1. Integrative Production TechnologyTheory and Applications
1.1 Global Economic Background
Production technology comprises the machinery, tools, infrastructure and know-how to make physical products. Therefore, production technology is the foundation of the manufacturing sector, including a vast range from small-scale enterprises using traditional production techniques [] to very large enterprises sitting atop a high and broad pyramid of parts and components suppliers collectively manufacturing complex products such as aircrafts (Eurostat ).
Globally, the manufacturing share of the Gross World Product (GWP ) is approximately 15 %, which amounts to nearly US$12 trillion (World Bank b).
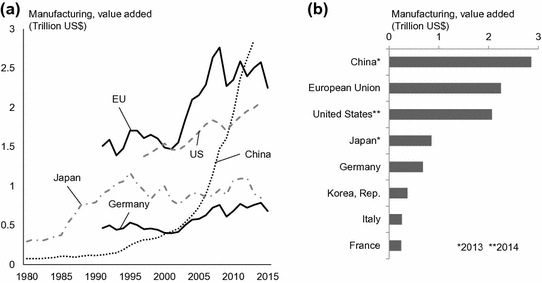
Fig. 1.1
Value added in manufacturing (US$) based on data by the World Bank (). a Development from 1980 to 2015. b Ranking of countries and the EU with respect to value added in manufacturing based on data from the year 2015
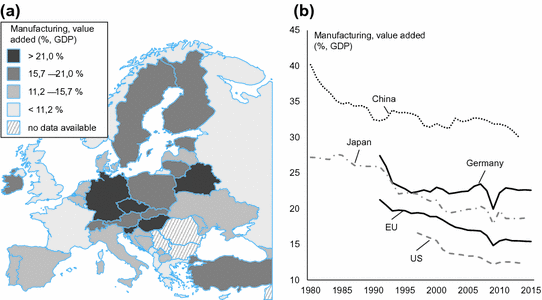
The share of manufacturing in the GDP is diverse across Europe and the world (see Fig. ). Further, there is no clear correlation between the wealth of a country and the share of manufacturing sector. Globally, the share of manufacturing in the GWP fell almost monotonously from 21 % in 1995 to 14 % in 2014. In particular, many rich countries have experienced a relative decline of the manufacturing sector. Prominent examples for this decline are the USA and the UK. For these, the share of manufacturing in GDP fell from 17 to 13 % and from 18 to 11 %, respectively, in only 10 years from 1997 to 2007, and stayed at that level since. In contrast, the respective share has been almost constant in Germany and China during this time.
Fig. 1.2
Share of manufacturing in GDP based on data by the World Bank (). a Situation in Europe in the year 2014. b Development from 1980 to 2015
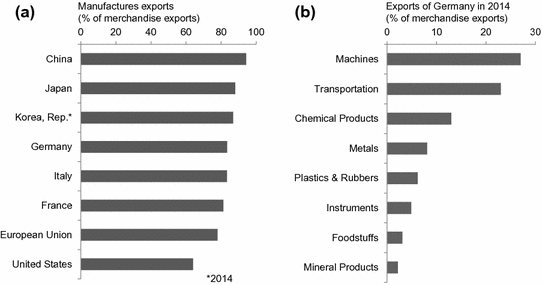
The importance of manufacturing for an economy is difficult to measure. Its share in GDP and GWP is only one indicator of many. While this share is relatively small (15 % of GWP), manufacturing contributes 71 % to global merchandise exports (World Bank ). Therefore, countries with a large manufacturing base are generally better at handling economic crises, as has been observed after 2009.
Fig. 1.3
Export data. a Share of manufactures in merchandise exports of leading manufacturing countries for the year 2015 based on data from the World Bank ()
Table 1.1
Ranking with respect to the economic complexity index (Simoes and Hidalgo )
Rank | Country | ECI |
|---|
| Japan | 2.25 |
| Switzerland | 2.10 |
| Germany | 2.05 |
| Sweden | 1.89 |
| USA | 1.80 |
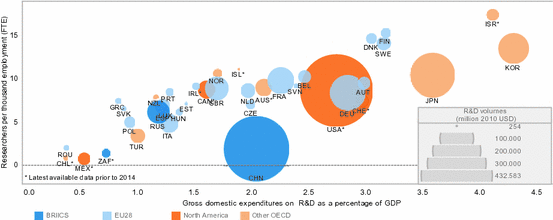
The ability to make a wide and complex product range requires not only the right people and infrastructure, but also a continuous investment in Research and Development (R&D). Therefore, there is a high correlation between ECI and R&D expenditure. Countries with a high ECI and a large manufacturing base typically devote more than 2.5 % of their GDP to R&D (see Fig. ). Therefore, the manufacturing sector is of great importance for a countrys innovation capacity. Further, innovation in manufacturing is often the basis for new or more efficient services, such as in civil aviation.
Fig. 1.4
Human and financial resources devoted to R&D (2014). The figure is adapted from the OECD (), an intergovernmental organization that includes mostly rich countries and has been visually edited by the authors
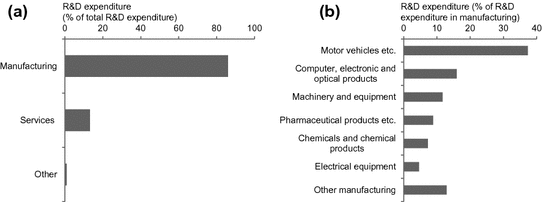
Fig. 1.5
Business enterprise R&D expenditure in Germany by industry sectors for 2013 (OECD )
The subsector of machinery and equipment has a special role within manufacturing. Comprising machinery and equipment that act independently on materials either mechanically or thermally or perform operations on materials (United Nations ).
Due to its central role, many countries consider manufacturing in general and the subsector of machinery and equipment as key factors for economic success. Nevertheless, the impact on society is, of course, not only macroeconomic. Innovation-driven productivity gains are often passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices (Manyika et al. ). In general, the maturity of production technology makes the difference with regard to price between products that are suitable for a small fraction of a population and the wide share. Electric cars, OLEDs and fiber composites are widely discussed examples that are now in the transition toward mass applicability.
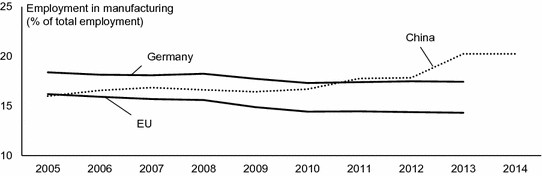
Manufacturing jobs are another big impact on society. In the period from 2005 to 2013, the number of manufacturing jobs in the EU declined by 10 %, while Germanys number rose by 1.8 %. During the same time, the relative share of manufacturing jobs with regard to total employment fell by 2 % in Europe and by 1 % in Germany (see Fig. ).
Fig. 1.6
Share of manufacturing employment based on data from (Eurostat ). The inclusion of rural Chinawhere approx. 50 % of Chinese are employedwill result in a lower share of manufacturing employment]
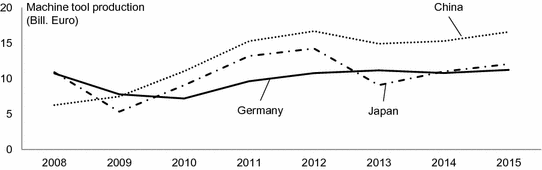
The competitiveness of a certain region with regard to manufacturing is influenced by many factors. As a framework for location analysis, Manyika et al. (). However, with respect to exports one will find the advanced economies like Germany and Japan in the top rankings. At the other end, easily tradeable goods with high labor intensity and low R&D efforts such as ordinary textiles are seldom manufactured in high-wage countries.
Fig. 1.7
World machine tool production of leading countries based on data from (VDW ) and earlier reports
Resource consumption is not only crucial for the competitiveness in energy and raw material-intensive areas in manufacturing, but also impacts society in terms of environmental changes. In 2014, almost 70 exajoules have been consumed in the European Union, which results in an average of 3 kW per capita. Here, the share of industry is approx. 17 % in the EU and 19 % in Germany (see Fig. ). Furthermore, the manufacturing sector is not only important with regard to potential energy savings in its own processes, but also indirectly contributes to energy and resource efficiency in transport, services and other sectors. Manufacturing innovations, for example, are necessary for efficient electric power generation and electromobility.