Amentes - Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age
Here you can read online Amentes - Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2017, publisher: Lulu.com, genre: Business. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Amentes: author's other books
Who wrote Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Capital is what you invest at the start in company. Capital is one of the most arguable things in business. All aspects of capital must be put on paper. Even if you start your business with the close friend, first rule is put all on paper in order to avoid any misunderstandings. Capital is what company use to start and for day to day operations. Sources for capital can be equity or credit.
Equity Capital or Credit Capital
Equity is normally represented in shares. Shareholders receive dividends when agreed as a return on their capital. Credit capital is a liability of the company. Source for credit is usually a financial institution like bank. The difference in equity and credit is obligatory payments. Shareholders can agree not to receive dividends in order to support business, whereas banks never refuse from payment. So, at some stage it is better to use equity then credit.
Cost of Capital
However, equity is expensive source of capital as you have to pay dividends and part of the company belongs to other shareholders. Credit can only cause loss of proprietorship when you fail to pay in time and you become bankrupt. Also, when company grows the equity also grows and it will be more expensive to buy out shares, on the other hand credit never arises if you pay on time and do not sign any additional credit agreements. Moreover, credit allows you to get tax reduction on amount of interest paid on credit. Interest is tax deductible expense.
So, it is up to you what to use for startup capital, but my advice is to use equity until you get constant revenue and then use credit to finance working capital.
There are no secrets to success.
It is the result of preparation, hard work,
and learning from failure.
Colin Powell
Dear reader, you hold in your hands not just a brochu re but several years of mistakes which cost me a lot . I hope this guidance will save you time and resources on your way to a dream of being self-employed, a dream of being your own boss.
Capitalization table
Capitalization table shows the amount of investment in equity and a share in the company.
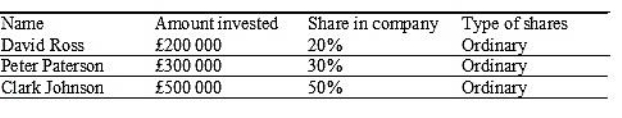
In a simple form it is like this:
Here it is obvious that Clark has power to make decisions in the company and David as a minority shareholder cannot. There are also can be private shares which have no right to vote but company has to pay them fixed dividends.
Additionally, you can add a date of exit, in other words when investor intend to sell his shares. For example, David Ross exit date is 01/01/2018 which means he will propose to current shareholders to buy out his share otherwise he will sell it to a third party.
Investor bonus
What is the purpose of investing? Of course, earn money and receive dividends. What if you would like to buy out company? You will need to provide investor bonus conditions in the investing contract. Investor bonus can be anything you agree. So, do not ignore this.
Startup cost is important part of the business plan and I would like to write wider about it.
Startup cost should be very precise. Again we can look through an example:
When starting a company, you need to plan all assets you would require to operate. Would you require PC or laptop? Probably yes. You would also need internet connection, printer, telephone and others.
Take your team and sit down. Do the brainstorming and write on the paper all you may need and prices. Then put the lists together and cross out all you definitely would not need at first.
Then think about workforce. You will need to hire employees. Put their annual salary and insurance on the list.
Utilities? Sure. Electricity, gas and water must be on the list, even if you have just an office, or even run your business from home (you should know that if you run your business from home your utilities can be tax deductible expense).
Stationaries and miscellaneous should be on the list.
Well, you have a list of things you need. Your office is set up and workforce is hired. But you need supplies (stock, raw materials and other depending on industry), should it be on the list? Of course!
Now you have a list of the startup cost. But your investor will probably ask you to take half of these expenses. Best businesses starts without investments. Remember the business that started from the parents` garage? John brought table, Lisa computer, father gave us tools and we started.
Sure, you do not need to start from scratch but many investors would like to keep startup capital to the minimum. Truly, if you start dentistry you need to buy a lot of expensive equipment. But if you start website shop you do not need an office in the centre of the London and an iMac.
Reduce your startup cost as much as you can and you will see the right amount to ask.
When we speak about operating expenses we normally included some of them in the startup cost already.
Operating expenses are expenses you have in accordance with your day to day routine of the business (core operation). Expenses or costs can be fixed or variable . Fixed costs (expenses) are continuous and constantly paid money. Fixed are utilities, rent, salaries, licenses, domain and server. Variables are cost of materials, wages, and others that connected to the volume of sales.
Operating expenses are crucial in the Cash flow forecast. When writing a business plan you should be very careful in measurements. You need to put real prices and save equilibrium with the revenue. When writing a business plan, your annual closing balance highly depends on expenses you have to keep them to the minimum.
Cost management is an art and science (3 year of University). There are many doctorate works about cost management and still there is no unique solution. So, you have to find your own way here.
Welcome to the business plan chapter. Business plan is one of the most trending and demanded paper work in the history of humanity. I am not scaling the problem, but if you go online and search for business plan, internet will show you so many links that your life time is not enough to read it all.
To begin with, business plans have different nature, which depend on purpose.
Let me start from the personal business plan. Here I understand a simple one sheet A4 with a scheme of future activity. Such business plan will consist of the four parts which are Idea, Clients, Money and Outcomes. In the idea section it is necessary to ask one question What am I going to do to earn money? It is not that easy to answer properly but it will bring certainty to your business. Then, in section clients ask you Where am I going to find my clients? This will guide you to the right place where you will find your client.
Third, think about the money. Here is important to clarify how much money you have and how much you want to return. Finally, specify outcomes of your business idea. Tell yourself truth about the purpose for your business and do not shy.
Here you are small example: My name is Artem . I would like to sell vegetable s from my local farm to the people in the centre of the Cambridge. I will reserve a trade place on the market square. The rent will cost me 10 coins, stock will cost 50 coins per 10 pumpkins. I am going to sell one pumpkin for 10 coins . So I need to sell 6 pumpkins to breakeven and +1 to earn. I am going to do it because I never saw good pumpkins on the market square and I heard people complain. I like eat pumpkins myself and I believe fresh vegetables are very healthy.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age»
Look at similar books to Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Business Intelligence: Tips for Fostering Entrepreneurship At Any Age and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.












