50MINUTES - Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing)
Here you can read online 50MINUTES - Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing) full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2018, publisher: 50Minutes.com, genre: Business. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing): summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing)" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
50MINUTES: author's other books
Who wrote Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing)? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing) — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing)" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:



- Names: value chain, Michael Porters value chain.
- Uses: improving competitiveness, reducing costs, increasing value creation.
- Why is it successful? It can be adapted to all types of business, drastically boosts performance and comprises a series of clear, well-defined steps.
- Key words: competitive advantage, value creation, analytical tool, subdivision of activities.
The Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter (born in 1947) is known for his work on competitive strategy, competitiveness and the economic development of nations, states and regions.
In the 1980s, he began looking into the concept of competitive advantage and developed a number of strategic theories in the book Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance (1985). Many of these theories were quickly adopted by businesses looking to improve their results.
According to him, companies achieve superiority through their mastery of competitive forces, known as Porters five forces. This is a key concept in modern management, and was explored by Porter in Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors (1980; republished with a new introduction in 1998).
A value chain is a series of actions which are carried out in order to deliver a valuable product or service to the market.
Any company, association or organisation that creates value and wants to improve its competitiveness can use the value chain to achieve its goals. The model allows businesses to analyse each of their activities in order to improve each step as much as possible, in this way maximising their competitive advantage. The value chain is a valuable tool in strategic management, as it works on the positioning of a product or service on the market.
The value chain has three main objectives:
- improve services
- reduce costs
- create value.
Before they can develop a competitive advantage, companies must understand the concept of value creation. This is an analytical system designed to break down the different functions of a company and examine their costs, with the goal of distributing resources throughout the chain as effectively as possible. This enables products to be strategically positioned on the market based on their cost or differentiation.
Costs can be reduced by:
- optimising the manufacturing process;
- purchasing raw materials at a lower cost;
- innovating;
- working on the functionality of a product for greater differentiation;
- increasing manufacturing quality;
- improving customer service;
- reducing delivery times through good logistical organisation.
An effective analysis of the companys different functions can boost productivity and lead to sustainable and profitable growth.
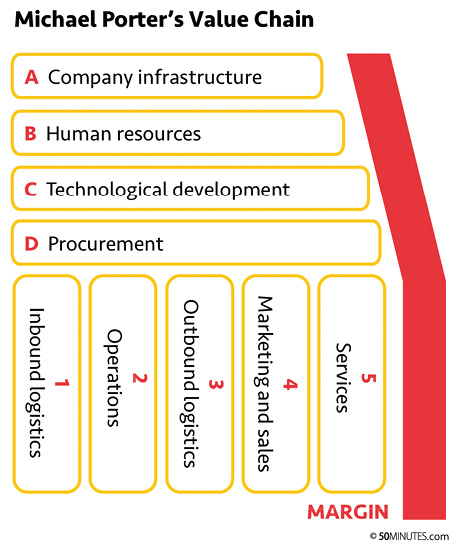
Porters model comprises nine major value-generating functions, which are divided into two categories:
- There are five primary activities that directly affect the added value of the final product. This category comprises the activities related to inbound logistics (1), operations (2), outbound logistics (3), marketing and sales (4) and services (5).
- There are four support activities which are indirectly involved in creating the final added value. These are the activities related to the companys infrastructure (1), human resources (2), technological development (3) and procurement (4).
The selection of value-generating activities
The selection of value-generating activities is based on three criteria:
- Do they rely on different economic mechanisms?
- Do they constitute a considerable fraction of the costs?
- Do they directly affect the competitive advantage?
Porter represents the business using a simple diagram, in which the primary activities are positioned vertically while the support activities are placed horizontally. The margin represents the difference between the final value of the product and the total costs linked to it (creation, launch, etc.). The size of the margin depends on the competitive advantage of each of the nine functions of the business. Every company has its own diagram, which will vary depending on numerous different factors, including its character, its industry, its positioning and its efficiency.
Competitive advantage
The competitive advantage of a company over its competitors can be seen by comparing their value chains. The quality of an activity has a direct impact on costs, customer satisfaction and the size of the margin. The analysis of a function does not always give a positive result, as it may turn out that some functions consume value or generate less value than the companys competitors.
The primary activities are the main functions organised within a company. They contribute directly to the creation of the product, marketing activity, sales policy, delivery to the end customer and the after-sales service. Although not all businesses operate in the same way, most of them carry out these five primary activities:
- (1) Inbound logistics refers to the procedure for acquiring resources, including raw materials, receipt of these materials, stock entry, etc.
- (2) Operations involve the use of raw materials, production of goods, quality testing, packaging, maintenance, etc.
- (3) Outbound logistics includes the output of inventory, order preparation, delivery to distributors and end customers, etc.
- (4) Marketing and sales includes promotion, communication, pricing, advertising, distribution channel management, etc.
- (5) Services involve repair, maintenance, after-sales services, etc.
The interconnectedness of primary activities
These activities are not independent of one another, and good control of one component can have a positive impact on the other elements of the chain. The various functions are interconnected, which can result in a series of consequences when there are changes to activities. These connections, which often go unnoticed, play an important role in cost management and competitive advantage.
Support activities contribute to the smooth running of operations by enabling the company to perform and coordinate its primary activities in order to maximise efficiency. They are:
- (A) Company infrastructure , which includes general, financial and administrative management, the legal department and the departments in charge of planning, quality control, etc.
- (B) Human resources , which is involved in recruitment, training, remuneration processes, skills management, organisation structure, bonus policy, layoffs, etc.
- (C) Research and development includes research and technology selection, the ability to innovate, the development of products or services, product safety, patent management, etc.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing)»
Look at similar books to Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing). We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Michael Porters Value Chain: Increase Value and Beat the Competition (Management & Marketing) and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.