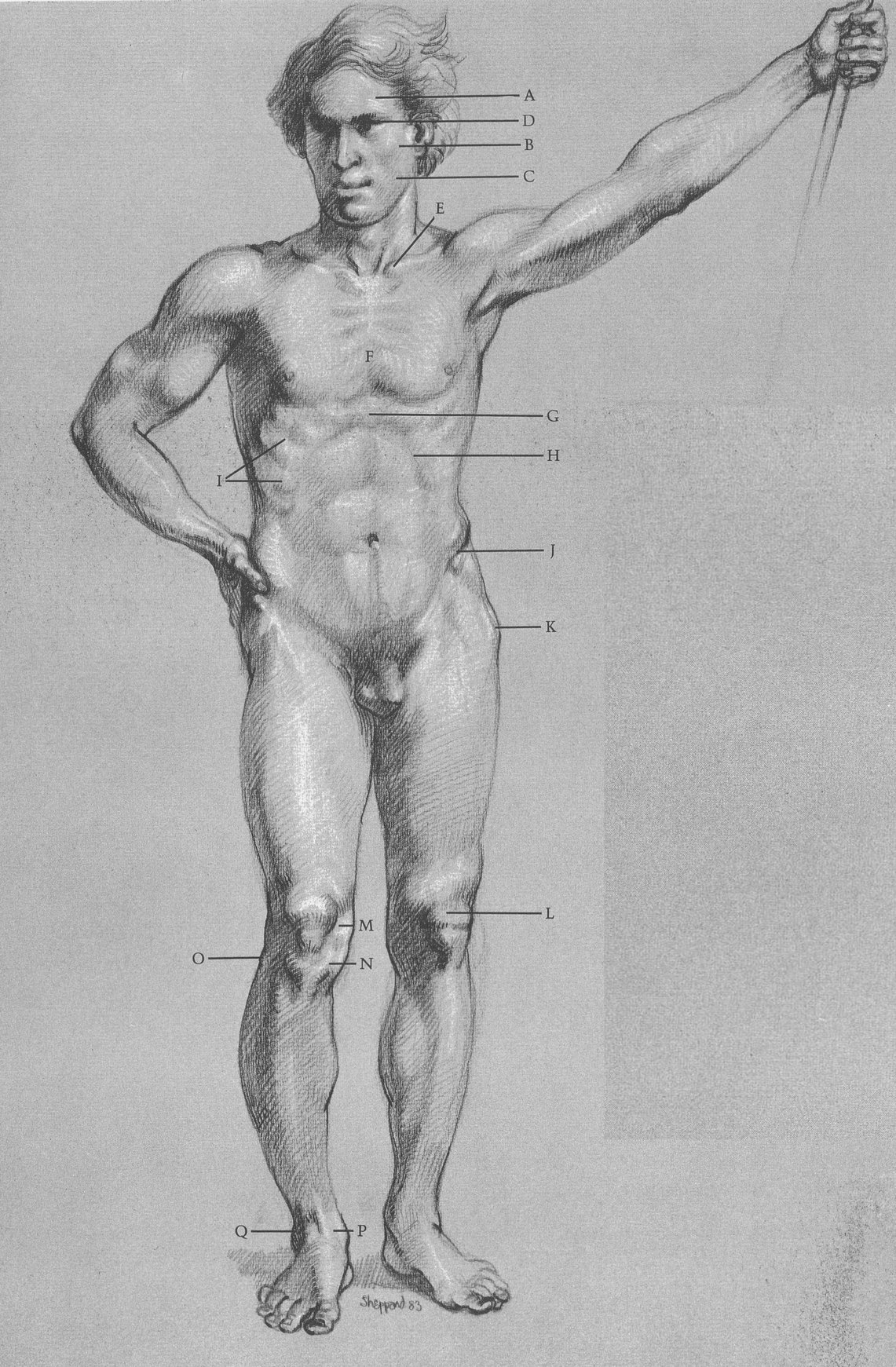
MALE FIGURE, FRONT VIEW
SURFACE ANATOMY
Muscles of skull are thin; bone is close to surface. Skull creates shapes of (A) forehead, (B) cheek, (C) jaw. (D) Eye is egg-shaped, sits in eye socket. (E) Clavicles start at head of (F) sternum, rising upward and back toward outside of shoulder. Note direction of first five ribs attached to sternum: first rib goes upward; second moves straight across; others point downward. (G) End of sternum protrudes. (H) Cavity of rib cage forms arch. (I) Lower ribs slant down from back to front. Pelvis holds stomach like basin. (J) Pelvic crest is prominent. (K) Hipbone is close to skin, clearly seen on male. Note oval shape of (L) kneecap. Silhouette of knee is created by (M) end of femur, (N) head of tibia. (O) Head of fibula creates bump. Ankle is formed by (P) end of tibia, (Q) end of fibula, making hinge joint for foot.
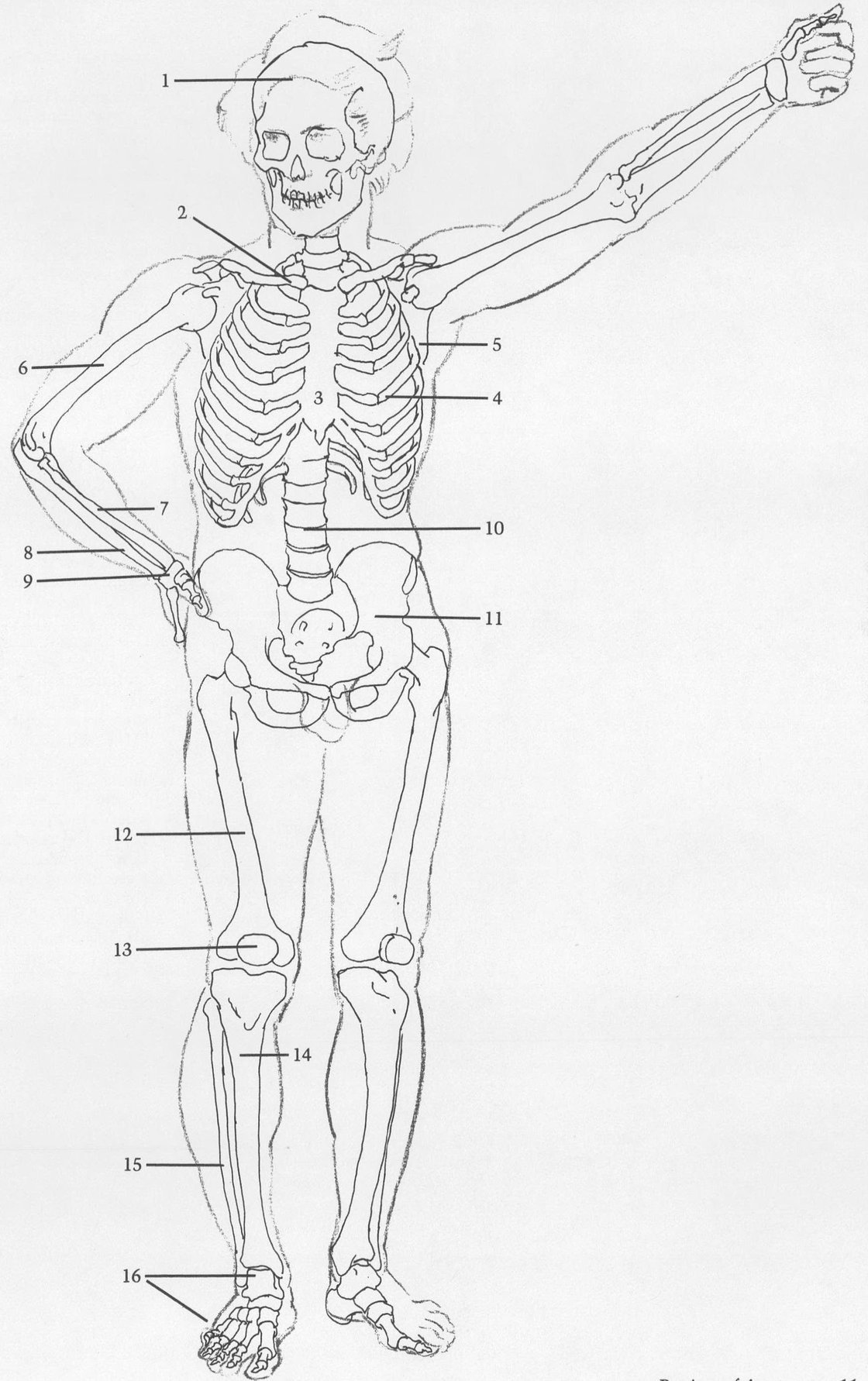
BONES
(1) Skull. (2) Clavicle. (3) Sternum. (4) Rib cage. First seven ribs attach by cartilage to sternum. Each of next three ribs attaches by cartilage to rib above. Eleventh, twelfth ribs do not attach to sternum and are called floating ribs. (5) Scapula. (6) Humerus. (7) Radius. (8) Ulna. (9) Wrist. Eight bones of wrist are treated here as one unit. (10) Spinal column is treated here as column of simple discs. (11) Pelvis. (12) Femur. (13) Kneecap. (14) Tibia. (15) Fibula attaches to rear of tibia head, intersecting tibia at ankle and descending further, thus making outside of ankle lower than inside. (16) Bones of foot.
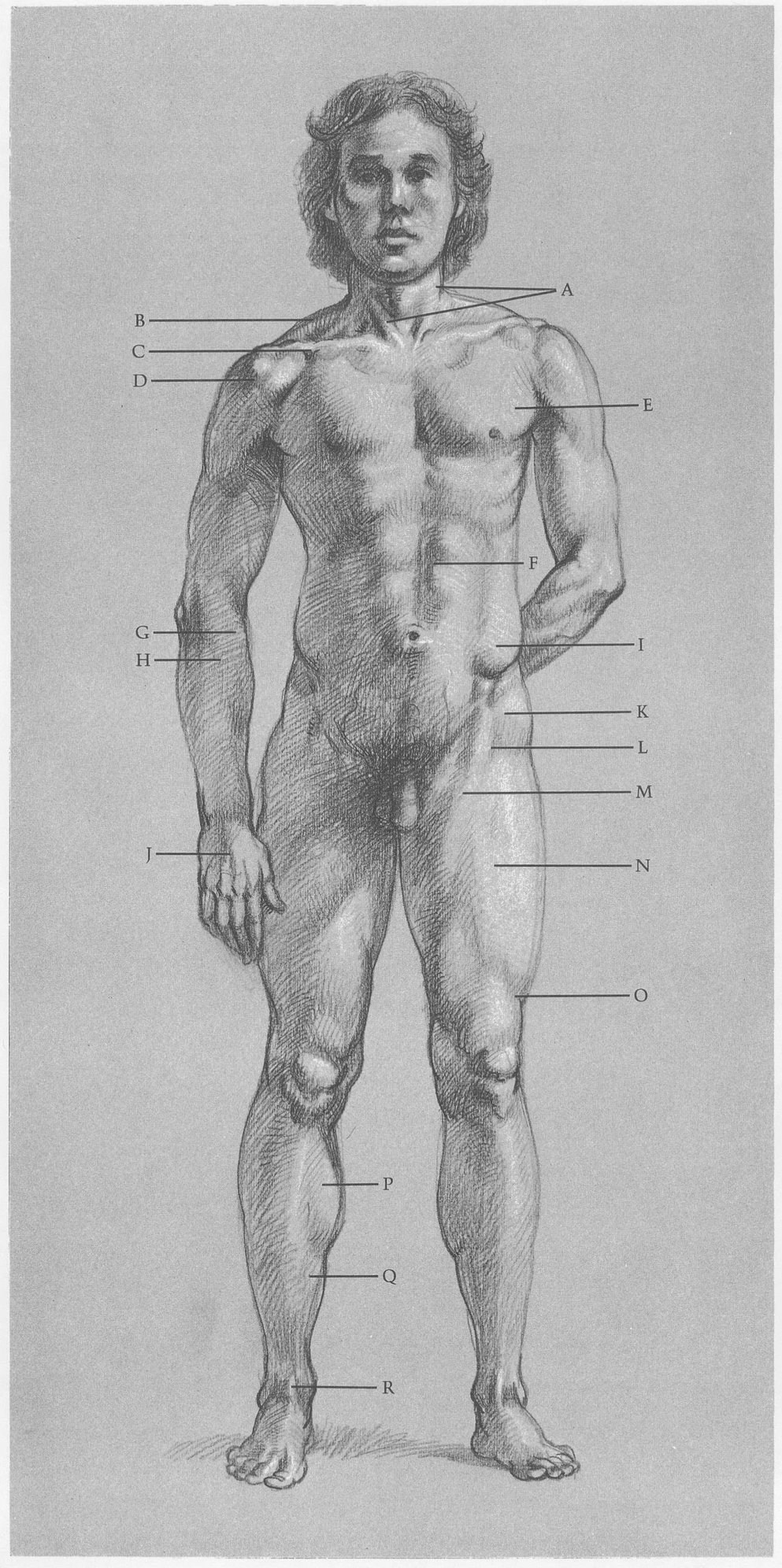
MALE FIGURE, FRONT VIEW
SURFACE ANATOMY
(A) Sternomastoid muscles create V shape. (B) Trapezius creates shoulder silhouette. (C) Pectoralis and deltoid meet to form cavity between them. (D) Note division of deltoid. (E) Pectoralis inserts into arm under deltoid. (F) Rectus abdominis is divided. (G) Long supinator and (H) wrist extensor both cross over from outside of elbow to thumb side of wrist. (I) External oblique inserts into top of pelvic crest. (J) Tendons of finger extensor are distinct. (K) Tensor fasciae latae angles toward outer contour. (L) See upside-down V where (M) sartorius and tensor fasciae latae overlap (N) rectus femoris. When knee is locked, (O) band of Richer pulls muscles in. (P) Gastrocnemius and (Q) soleus are calf muscles that attach in back of leg; they are seen from front. (R) Tendon of big toe extensor is prominent.
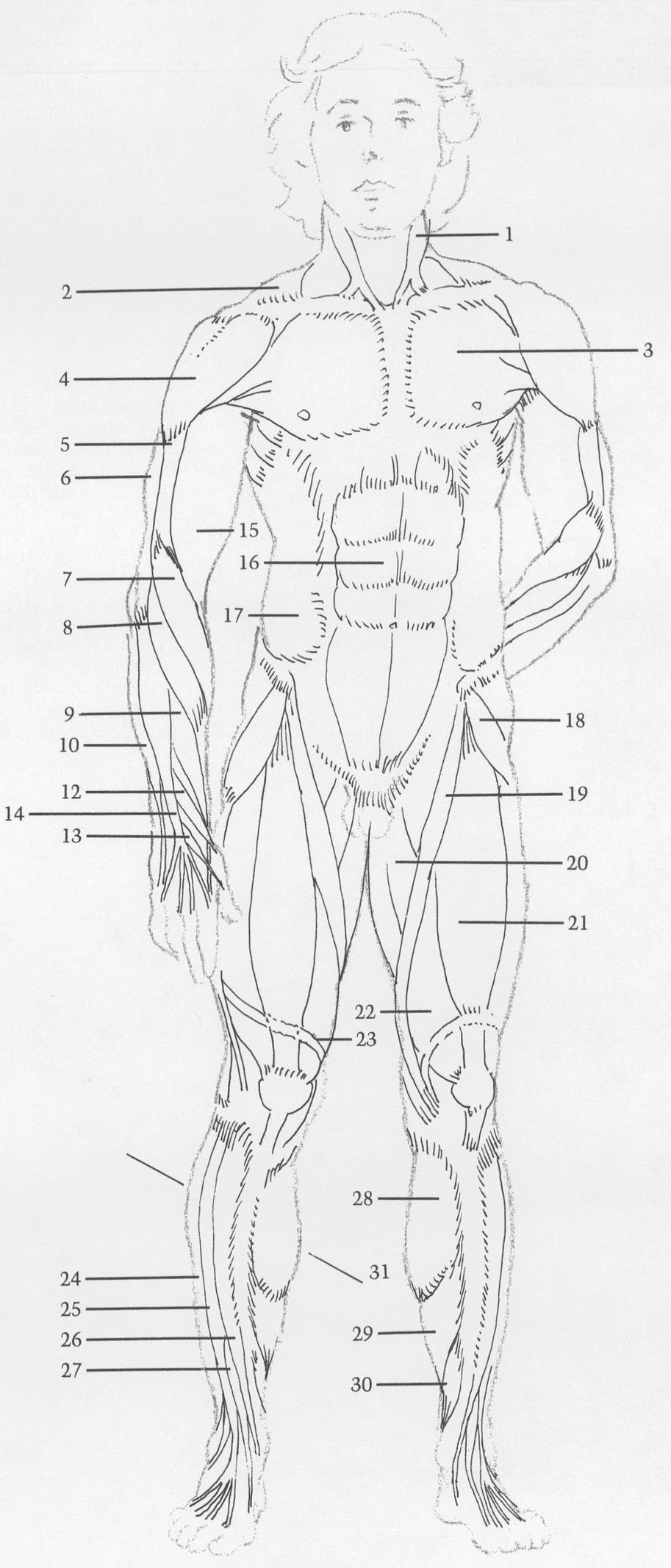
MUSCLES
(1) Stermomastoid. (2) Trapezius originates in back, inserts on top outside area of clavicle. (3) Pectoralis. (4) Deltoid. (5) Brachialis. (6) External head of triceps (one of three heads of triceps muscle). (7) Long supinator (turns forearm, palm out). (8, 9, 10) Extensors of wrist. (11) Abductor of thumb (pulls thumb toward back of hand). (12, 13) Extensors of thumb. (14) Extensor of fingers. (15) Biceps. (16) Rectus abdominis. (17) External oblique. (18) Tensor fasciae latae. (19) Sartorius. (20) Abductors. Several muscles are treated here as one unit. (21) Rectus femoris. (22) Vastus. Two parts are treated as one large muscle under rectus femoris. (23) Band of Richer changes shape of thigh when knee is locked. (Many bands that hold muscles in place are omitted). (24) Long peroneus. (25) Long extensor of toes. (26) Tibialis anterior. (27) Extensor of big toe. (28) Gastrocnemius. (29) Soleus. (30) Long flexor of toes. (31) Inside calf muscle mass is lower than outside mass.
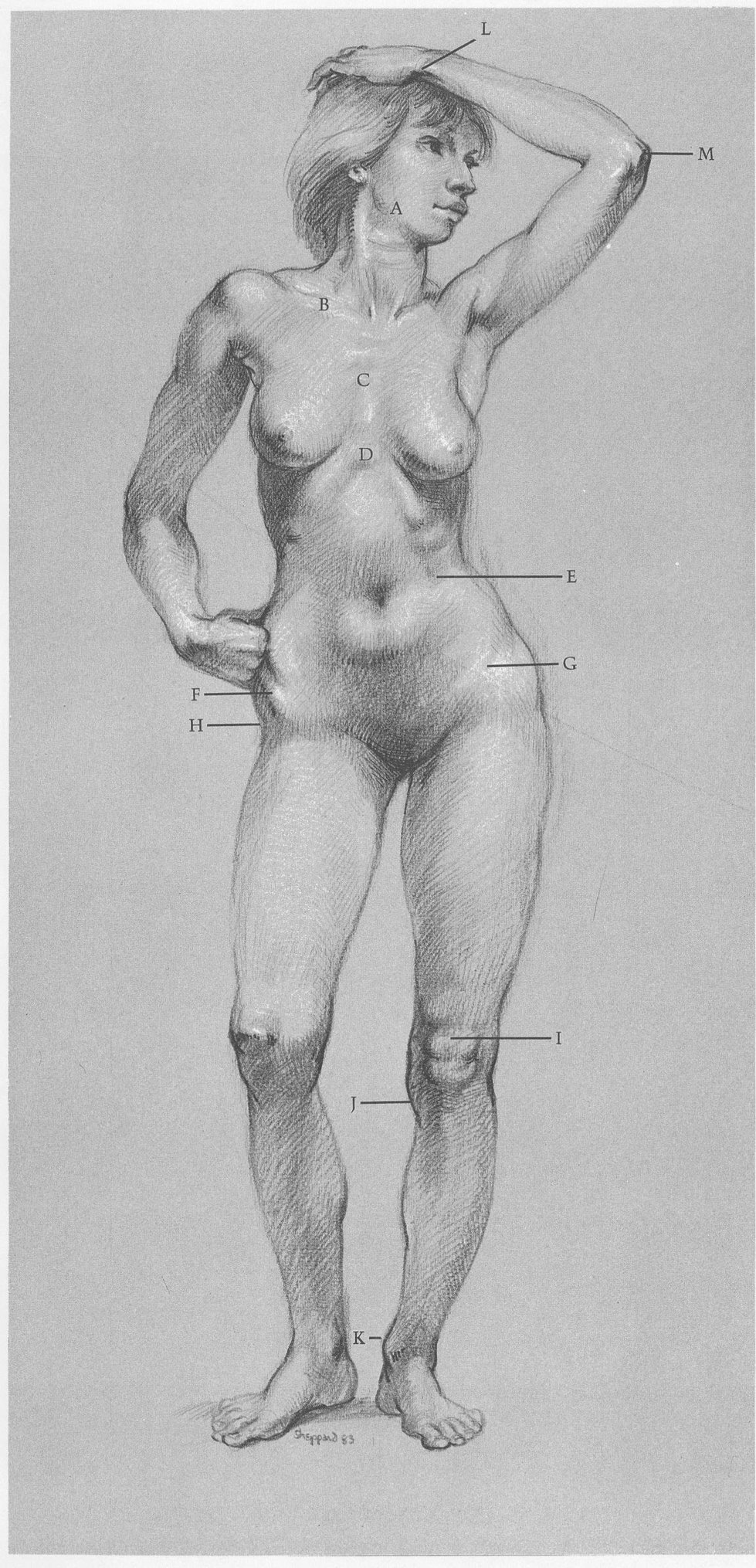
FEMALE FIGURE, FRONT VIEW
SURFACE ANATOMY
(A) Jawbone determines contour of face. (B) Note slant of clavicle. (C) Sternum shows rib attachments. (D) Cavity of ribcage is narrower on female than on male. (E) Lower ribs are evident. (F) Female pelvis is wider than male. (G) Crest of pelvis is partly covered by body fat. (H) Hipbone is close to skin, creating cavity on hip surface of females and fat males. (I) Kneecap and fat below form figure 8. (J) Shape of head of tibia slants inward. (K) Inside of ankle is always higher than outside. (L) End of ulna is prominent on little finger side of wrist. (M) Head of ulna forms elbow.
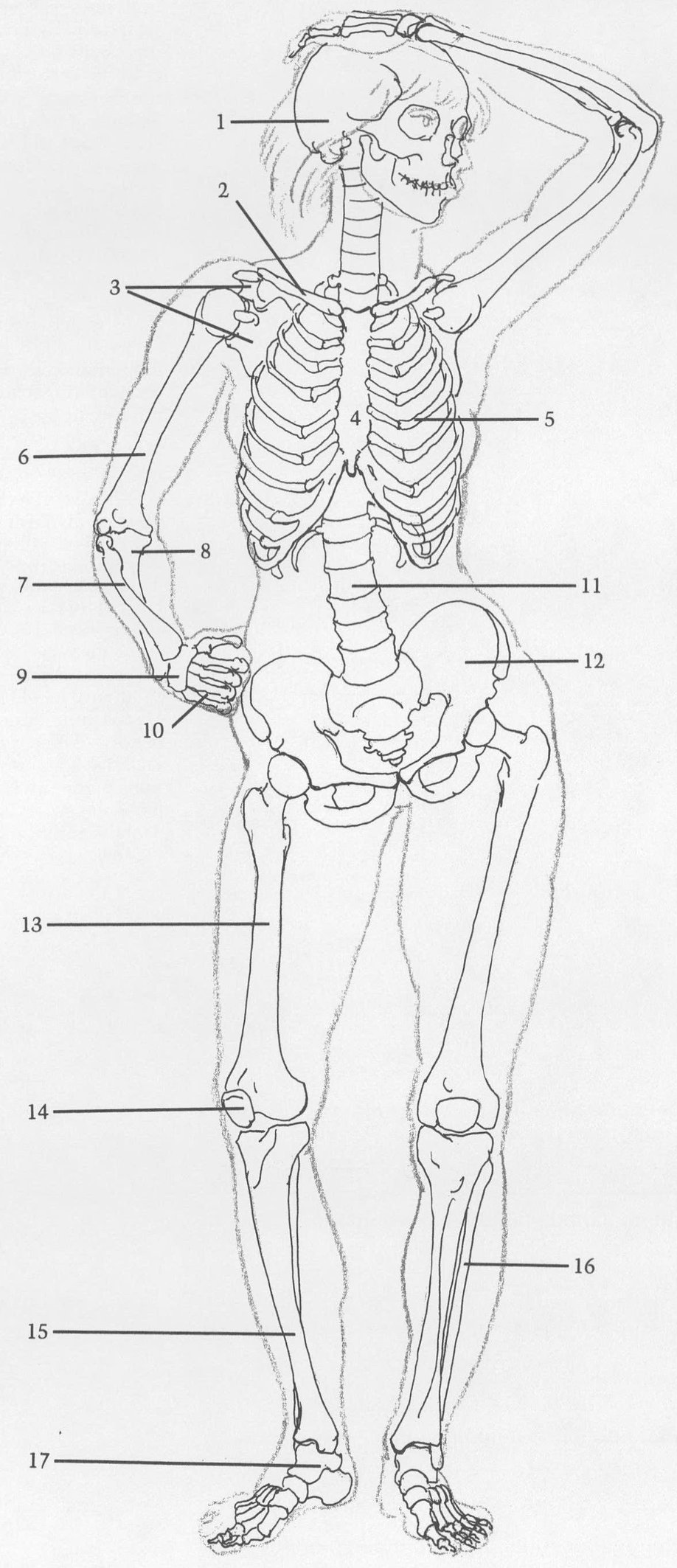
BONES
(1) Skull. (2) Clavicle. (3) Scapula. Clavicle and scapula form shoulder socket for humerusa ball and socket joint. (4) Sternum. (5) Rib cage. (6) Humerus. (7) Radius is always on outside of elbow and thumb side of wrist. Radius head, at elbow, is small. End of radius, at wrist, is large. (8) Ulna is on inside of elbow. Head is large; end is small. (9) Wrist. (10) Bones of the palm. (11) Spinal column. (12) Pelvis. Female pelvis is usually wider than male with crests projecting farther forward. (13) Femur. (14) Kneecap. (15) Tibia. (16) Fibula. Inside of ankle is always higher than outside. (17) Bones of foot.
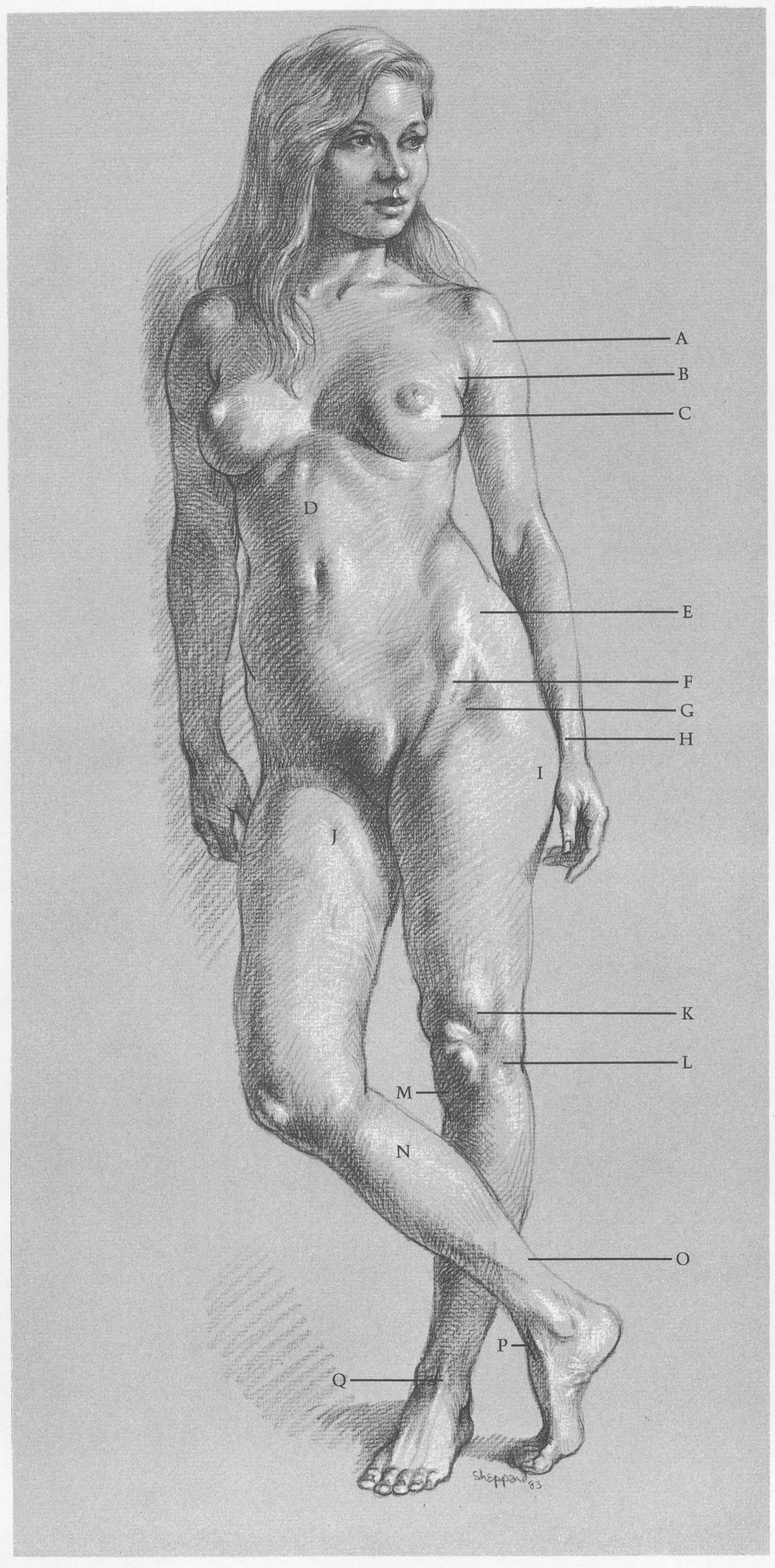
FEMALE FIGURE, FRONT VIEW
SURFACE ANATOMY
(A) Deltoid attaches to clavicle. (B) Pectoralis lies beneath (C) breast. (D) Vertical division of rectus abdominis is distinctexcept on extremely fat figures. (E) External oblique and female body fat cover most of pelvic crest. (F) Sartorius helps to form (G) upside down V shaped cavity. (H) Tendon of thumb extensor makes sharp ridge. (I) Female body fat covers hipbone. (J) Indentation is formed by sartorius. (K) Outside of vastus is prominent when knee is locked. (L) Iliotibial band descends outside of thigh like stripe, attaches to outside of tibia head. (M) Small fat deposit appears under kneecap. (N) Calf muscles attach to heel bone by (O) Achilles tendon. (P) Tibialis anterior tendon makes bridge between ankle and foot. (Q) Tendon of toe extensor is prominent.