Ramesh P. Singh - Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts
Here you can read online Ramesh P. Singh - Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2021, publisher: Elsevier, genre: Romance novel. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts
- Author:
- Publisher:Elsevier
- Genre:
- Year:2021
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
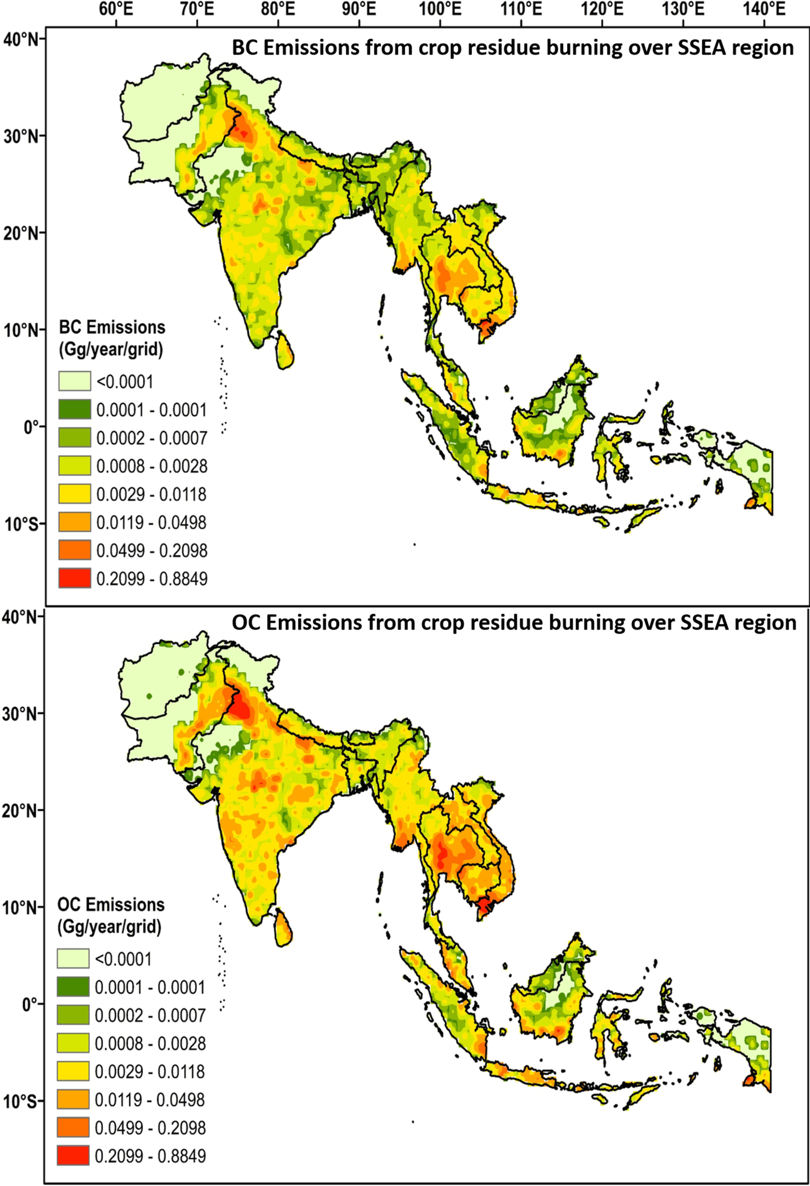
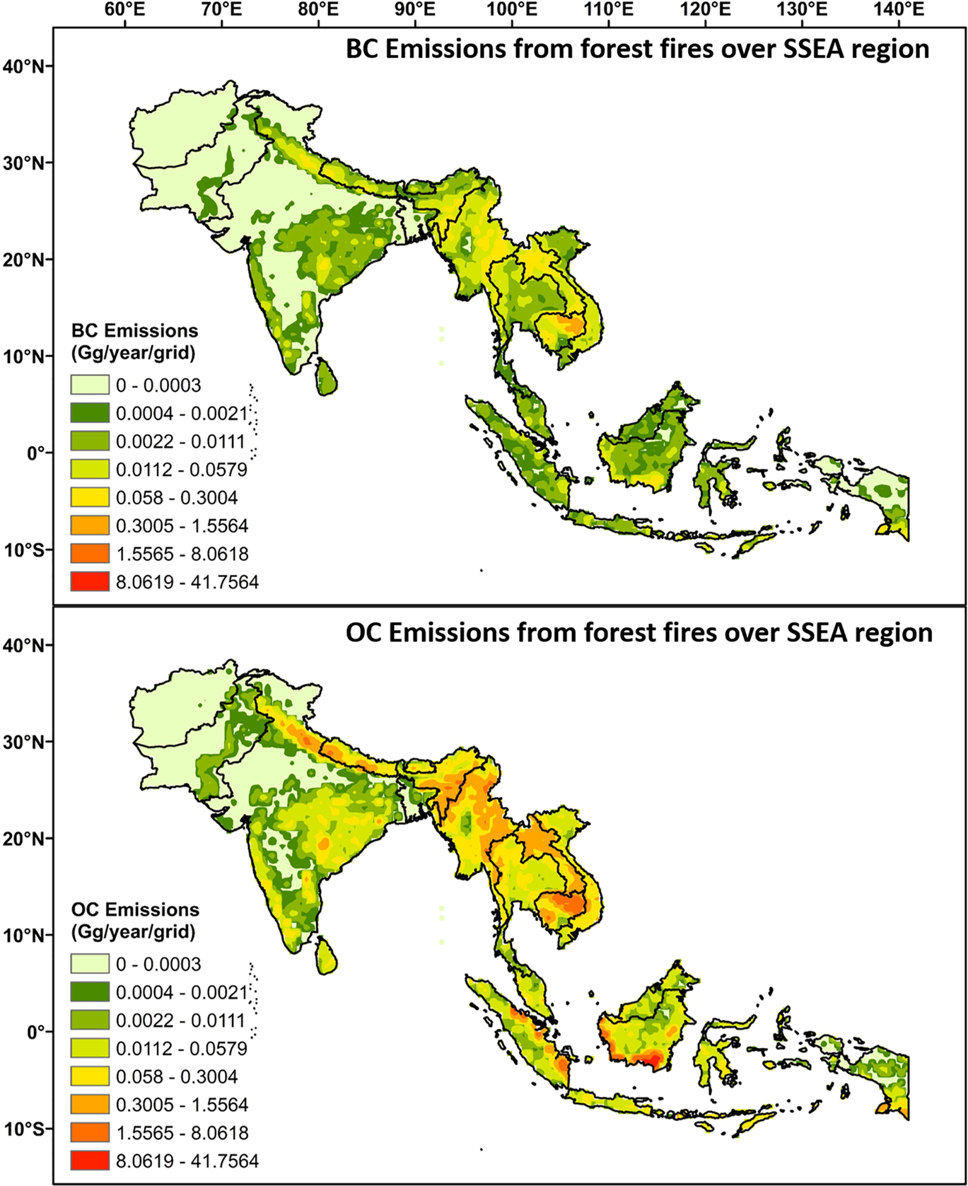
Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts provides a concise yet comprehensive treatment of all aspects of pollution and air quality monitoring, across all of Asia. It focuses on key regions of the world and details a variety of sources, their transport mechanism, long term variability and impacts on climate at local and regional scales. It also discusses the feedback on pollutants, on different meteorological parameters like radiative forcing, fog formations, precipitation, cloud characteristics and more. Drawing upon the expertise of multiple well-known authors from different countries to underline some of these key issues, it includes sections dedicated to treatment of pollutant sources, studying of pollutants and trace gases using satellite/station based observations and models, transport mechanisms, seasonal and inter-annual variability and impact on climate, health and biosphere in general.
Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts is a useful resource for scientists and students to understand the sources and dynamics of atmospheric pollution as well as their transport from one continent to other continents, helping the atmospheric modelling community to model different scenarios of the pollution, gauge its short term and long term impacts across regional to global scales and better understand the ramifications of episodic events.
- Covers all of Asia in detail in terms of pollution
- Focuses not only on local pollution, but on long-term transport of these pollutants and their impacts on other regions as well as the globe
- Includes discussion of both particulate matter and greenhouse gases
- Serves as a single resource on Asian air pollution and Impacts from the most current research across the globe including the US, Asia, Africa and Europe
Ramesh P. Singh: author's other books
Who wrote Asian Atmospheric Pollution: Sources, Characteristics and Impacts? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.