Cover: shutterstock
Bibliographische Information der Deutschen Bibliothek
Die Deutsche Bibliothek verzeichnet diese Publikation in der Deutschen Nationalbibliographie; detaillierte bibliographische Daten sind im Internet ber http://dnb.ddb.de abrufbar.
Mller, Bodo und Poth, Ulrich:
Coatings Formulation: An International Textbook
3rd Completely Revised Edition
Hanover: Vincentz Network 2017
European Coatings // Library
ISBN 978-3-86630-122-1
2017 Vincentz Network GmbH & Co. KG, Hanover
Vincentz Network, Plathnerstr. 4c, 30175 Hanover, Germany
T +49 511 9910-033, F +49 511 9910-029,
This work is copyrighted, including the individual contributions and figures.
Any usage outside the strict limits of copyright law without the consent of the publisher is prohibited and punishable by law. This especially pertains to reproduction, translation, microfilming and the storage and processing in electronic systems.
Exclusion of liability
It should be noted that this book reflect the authors personal views, based upon their own knowledge. This does not absolve readers of the responsibility of performing their own tests with respect to the uses and applications of various processes or products described herein, and/or of obtaining additional advices regarding the same. Any liability of the authors is excluded to the extent permitted by law, subject to all legal interpretations.
Discover further books from European Coatings Library at:
www.european-coatings.com/shop
Layout: Danielsen Mediendesign, Hanover, Germany
eBook-Herstellung und Auslieferung:
readbox publishing, Dortmund
www.readbox.net
European Coatings Library
Bodo Mller Ulrich Poth
COATINGS FORMULATION
An International Textbook
3rd Revised Edition
Preface

The authors were not surprised by the success of the first and second edition, as there had been no comparable reference book on the market that provided detailed explanations of recipes and formulations. Although guide formulations abound, meaningful and informed selections accompanied by notes and evaluations are in short supply. The authors have therefore gladly taken on the task of revising and updating the second edition. To this end, they have replaced outdated guide formulations, eliminated errors and added several new figures.
Developing paint recipes or paint formulations is an important part of paint and coatings technology. Unfortunately, paint recipes are listed in very few publications because they are closely guarded secrets of the paint and coatings industry. While starting formulations are available from the manufacturers of raw materials, they cannot be used for a textbook without careful selection and revision beforehand.
This book will teach paint formulation in two steps. Each chapter will first describe the chemical composition of and, especially, the binders for the type of paint presented. This will then be followed by formulation advice and an analysis of existing recipes (e.g. starting formulations). This analysis consists in calculating the important characteristic values of coatings, such as the pigment/binder ratio, pigment volume concentration and, as necessary, the hardener addition level. Finally, examples of how to develop a real-life paint formulation are provided in the case of the most important types of coatings. All calculations based on recipes and formulations are worked through step by step and should therefore be intelligible to beginners, as well.
The skills acquired in dealing with these recipes can also be employed in other applications, such as adhesives and sealants. This book focuses on the paint formulation itself, and how to arrive at it.
Of the many various paint and coating systems available, the selection provided in this textbook features the most important types. The formulations have been developed mostly from starting formulations or patent examples and cannot be used to produce paints without further ado. Patent restrictions or registered trade marks ( or ) are not mentioned explicitly. Furthermore, it should be noted that product and trade names may change as a result of mergers and acquisitions. Nonetheless, most of the raw materials described herein or their equivalents should be available worldwide.
This textbook seeks to familiarize laboratory assistants, engineers and chemists with the practice of formulating paints. It presupposes a basic knowledge of chemistry, binders, pigments and additives. It will also serve as a reference work for all readers interested in paints and coatings.
Wrzburg and Mnster, Germany in January 2017
Bodo Mller, Ulrich Poth: Coatings Formulation, 3 rd Edition Copyright 2017 by Vincentz Network, Hanover, Germany

Contents


Part I Basics
Introduction
1.1 Preliminary remarks
Paints are semifinished products (intermediates); the end products are the coated objects. Paints are used in a wide variety of applications ().
shows that protective paints for buildings accounted for the largest proportion, followed by paints for general industry and other applications. All these different paint systems (with exception of printing inks) will be described in this textbook, especially with regard to problems of paint formulation.
1.2 Comments on environmental protection
The general public unfortunately has a negative image of paints because organic solvents are emitted into the atmosphere when solvent-borne paints are applied. In the past, most decorative or protective paints were solvent-borne. In this chapter, we would like to redress this negative image by describing the emissions-lowering measures that have been taken to improve the environmental safety performance of coatings.
In Germany, emissions into the atmosphere are regulated by TA Luft, which limits the level of organic solvents that may be emitted during paint application. This legislation therefore actively contributes to environmental protection. There are three ways to lower the level of organic solvents emitted from paint formulations (see next page):
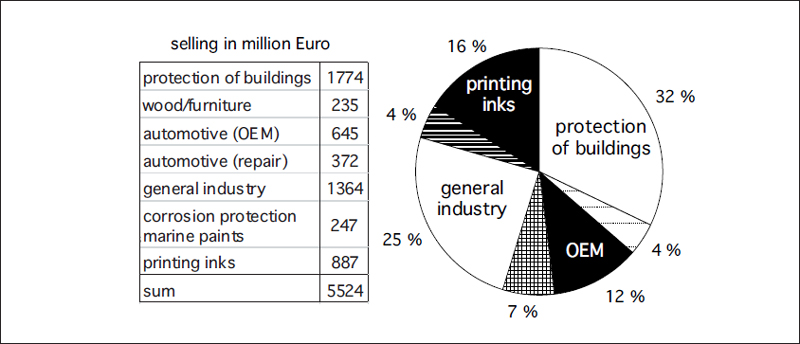
Figure I-1.1: Analysis of paint and printing ink selling in Germany in 2014
Source: Lack im Gesprch, 122, April 2015
Table I-1.1: Classification of solvent-borne (pigmented) paints
paints type | nonvolatile matter (wt.%) |
low-solids | < 30 |
normal-solids | 30 to 60 |
medium-solids | 60 to 70 |
high-solids | > 70 (sometimes > 80) |
ultra-high-solids | > 90 |
Use high-solids paints (paints with a high content of non-volatile matter and therefore low content of organic solvents)
Next page

















