Preface
Motivation
This book is designed as a part of "The Complete MBA Coursework Series," established to equip the professionals and students with eminent capabilities and hone their skillset. The motivation behind this series is the need to establish a thorough and complete MBA coursework, following the core and elective courses of prestigious institutions like Harvard and Wharton's Business Schools. With this self-motivated study of the MBA curriculum, students and professionals can tailor their MBA according to their interests and requirements. Thus, embarking on this self-study MBA coursework rather than a traditional, costly, and lengthy MBA degree program is worth the time.
MBA degree programs are very costly, although the skill boost associated is worth acquiring. Thus, as a part of the MBA coursework series, the following book helps the students learn the basic terminologies and techniques associated with Enterprise and Model Risk management. This book does not attempt to provide a self-contained discussion of Enterprise and Model Risk management . Instead is a decent introduction to Enterprise and Model Risk management courses used in top MBA programs. Further, the introductory is stemmed from our professional experience. Finally, we want to thank Hina Aslam and Sara Aslam for providing us with many suggestions and valuable feedback on this book.
Prerequisites
To make the book as accessible as possible, the reader should have a basic working knowledge of Business and relevant terminologies. However, prior exposure to an undergraduate Enterprise and Model Risk management program is not required. The emphasis throughout the book is on the understanding of basic terminologies and the valid application of Risk Management to real-world business practices.
Final few words
Thank you for buying this book, and feedback is highly appreciated for enhancing future versions. I hope that all readers gain something useful from this book and boost their knowledge of Management techniques that the author aimed at while writing it.
Although this book has been thoroughly checked and proofread; typos, errors, inconsistencies in instances where I have got it wrong are bound to sneak in. Any readers spotting such errors or addressing certain questions or comments are kindly requested to contact our customer service through this e-mail ( ) before writing any review online. Finally, feel free to return the book and ask for a refund if unsatisfied.
A Tale of Two Brothers
Hicham and Mohamed Ibnalkadi
Introductory.books@gmail.com
Introduction to
Enterprise and Model Risk management
CHAPTER 1
Concept of Risk Financial & Enterprise
1.1. Risk
Risk is characterized in financial terms as the chance that a result or speculation's simple additions will contrast from a typical result or return. Risk incorporates the chance of losing a few or the entirety of a unique venture.
Quantifiably, the risk is typically evaluated by thinking about recorded practices and results. In general, the standard deviation is a typical measurement related to risk. Standard deviation gives a proportion of the instability of advantage costs compared to their exact midpoints in a given time.
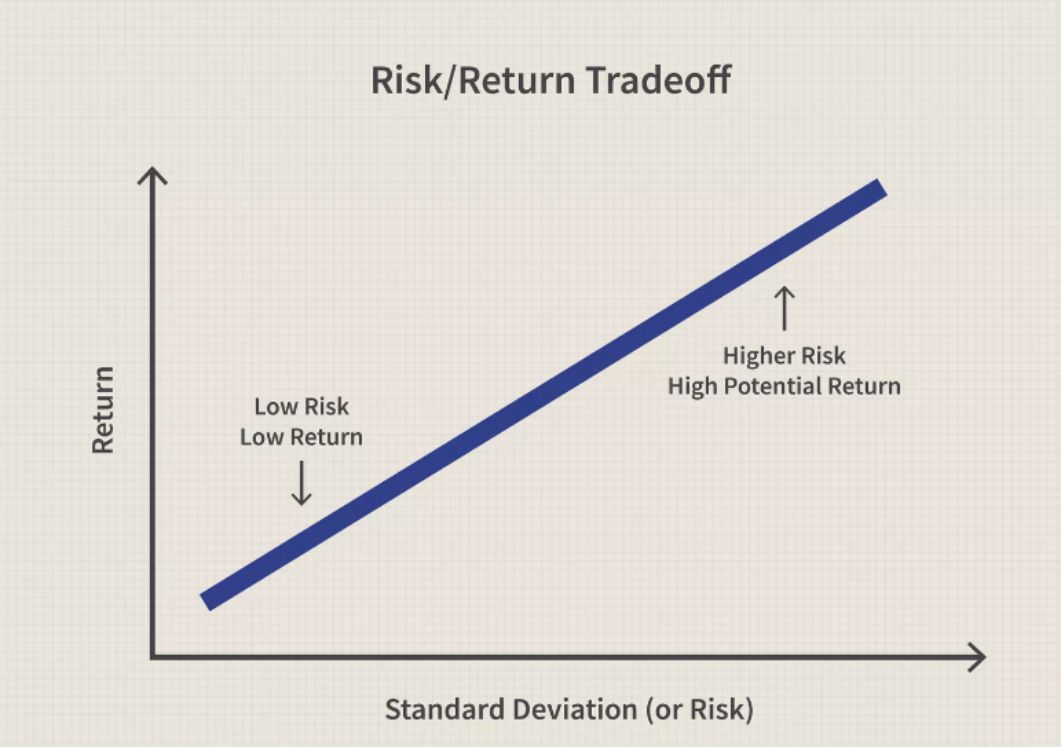
It is generally conceivable and judicious to oversee contributing risks by understanding the fundamentals of risk and how it is estimated. Learning the risks of various situations and a portion of the approaches to oversee them comprehensively will help a wide range of speculators and business chiefs evade pointless and expensive misfortunes.
1.2. Basics of Risk
Everybody is presented with some kind of risk consistently regardless of whether it is from driving, strolling down the road, contributing, capital arranging, or something different. A financial specialist's character, way of life, and age are the top components to consider for singular speculation management and risk purposes. Every speculator has a unique risk profile that decides their eagerness and capacity to withstand hazards. As a rule, speculators anticipate that more significant yields should make up for facing those challenges as speculation risks rise.
A critical thought in finance is the connection between risk and return. The more noteworthy the measure of risk a financial specialist is eager to take, the more prominent the possible return. Risk can come in different manners, and speculators should be made up for taking on additional risk. For instance, a U.S. Depository security is viewed as perhaps the most secure venture and contrasts with corporate security, giving a slower return pace. An enterprise is substantially more liable to fail than the U.S. government. Since the default risk of putting resources into corporate security is higher, financial specialists are offered a higher return pace.
1.3. Financial Risk
The financial risk is the chance of losing cash on speculation or undertaking. Some more normal and unmistakable financial risks are credit risks, liquidity risks, market risks, inflation risks, interest rate risks, and operational risks.
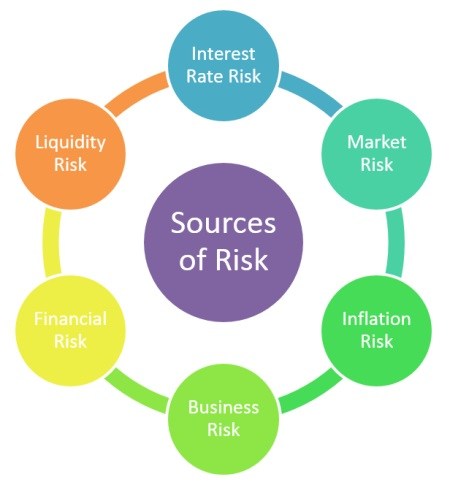
Financial risk is a kind of risk that can bring about the loss of cash-flow to invested individuals. It can mean they cannot control financial strategy and default on securities or other obligation issues for governments. Enterprises likewise face the chance of default on obligations they embrace; however, they may encounter disappointment in an endeavor that causes financial weight on the business.
Business sectors face financial risks because of different macroeconomic powers, changes to the market loan cost, and the chance of default by parts or enormous companies. People face financial risk when they settle on choices that may endanger their pay or capacity to pay an obligation they have expected. Financial risks are all over and come in numerous sizes, influencing everybody. You ought to know about every financial risk. Realizing the threats and how to secure yourself will not wipe out the risk, yet it can moderate their damage.
1.4. Financial Risk for Business
It is costly to construct a business starting from the earliest stage. Eventually, in any organization's life, the business may need to look for outside funding to develop. This requirement for subsidizing makes a financial risk to both the business and any financial specialists or partners putting resources into the organization.
Acknowledge riskotherwise called default riskis the peril related to obtaining cash. When the borrower becomes incapable of reimbursing the advance, they will default. Credit risk speculators experience the ill effects of diminished salary from advance reimbursements, just as lost head and intrigue. Lenders may likewise encounter an ascent in costs for an assortment of the obligation. At the point when just one or a modest bunch of organizations are battling, it is known as a particular risk. This threat, identified with an organization or little gathering of organizations, incorporates issues identified with capital structure, financial exchanges, and introduction to default. The term is commonly used to mirror a speculator's vulnerability of gathering returns and the potential for financial misfortune. Organizations can encounter operational risk when they have helpless administration or defective financial thinking. Given inward factors, this is the risk of neglecting to prevail in its endeavors.