Animal
Pollinators
by Jennifer Boothroyd
Expand learning beyond the printed book. Download free, complementary
educational resources for this book from our website, www.lerneresource.com.
Copyright 2015 by Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. International copyright secured. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in
a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any meanselectronic, mechanical, photocopying,
recording, or otherwisewithout the prior written permission of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc., except
for the inclusion of brief quotations in an acknowledged review.
The images in this book are used with the permission of: iStockphoto.com/crscredon, p. 4;
iStockphoto.com/KLSbear, p. 5; BSP/UIG/Getty Images p. 6; O.DIGOIT/Alamy, p. 7; Brian
Murphy/Alamy, p. 8; Merlin D. Tuttle/Science Source, pp. 9, 10, 12; Merlin D. Tuttle/BCI/Getty
Images, pp. 11, 13; ANT Photo Library/Science Source, p. 14; Garbutt/NHPA/Photoshot/Newscom,
p. 15; Robert Dant/Alamy, p. 16; Rick & Nora Bowers/Alamy, p. 17; Murray Cooper/Minden
Pictures/Getty Images, p. 18; iStockphoto.com/BirdImages, p. 19; Edward Parker/Alamy, p. 20;
AP Photo/Andrew Shurtleff, p. 21; Bill Bachman/Alamy, p. 22.
Front cover: iStockphoto.com/YanC.
Main body text set in ITC Avant Garde Gothic Std Medium 21/25.
Typeface provided by Adobe Systems.
Lerner Publications Company
A division of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
241 First Avenue North
Minneapolis, MN 55401 USA
For reading levels and more information, look up this title at www.lernerbooks.com.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Boothroyd, Jennifer, 1972
Animal pollinators / by Jennifer Boothroyd.
pages cm. (First step nonfiction. Pollination)
Includes index.
ISBN 9781467757416 (lib. bdg. : alk. paper)
ISBN 9781467762236 (eBook)
1. PollinationJuvenile literature. 2. Pollination by animalsJuvenile literature. I. Title.
II. Series: First step nonfiction. Pollination.
QK926.B65 2015
571.8642dc23 2014017713
Manufactured in the United States of America
1 CG 12/31/14
Table of Contents
Pollination
Flowers make pollen. Most
pollen looks like yellow dust.
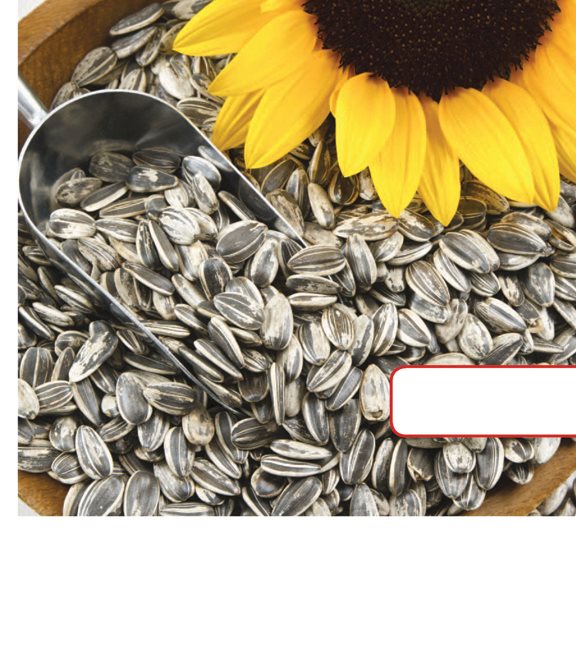
These are
sunflower seeds.
Flowers use pollen to grow
seeds.
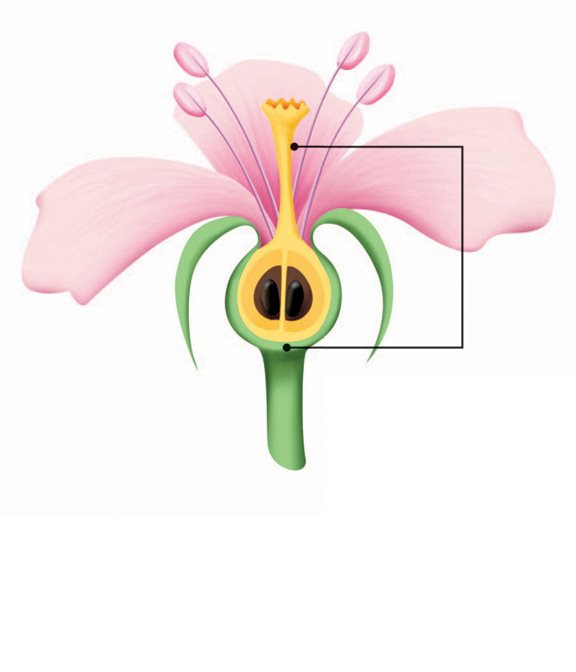
carpel
Pollination happens when pollen
moves into a flowers carpel.
Then the flower can make seeds.
Pollinators help pollen move
to a flowers carpel. Many
animals are pollinators.
How Do Animals Pollinate?
Some animals drink nectar
from flowers.
Nectar tastes
sweet.
Animals get nectar with
their tongues.
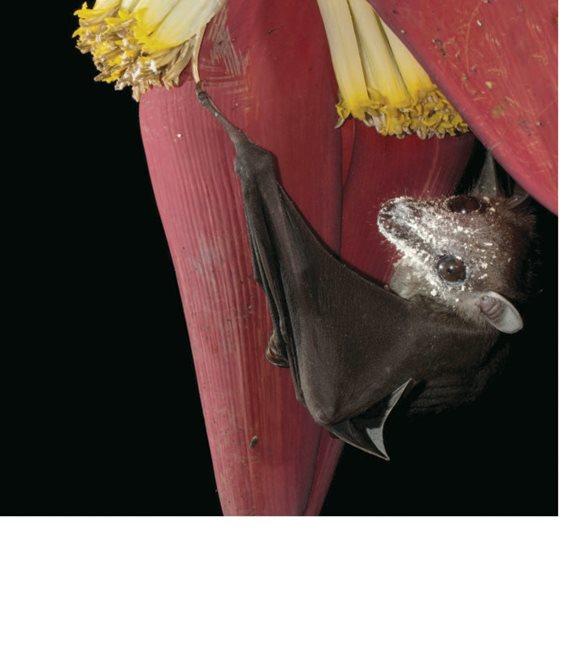
Bats drink nectar from
flowers.
Pollen sticks to the bat.
The pollen rubs off on the
flowers carpel.
Kinds of Animal Pollinators
Bats are one kind of
animal pollinator. But there
are many others.
Honey possums
live in Australia.
Honey possums pollinate
flowers.
Lemurs live in
Madagascar.
Lemurs pollinate flowers.
Pollen sticks to
this lizards scales.
Some small lizards pollinate
flowers.
Pollen sticks to the
doves feathers.
Doves pollinate flowers.
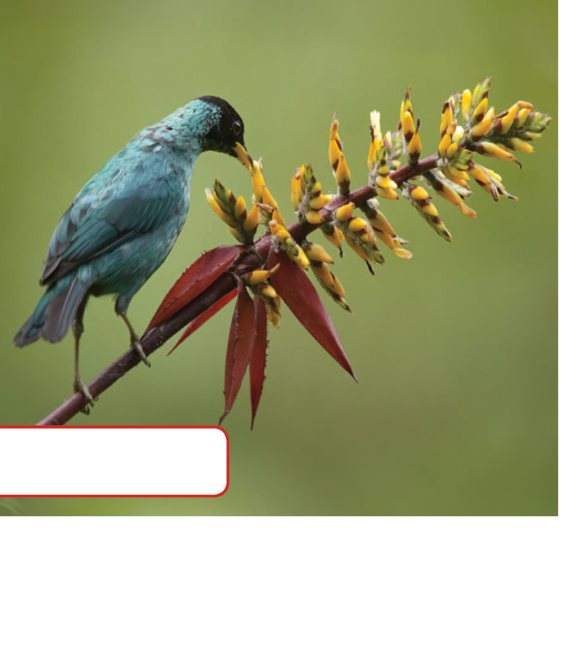
Many honeycreepers
live in Hawaii.
Honeycreepers pollinate
flowers.
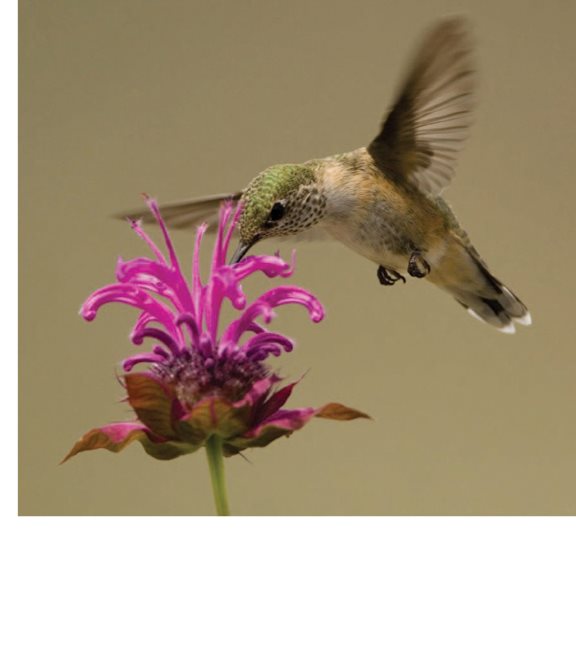
Hummingbirds pollinate
flowers.
Human Pollinators
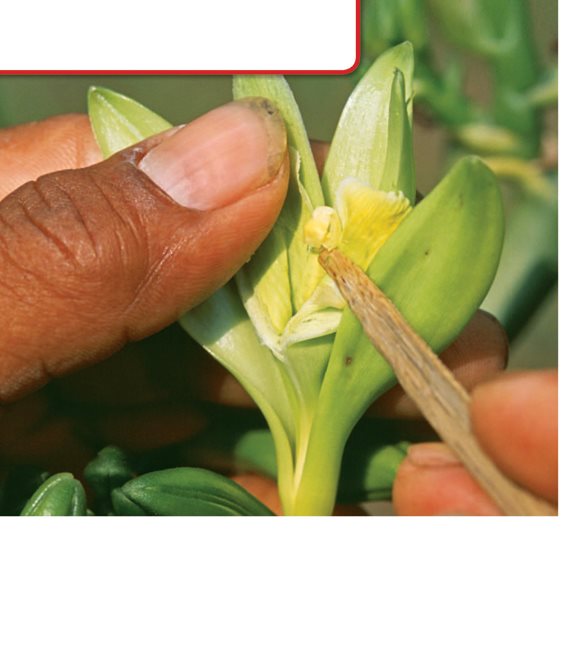
Humans also pollinate
flowers.
Hand- pollination can help
plants grow better fruit.
It takes a lot of helpful
animals and humans to
pollinate flowers.
Glossary
carpel a part of a flower
that stores eggs
nectar a sweet liquid made
in flowers
pollen a powder made
inside flowers
pollinators animals, humans,
or wind that pollinate
flowers