Producer & International Distributor
eBookPro Publishing
www.ebook-pro.com
Improve your Sexual Performance
Ofer Sela & Eli Gabay
Copyright 2020 Ofer Sela
All rights reserved; No parts of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, or by any information retrieval system, without the permission, in writing, of the author.
Translation from the Hebrew by Jonathan Boxman
Contact:
Contents
Opening words
Over the past few years open discussions of sexual functionality in men has become acceptable and legitimate, and many men seek solutions to their intimate problems. Around 70% of men aged 50 and above suffer from decreased sexual function. Those who seek remedies for their condition will find that they are few and hard to come by.
The appearance of specific medications, such as Viagra, was supposed to solve all problems in this field, but this is not the case, and many problems remain unsolved. Functional training, in which the man takes charge of his problems, is therefore an extremely important approach for those suffering from erectile disfunction. Men suffering from coronary and cardiovascular ailments and diabetes, as well as patients recovering from a prostate, bladder and pelvis operations will learn much from the book and the exercises it recommends.
I congratulate the authors who have provided from their considerable experience to men yearning for healing and improvement in their quality of life.
Prof. Jack Baniel
Urological Array Director, Rabin Medical Center Petah Tikvah.
Introduction
You do not remember exactly when it happened, but you do know that it is no longer as it was. Your body is older, it absorbs blows that rain down upon it, and your sexual prowess falter and sometimes fade away completely.
Now you are prepared to admit to yourself that your quality of life has substantially declined due to deficient sexual function.
It is important to know that you are not alone: every year, according to the estimates, some 70,000 men join the club of those suffering from sexual dysfunction. Nonetheless, your problem, and that of all these other men is not insoluble - but unfortunately, only a small portion of them seek aid. The deficiencies in this intimate field are triggered by many factors, including diabetes, coronary and vascular problems, respiratory disorders (asthma, COPD), post prostate resection complications, orthopedic problems - and also psychological issues (performance anxiety, etc.).
In many cases the deficiency derives from a combination of many factors, and so the treatment might involve many different professionals from the relevant disciplines specializing in these problems, such as uro-sexologists, orthopedics, physiotherapists, psychologists, sexual therapists, and so forth. Furthermore, a wide variety of professional tools and methods can be deployed to aid you in halting decline and even improving your situation.
In this book, we chose to present a new method to strengthen the functionality of the pelvic floor muscles that are a central component in male sexual health. This approach presents, for the first time, the way to harness the full sexual potential of every man, be he healthy or suffering from a sexual performance impairing illness.
In the first chapter we will provide you with a reader friendly explanation of the pelvic floor and its connection to sexual function. We will then review the male populations whom this book may aid, and their particular issues, explain the functional training approach, and then, together with you, practice using our pelvic floor muscles.
In order to study the principles of the method in depth, we recommend reading the entire book prior to preparing the training program.
Ofer Sela B.P.T
Eli Gabay B.P.T
Please contact us with any question, comments, calls for help, or request:
Email:
1. Pelvic Floor
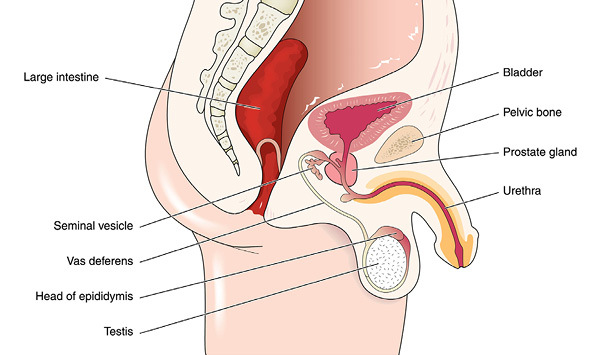
The pelvic floor is the title given to several tissues muscles, blood vessels, nerves and more that lie above the lower bones of the pelvic area, at the bottom of the stomach cavity. This floor separates the pelvic bones and the organs of the small pelvis, which include the organs of the urinary system (the bladder, the urethra, and the rectum), the reproductive system (male prostate, female womb and the vagina) and aids in setting them in place and safeguarding them so they can fulfill their purpose. The floor has two holes: the front, where the urethra and the vagina are located, and the posterior where the rectum is located.
The muscles of the pelvic floor are usually classified into three layers:
The external layer:
The muscles closest to the tail bone, with two muscles that are vital to the erection process (description in the following pages).
The middle layer:
Includes the urethra compressor, sphincter urethra and deep transverse perineal muscles. Through their connection with the deep stomach muscles they constitute an additional pillar of stabilization to the hip bones and the lower waist vertebrae. Furthermore, by increasing the internal stomach pressure they support the urethral sphincters.
The deep layer:
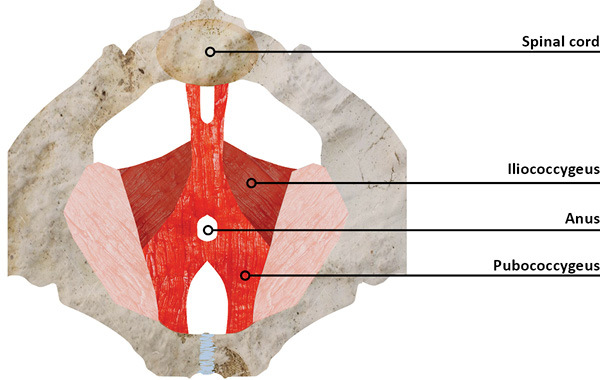
Provides the primary support for the pelvic organs, including the iliococcygeus pubococcygeus and ischiococcygeus muscles - the first and the second are called levator ani since they help raise the anal sphincter.
The structure of the female pelvis differs in order to enable them to give birth, whereas men possess two additional muscles in the pelvic floor and the prostate, but in principle the pelvic structure of both genders is similar.
Pelvic muscles have several important roles:

Support of the organs of the stomach the liver, the intestine and so forth, in a manner that prevents them from leaning too much on the organs above them and prevents a rupture in the diaphragm (the diaphragm is the ceiling of the stomach cavity for which the pelvic floor serves as a floor).

Protection of the pelvis connective tissues (a type of tissue which separates various organs, protects them, and

provides them with structural support), and prevention accelerated and damaging degradation. Harming these connective tissues due to slow and ineffective muscle activity, may result in medical problems for both men and women such as uterine or rectal prolapse.

Control of passing urine and defecation, as part of the ring muscles, by contracting the muscles that prevent the bladder from involuntary release. Pelvic prolapse may result in urinary incontinence following sudden actions such as sneezing or coughing, and sometimes even absent any external stimulation.










 Support of the organs of the stomach the liver, the intestine and so forth, in a manner that prevents them from leaning too much on the organs above them and prevents a rupture in the diaphragm (the diaphragm is the ceiling of the stomach cavity for which the pelvic floor serves as a floor).
Support of the organs of the stomach the liver, the intestine and so forth, in a manner that prevents them from leaning too much on the organs above them and prevents a rupture in the diaphragm (the diaphragm is the ceiling of the stomach cavity for which the pelvic floor serves as a floor).