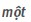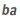Basic grammar 1 Word forms Single words A Vietnamese word can have one of the following four structures: a) A vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker.

b) A vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker plus a final consonant.

c) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker.
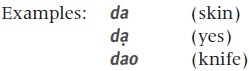
d) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker and a final consonant.

Compound words Two or more single words (syllables) may be joined together to form a compound word. Conjunctive compound words A conjunctive compound word is formed by two different single words.
Examples: 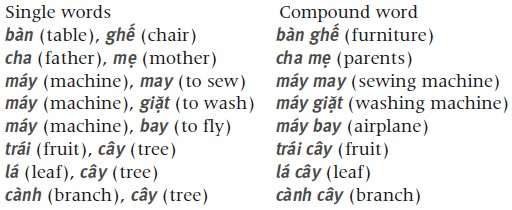 Reduplicative compound words A reduplicative compound word is formed by a reduplication of the entire stem, or by a part of it affixed to itself, or by a meaningful single word plus a meaningless structural element. Examples:
Reduplicative compound words A reduplicative compound word is formed by a reduplication of the entire stem, or by a part of it affixed to itself, or by a meaningful single word plus a meaningless structural element. Examples: 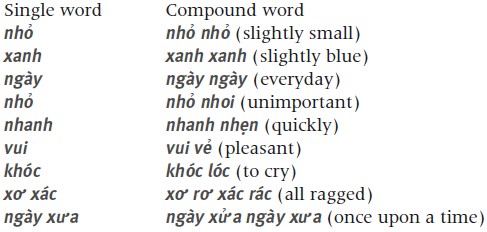 Free compound words A free compound words is formed by two or three single words, which do not follow the above formation. There are not many free compound words in Vietnamese. Examples:
Free compound words A free compound words is formed by two or three single words, which do not follow the above formation. There are not many free compound words in Vietnamese. Examples:  Important notes a) Vietnamese words may be classified as follows: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, numeral, exclamation, adverbial particle. b) Vietnamese words never change in number, gender, person or tense. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese.
Important notes a) Vietnamese words may be classified as follows: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, numeral, exclamation, adverbial particle. b) Vietnamese words never change in number, gender, person or tense. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese.
Therefore, there are often two words to designate the same thing, one coming from Chinese and the other being pure Vietnamese. d) Idioms are phrases with a fixed structure. They have a special formation with rhythms.
Examples:  2 The basic sentence structure A sentence is made up of one or more phrases. It provides a complete expression of meaning. It expresses a statement, a question, a command, or an exclamation. In the written form it begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, a question mark or an exclamation mark.
2 The basic sentence structure A sentence is made up of one or more phrases. It provides a complete expression of meaning. It expresses a statement, a question, a command, or an exclamation. In the written form it begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, a question mark or an exclamation mark.
Sometimes a sentence may not have a subject or a verb. Phrases A phrase is a compound of two or more words which together make up a particular element of a sentence (e.g. the subject or the predicate). There are four types of phrases: noun phrases, verb phrases, adjectival phrases and adverbial phrases. Example: 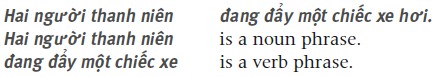 Simple sentences A simple sentence normally consists of two parts, a subject and a predicate. The subject and the predicate can be single words or phrases.
Simple sentences A simple sentence normally consists of two parts, a subject and a predicate. The subject and the predicate can be single words or phrases.
Examples:  In a simple sentence, there may be more than one subject or predicate. Examples:
In a simple sentence, there may be more than one subject or predicate. Examples:  (Mr Nam and I went to have a Vietnamese meal: 2 subjects + 1 predicate)
(Mr Nam and I went to have a Vietnamese meal: 2 subjects + 1 predicate) 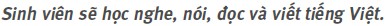 (Students will learn to listen to, speak, read and write Vietnamese: 1 subject + 4 predicates) Optional parts of a sentence Many sentences have an optional part which is dependent on the main part; it modifies the whole sentence and cannot, therefore, stand independently as a sentence. It is an adverb or an adverbial phrase of time, place, manner, purpose, etc. The optional part of a sentence may be put at the beginning of a sentence or at the end, but in Vietnamese, 80% of them have to be put at the beginning of the sentence. Examples:
(Students will learn to listen to, speak, read and write Vietnamese: 1 subject + 4 predicates) Optional parts of a sentence Many sentences have an optional part which is dependent on the main part; it modifies the whole sentence and cannot, therefore, stand independently as a sentence. It is an adverb or an adverbial phrase of time, place, manner, purpose, etc. The optional part of a sentence may be put at the beginning of a sentence or at the end, but in Vietnamese, 80% of them have to be put at the beginning of the sentence. Examples:
| Optional part | Main part |
 |  |
| (On Monday, | I will go to school.) |
 |  |
| (On the table, | there are 3 books.) |
Compound sentences A compound sentence is made up of two simple sentences linked by a conjunctive particle. Examples:

(Because it is beautiful today, I am going out.)
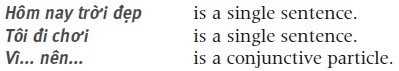

(While my mother is working, my younger brother is studying.)
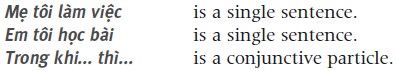
Terms of address In place of a pronoun equivalent to English you, Vietnamese uses a range of kinship terms and honorifics as terms of address.
The use of these is explained at the beginning of Chapter . The Vietnamese phrases listed often require a choice to be made according to whether the addressee is male or female.
















 b) A vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker plus a final consonant.
b) A vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker plus a final consonant.  c) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker.
c) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker. 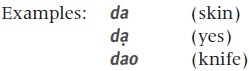 d) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker and a final consonant.
d) An initial consonant plus a vowel or vowel cluster with or without a tone marker and a final consonant.  Compound words Two or more single words (syllables) may be joined together to form a compound word. Conjunctive compound words A conjunctive compound word is formed by two different single words.
Compound words Two or more single words (syllables) may be joined together to form a compound word. Conjunctive compound words A conjunctive compound word is formed by two different single words.  Reduplicative compound words A reduplicative compound word is formed by a reduplication of the entire stem, or by a part of it affixed to itself, or by a meaningful single word plus a meaningless structural element. Examples:
Reduplicative compound words A reduplicative compound word is formed by a reduplication of the entire stem, or by a part of it affixed to itself, or by a meaningful single word plus a meaningless structural element. Examples: 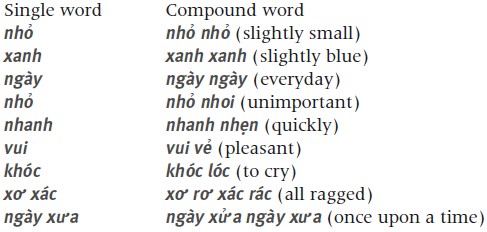 Free compound words A free compound words is formed by two or three single words, which do not follow the above formation. There are not many free compound words in Vietnamese. Examples:
Free compound words A free compound words is formed by two or three single words, which do not follow the above formation. There are not many free compound words in Vietnamese. Examples:  Important notes a) Vietnamese words may be classified as follows: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, numeral, exclamation, adverbial particle. b) Vietnamese words never change in number, gender, person or tense. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese.
Important notes a) Vietnamese words may be classified as follows: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, numeral, exclamation, adverbial particle. b) Vietnamese words never change in number, gender, person or tense. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese. c) More than half of Vietnamese words are derived from Chinese. 2 The basic sentence structure A sentence is made up of one or more phrases. It provides a complete expression of meaning. It expresses a statement, a question, a command, or an exclamation. In the written form it begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, a question mark or an exclamation mark.
2 The basic sentence structure A sentence is made up of one or more phrases. It provides a complete expression of meaning. It expresses a statement, a question, a command, or an exclamation. In the written form it begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, a question mark or an exclamation mark.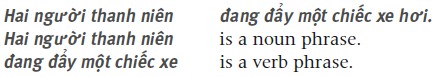 Simple sentences A simple sentence normally consists of two parts, a subject and a predicate. The subject and the predicate can be single words or phrases.
Simple sentences A simple sentence normally consists of two parts, a subject and a predicate. The subject and the predicate can be single words or phrases. In a simple sentence, there may be more than one subject or predicate. Examples:
In a simple sentence, there may be more than one subject or predicate. Examples:  (Mr Nam and I went to have a Vietnamese meal: 2 subjects + 1 predicate)
(Mr Nam and I went to have a Vietnamese meal: 2 subjects + 1 predicate) 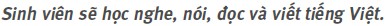 (Students will learn to listen to, speak, read and write Vietnamese: 1 subject + 4 predicates) Optional parts of a sentence Many sentences have an optional part which is dependent on the main part; it modifies the whole sentence and cannot, therefore, stand independently as a sentence. It is an adverb or an adverbial phrase of time, place, manner, purpose, etc. The optional part of a sentence may be put at the beginning of a sentence or at the end, but in Vietnamese, 80% of them have to be put at the beginning of the sentence. Examples:
(Students will learn to listen to, speak, read and write Vietnamese: 1 subject + 4 predicates) Optional parts of a sentence Many sentences have an optional part which is dependent on the main part; it modifies the whole sentence and cannot, therefore, stand independently as a sentence. It is an adverb or an adverbial phrase of time, place, manner, purpose, etc. The optional part of a sentence may be put at the beginning of a sentence or at the end, but in Vietnamese, 80% of them have to be put at the beginning of the sentence. Examples:



 (Because it is beautiful today, I am going out.)
(Because it is beautiful today, I am going out.) 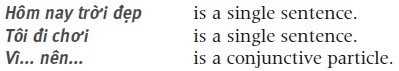
 (While my mother is working, my younger brother is studying.)
(While my mother is working, my younger brother is studying.) 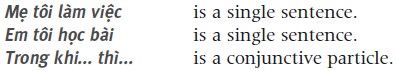 Terms of address In place of a pronoun equivalent to English you, Vietnamese uses a range of kinship terms and honorifics as terms of address.
Terms of address In place of a pronoun equivalent to English you, Vietnamese uses a range of kinship terms and honorifics as terms of address.