Table of Contents
Landmarks
Contents
Acknowledgments
Foreword
Preface
Cardiovascular Medicine Questions
Cardiovascular Medicine Answers and Critiques
Endocrinology and Metabolism Questions
Endocrinology and Metabolism Answers and Critiques
Gastroenterology and Hepatology Questions
Gastroenterology and Hepatology Answers and Critiques
General Internal Medicine Questions
General Internal Medicine Answers and Critiques
Hematology Questions
Hematology Answers and Critiques
Infectious Disease Medicine Questions
Infectious Disease Medicine Answers and Critiques
Nephrology Questions
Nephrology Answers and Critiques
Neurology Questions
Neurology Answers and Critiques
Oncology Questions
Oncology Answers and Critiques
Pulmonary Medicine Questions
Pulmonary Medicine Answers and Critiques
Rheumatology Questions
Rheumatology Answers and Critiques
Color Plates
Erratahttp://www.acponline.org/acp_press/essentials/errata.html
Section 1. Cardiovascular Medicine
Questions
[Basic]
A 66-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for left-sided chest pain that began at rest, lasted for 15 minutes, and has since resolved. A similar episode occurred at rest yesterday. Pertinent medical history includes hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current medications are amlodipine, glyburide, and aspirin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 125/65 mm Hg, heart rate is 70/min, and respiratory rate is 12/min. Estimated central venous pressure is 6 cm H2O, carotid upstroke is normal, there are no cardiac murmurs, and the lung fields are clear.
Laboratory findings include an elevated serum troponin I level. Electrocardiogram is shown. Chest radiograph is normal.
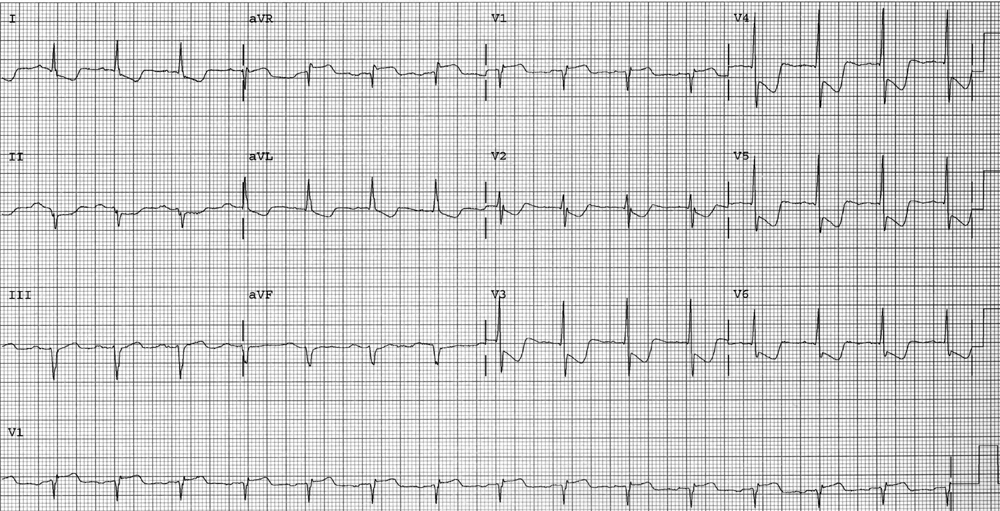
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Chronic stable angina
- Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- Unstable angina
[Basic]
A 63-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital with pleuritic chest pain, diaphoresis, and dyspnea of 1 hour's duration. The pain is not affected by food, antacids, or exertion. It may be worse when supine and with deep breathing. She has a 10-year history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Her medications are chlorthalidone and lovastatin.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.8C (100.0F), blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg (both arms), heart rate is 108/min, and respiration rate is 22/min. Cardiovascular examination reveals a regular rhythm and a biphasic, scratchy sound best heard at the lower left sternal border. No murmur, S3, or S4 is heard. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The jugular venous pressure is normal and no peripheral edema is noted.
The electrocardiogram shows sinus tachycardia with diffuse ST elevation. Troponin level and chest radiograph findings are normal.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Acute pericarditis
- Aortic dissection
- Pulmonary embolism
[Basic]
A 78-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for new-onset chest pain. He describes a crushing pain that is located in the left substernal area and has been present for 10 hours. He has had no prior episodes of chest pain. His medical history is notable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Current medications are aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg in both arms, pulse is 100/min, and respiration rate is 16/min. There is no jugular venous distention and no cardiac murmurs or rubs. The lungs are clear.
Laboratory results are notable for elevated levels of serum creatine kinase and troponin I. The initial electrocardiogram is shown. Chest radiograph is normal.
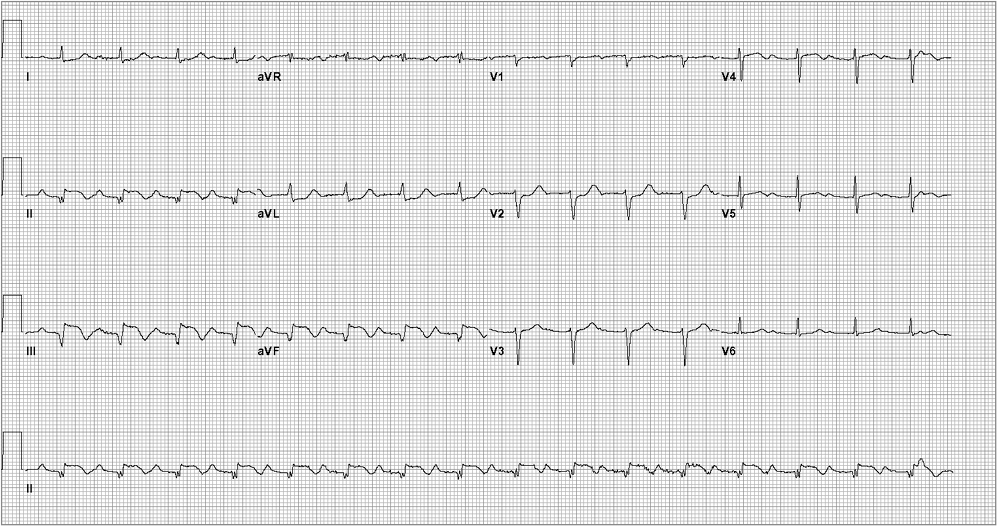
Which of the following is the best management for this patient?
- Chest CT with contrast
- Echocardiogram
- Percutaneous coronary intervention
- Thrombolytic therapy
[Basic]
A 50-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-hour episode of epigastric discomfort and dyspnea during exercise that is relieved by rest. He is now pain free. The patient states a similar episode occurred on three previous occasions, but he did not seek medical advice. He has been using antacids for the past 6 weeks with partial relief. He reports no fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, or postprandial abdominal pain. He has a 15-year history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia; his only medication is chlorthalidone.
On physical examination, he is afebrile, blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg, pulse rate is 88/min, and respiration rate is 14/min. BMI is 28. Estimated central venous pressure is normal. Cardiac examination reveals a regular rhythm. The S2 is normal, and an S4 is heard at the apex; no murmurs or other extracardiac sounds are heard. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is not tender to palpation.
Complete blood count and troponin level are normal as are the electrocardiogram and chest radiograph.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acute pericarditis
- Aortic dissection
- Ischemic heart disease
- Peptic ulcer disease
[Advanced]
A 52-year-old woman is evaluated in the emergency department for ongoing substernal chest pressure associated with nausea, diaphoresis, and lightheadedness. Her symptoms began 3 hours ago. She has hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Her medications are hydrochlorothiazide, pravastatin, and aspirin.
On physical examination, her blood pressure is 84/62 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respiration rate is 20/min. Cardiac auscultation reveals distant heart sounds with an S4. The lungs are clear bilaterally; estimated central venous pressure is elevated at 11 cm H2O.
Electrocardiogram with right-sided precordial leads is shown. (Leads V1 through V6 are recorded from the right side of the chest.)
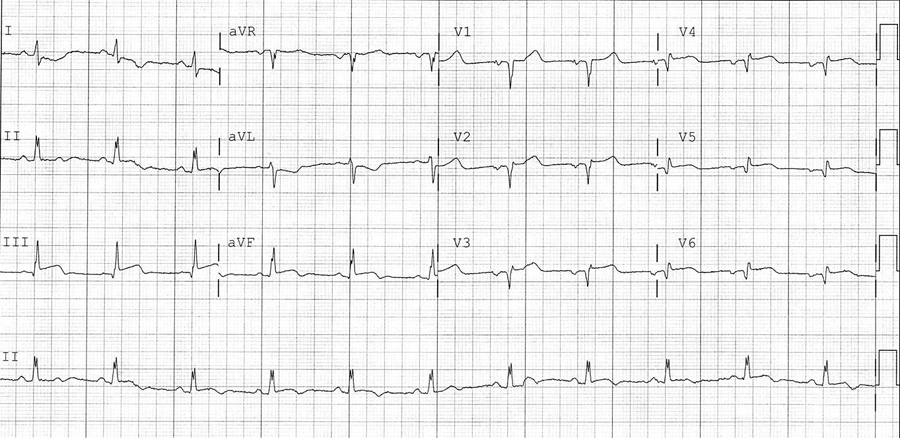
Which of the following should be given next in the treatment of this patient?
- Dobutamine intravenously
- Metoprolol intravenously
- Nitroglycerin sublingually
- 0.9% saline intravenous bolus
[Basic]
A 58-year-old woman is evaluated in the emergency department for substernal chest pain of 18 hours' duration. She describes the pain as a tightening that is not associated with eating or exertion and that radiates to the neck. The pain is not accompanied by dyspnea, nausea, or diaphoresis and is not associated with exertion. She also reports symptoms of occasional heartburn and acid regurgitation. She had a similar episode of substernal chest pain 1 month ago, and an exercise stress test that achieved 90% her predicted maximal heart rate showed no ischemia. The patient's medical history is otherwise unremarkable.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.2C (99.0F), blood pressure is 130/74 mm Hg, pulse rate is 88/min, and respiration rate is 16/min; BMI is 32. The cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Electrocardiography shows nonspecific ST-segment and T-wave abnormalities, which are unchanged from several previous examinations.











