Earthquakes
William B. Rice
Earthquakes
Publishing Credits
Associate Editors
Creative Director
James Anderson
Lee Aucoin
Torrey Maloof
Illustration Manager
Editorial Director
Timothy J. Bradley
Dona Herweck Rice
Publisher
Editor-in-Chief
Rachelle Cracchiolo, M.S.Ed.
Sharon Coan, M.S.Ed.
Science Consultant
Scot Oschman, Ph.D.
Teacher Created Materials
5301 Oceanus Drive
Huntington Beach, CA 92649-1030
http://www.tcmpub.com
ISBN 978-1-4333-0309-8
ePUB ISBN 978-1-5457-1552-9
2010 Teacher Created Materials Publishing, Inc.
Table of
Contents
Always
Changing
Nothing ever stays the same.
People through time have said that
very thing, and it is true. No matter
what something is, in time it will
change. Things that do not seem
to change at all will change. Even
Earth itself changes.
If you were sitting in the same
spot you are now, ten million years
ago, you would see a different world.
Not only would everything people
have built be gone but the land would
also be different. The mountains in
the distance might not be there. The
rocks on the sides of those mountains
might be below ground. Nearby
valleys might be below the ocean.
The earth shifts and changes all
the time. Much of the change is very
slow. But sometimes the changes
come fast, even in an instant.
This valley was created over millions of years.
Sloooowwww
It can take a mountain
range hundreds of millions
of years to form. Most
changes to the planet are
very slow.
What Makes an
Earthquake?
What could possibly happen to make the Earth change fast? One
big factor is an earthquake . An earthquake is the movement of land
caused by plates in the Earths crust rubbing past, into, or against
each other. When this happens, sometimes the plates get stuck.
Pressure builds. When the plates cant take the pressure anymore,
they give way. The pressure must go somewhere. Earthquake!
This crack in the Earths surface was
caused by an earthquake at a fault line.
Earthquakes can have dramatic
effects on people and the land.
Thousands of small earthquakes happen every day around the
planet. They are so small that no one feels them. Only a few dozen
each year can be felt by people on the surface. Of those, a small
few are felt by many people and do a great deal of damage. Large
earthquakes change the land quickly. The land can crack, shift, rise,
or fall. Everything on or near it is affected.
Seismologists
Scientists who study earthquakes
are called seismologists (size
MOL-uh-jists). Seismologists use
machines to sense earthquakes that
people can and cannot feel. The
machines help seismologists learn
about earthquakes and the Earth.
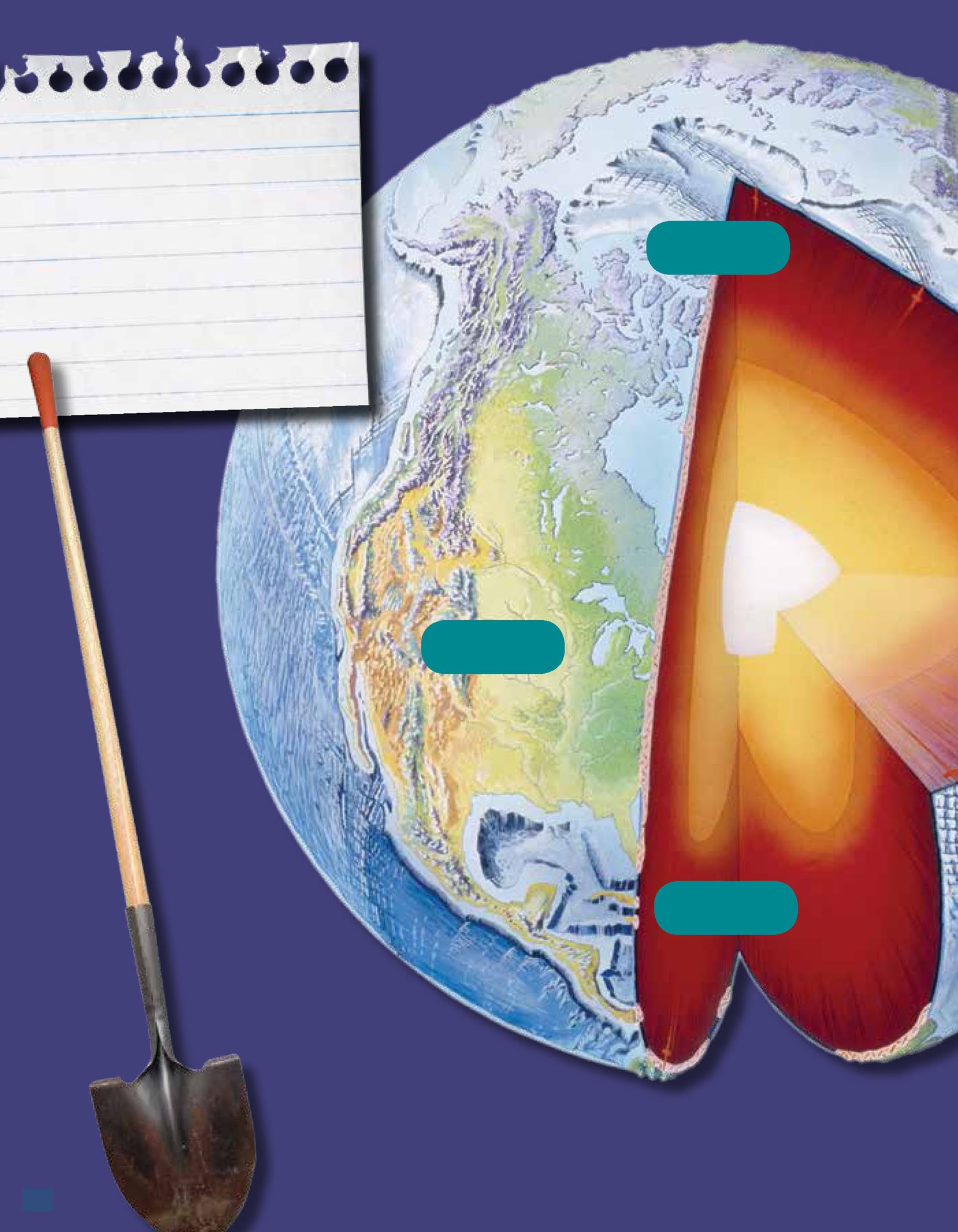
Crusty
Earths crust is about
40 kilometers (25 miles)
thick at the continents.
It is about 7 kilometers
(4 miles) thick under
the oceans.
crust
plate
mantle
A Long
Way to Dig
If you wanted to reach Earths center, you would
have to dig down 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles).
Plate
Movement
Earths outer layer, the crust , is not one solid,
smooth piece. It is broken up into many large
pieces. Each piece is called a plate . The plates
are made of Earth materials such as rocks and
minerals. Some plates are larger than continents.
Some plates are smaller, like a country. Either
way, plates are huge.
Earth is made of many layers. The crust
is rigid and brittle. It sits on top of the mantle ,
which is more fluid. Earths plates float on top of
the liquid rock beneath them. As the liquid mantle
flows, the plates float along as well. As they float,
they rub against each other in different ways. No
matter which way they meet, earthquakes will
happen.
The surface
that you see
around you is
part of Earths
crust.
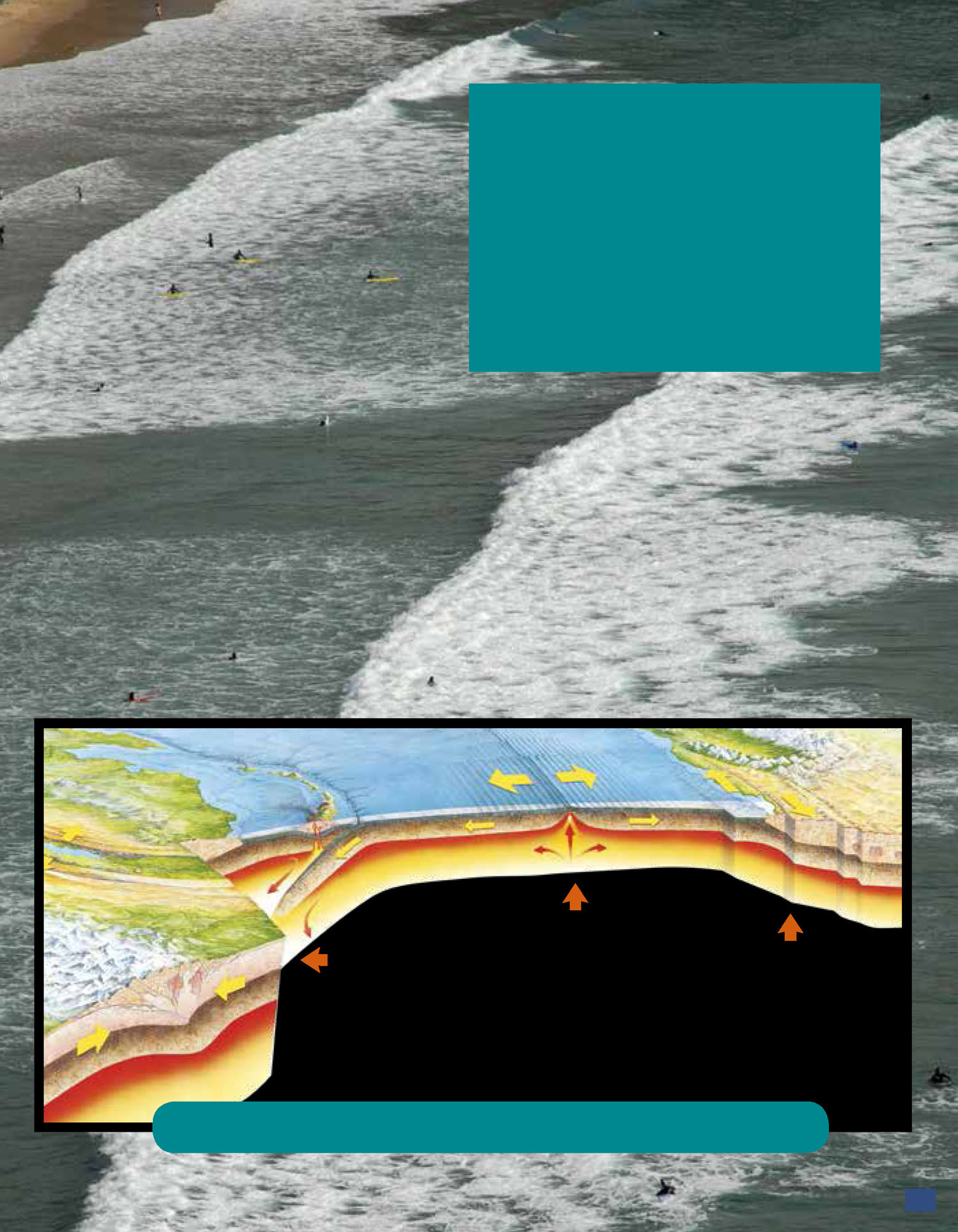
The place where plates meet is
called a boundary . There are three
main types of boundaries. They
are convergent (kuhn-VUR-juhnt),
divergent (di-VUR-juhnt), and
transform . The difference among
them is the way in which the plates
move in relation to each other.
A convergent boundary is where
two plates move toward each other.
When they meet, one of the plates
usually moves on top of the other.
A divergent boundary is where
two plates move away from each
other. New crust is made as they
move apart. A transform boundary
is where two plates slide past each
other.
These boundaries have helped
to make many features on Earths
surface. These features are things
such as mountains, valleys, and
islands. New features are being
created all the time.
Growing Earth
The Atlantic Ocean is spreading
about two centimeters ( inch)
per year. That is a growth during