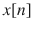Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2018
Orhan Gazi Understanding Digital Signal Processing Springer Topics in Signal Processing 10.1007/978-981-10-4962-0_1
1. Sampling of Continuous Time Signals
Signal is a physical phenomenon that carries information. This physical phenomenon is described by mathematical functions, and usually the signal and its mathematical function are used for one another, i.e., synonymous. For instance, when we talk about a sinusoidal signal, we use the sinusoidal function, a mathematical function, to characterize the signal, and the name sinusoidal is used for the signal. Signals are usually depicted in graphs to observe their behavior and analyze them. Sinusoidal signals are the main signals and all the other signals can be considered as being made up of sinusoidal signals with different frequencies and amplitudes. That is to say, any continuous time signal can be written as sum of sinusoidal signals with different frequencies and amplitudes. Rectangular signal , square pulse signal, impulse train signal, triangle signal can be given as examples of continuous time signals.
Digital signals are obtained from continuous time signals via sampling operation. Digital signals are represented as mathematical sequences, and the elements of these sequences are nothing but the amplitude values taken from continuous time signals at every multiple of the sampling period. Since in the last several decades a huge improvement is achieved at the development of the digital devices, it has become almost a must especially for electrical engineers to have a good knowledge of digital signals. Digital signals are almost available in every part of our life. Computers, TVs, speakers, mobile phones, house equipment, and most of the other electronic devices process digital signals. In this chapter, we discuss the construction of digital signals via sampling operation, their spectral analyses, the case of aliasing, and reconstruction of a continuous time signal from its samples.
1.1 Sampling Operation for Continuous Time Signals
Let
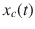
be a continuous time signal. We take samples from the amplitudes of this signal at every multiple of

which is called sampling period and form a mathematical sequence. The obtained mathematical sequence is called digital signal.
The sampling operation is described by the formula
where

is of integer type and
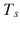
is the sampling period.
The block diagram of the sampling operation is depicted in Fig..
Fig. 1.1
Sampling operation of a continuous time signal
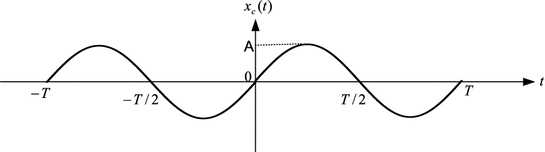
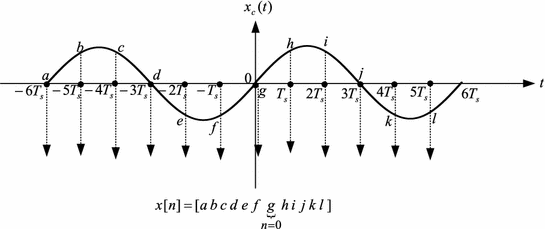
Lets now try to explain the sampling operation on a sinusoidal signal. The graph of the sinusoidal signal with period T is given in Fig..
Fig. 1.2
Sine signal with period
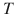
Lets now take some samples from the sine signal in Fig..
Fig. 1.3
Sampling of the sine signal
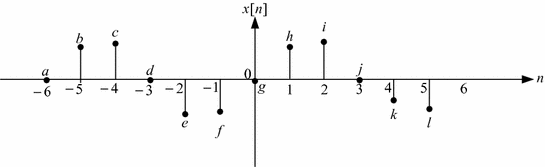
The sampled amplitude values are placed into an array and expressed as a mathematical sequence. The mathematical sequence obtained from the above sampling operation can be written as
which is a digital signal obtained from a continuous time signal. The obtained mathematical sequence can also be displayed graphically as in Fig..
Fig. 1.4
Digital sine signal
If starting index value, i.e.,
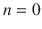
, is not indicated in the mathematical sequence, the index of the first element is accepted as
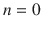
.
Graphical illustration is usually employed for easy understanding of the sampling operation and to interpret the meaning of the received signal. Lets consider the sampling of sine signal again and write a mathematical expression for the digital sine signal. The continuous time sinus signal with period
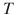
is written as
If the continuous time signal in () is sampled with sampling period

, we obtain the digital signal

whose mathematical expression can be calculated as
By giving negative and positive values to
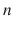
we obtain the amplitude values of digital sine signal which can be shown as
Example 1.1
Find the frequency and period of the continuous time signal
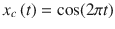
. Sample the given continuous time signal with sampling period T s = 1/8 s and obtain the digital signal
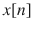











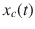 be a continuous time signal. We take samples from the amplitudes of this signal at every multiple of
be a continuous time signal. We take samples from the amplitudes of this signal at every multiple of  which is called sampling period and form a mathematical sequence. The obtained mathematical sequence is called digital signal.
which is called sampling period and form a mathematical sequence. The obtained mathematical sequence is called digital signal.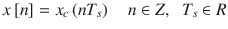
 is of integer type and
is of integer type and 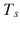 is the sampling period.
is the sampling period.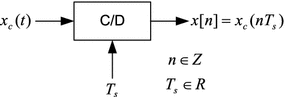
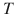
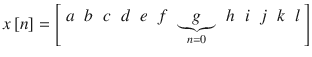
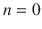 , is not indicated in the mathematical sequence, the index of the first element is accepted as
, is not indicated in the mathematical sequence, the index of the first element is accepted as 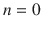 .
.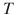 is written as
is written as 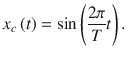
 , we obtain the digital signal
, we obtain the digital signal  whose mathematical expression can be calculated as
whose mathematical expression can be calculated as 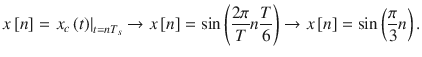
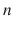 we obtain the amplitude values of digital sine signal which can be shown as
we obtain the amplitude values of digital sine signal which can be shown as 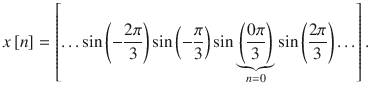
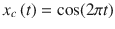 . Sample the given continuous time signal with sampling period T s = 1/8 s and obtain the digital signal
. Sample the given continuous time signal with sampling period T s = 1/8 s and obtain the digital signal