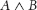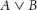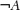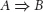Die, my dear doctor? Thats the last thing I shall do! (Last words of Lord Palmerston)
What Is Logic?
Logic is many things. Its a field of knowledge, its a set of techniques, its a guide to critical reasoning, and its a route to understanding the abstract structure of language, mathematics and computing. It is useful in daily life. It helps us think more cogently, to argue more effectively, to read and to listen more critically. And it is the gateway to some of the most profound ideas of human thought.
Logical structures give us insight and perspective. Logic empowers thought.
But logic is not a closed body of doctrine. Like any significant domain of human endeavor, its a work in progress, a field of active research. In this book and on the associated website we bring you seasoned tools and well-established results, but we also take you to the frontiers of logical research. We introduce you to ideas that are new, controversial, and incomplete.
Logic is continually advancing. New logics appear all the time, bringing insights, ideas, and connections. New logicians are born every year. Logic is a vast field; there are discoveries to be made in all directions.
And beyond the usefulness of logic, beyond its power and intrigue, logic is beautiful. The best logical arguments are works of art. They inspire the same feelings of joy, revelation, and peace we find in masterpieces of poetry and music. And they fill us with awe for the men and women who gave them birth.
We invite you to join us.
Chapter One
First, a word about this chapter. Lets say youre going to learn to swim. Youre 5 years old and a little afraid of the water. Your swimming teacher tells you not to be afraid, and picks you up and throws you into the pool!
You immediately start thrashing about with your arms and legs. Youre really scared, but after a few seconds, you notice that youre not drowning, youre keeping your head above water. In a few more seconds, youve made your way to the side of the pool and youre hanging on to the edge trying to figure out what happened.
You didnt drown because everyone is born with swimming reflexes and instincts. When your teacher threw you in, those reflexes took command and saved you. Now that its over, youre not as frightened of the water. Youve been in the middle of the pool and survived.
This chapter is a little like that first swimming lesson. You may never have studied logic, but you do, in fact, know quite a bit. If you didnt, you could hardly speak, let alone make your way in the world.
Were going to throw everything at you. Youll be surprised at how easy it is to understand the symbols. Its easy because the logical ideas represented by the symbols are basic ideas that youve worked with all your life.
Logic can seem scary at first. If you dont know what they mean, strange symbols
can appear frightening
But dont panic. The symbol just means everything. Youll see how it works in a moment. Its not as mean as it looks.
1.1 Introducing Formal Logic
There was only one catch and that was Catch 22, which specified that a concern for ones own safety in the face of dangers that were real and immediate was the process of a rational mind. Orr was crazy and could be grounded. All he had to do was ask; and as soon as he did, he would no longer be crazy and would have to fly more missions. Orr would be crazy to fly more missions and sane if he didnt, but if he was sane he had to fly them. If he flew them he was crazy and didnt have to but if he didnt want to he was sane and had to. (Joseph Heller, Catch-22)
We begin with connectives, the logical operations that link sentences to each other. We dont have many connectives; theyre all familiar to you. You know them as and, or, not, if then, and if and only if. Connectives allow us to create complex statements from simple statements. Suppose A and B are statements. Then well use
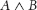
to say that both A and B are true. Well use
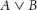
to mean that at least one of A, B is true (A is true or B is true or both are true). Well use
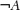
to mean that A is not true. Well use
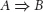
to mean that if A is true then so is B. And finally well use
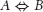
to mean that A is true if and only if B is true, that is, A and B have the same truth value.
Lets say we have these statements:
P: George is late to the meeting.
Q: The meeting is in Detroit.
R: George brings a casserole.
Example
How do we say that either George will be late or hell bring a casserole?
Answer:
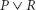
Example
What does Q P mean?
Answer: If the meeting is in Detroit then George will be late.
Example
Represent the following with symbols: The meeting is in Detroit and either George doesnt bring a casserole or George is late.
Answer: Q (R P) Note the use of parentheses here. Well say more about this later.
Exercises Introducing Formal Logic
Odd-numbered solutions begin on page 350
Translate the following sentences using P, Q, and R from above.
1. George is late and the meeting is in Detroit.
2. If the meeting is in Detroit, then George brings a casserole.
3. Either George is late or he does not bring a casserole.
4. George brings a casserole if and only if the meeting is in Detroit.
5. If George does not bring a casserole, he is not late.
6. If the meeting is in Detroit then George brings a casserole, and if George brings a casserole then he is late.
7. The meeting is in Detroit if and only if both George is late and he doesnt bring a casserole.
8. The meeting is in Detroit, and either George is late or he brings a casserole.
Determine the meaning of each of the following sentences.
9. PR
10. RQ
11. QP
12. RQ
13. P (QR)
14. P (QR)
15. R (QP)
16. Q (PR)
The Greek philosopher Epimenides is credited with formulating a paradox that has stimulated some of the most important advances in logic from the classical period right up to yesterday afternoon (we guarantee this, no matter when you are reading these words). He, a Cretan, put it this way:
All Cretans are Liars.
Since Epimenides was a Cretan, he was asserting that he is a liar, meaning that what he says is false. So its false that all Cretans are liars. So maybe hes not a liar. So what he is saying is true? So he is a liar! So its false! So its true! Paradox!
The paradox isnt perfect. Epimenides might be a liar, but some Cretans (not Epimenides) could be truth-tellers. But we can refine it.
Next page