Part I
General Principles and Techniques
Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016
Sanjeev Sabharwal (ed.) Pediatric Lower Limb Deformities 10.1007/978-3-319-17097-8_1
1. Etiology of Lower Limb Deformity
Viral V. Jain 1
(1)
Department of orthopedic Surgery, Cincinnati Childrens Hospital Medical Center, 3333 Burnet Avenue MLC# 2017, Cincinnati, OH 45229, USA
Viral V. Jain (Corresponding author)
Email:
Keywords
Lower limb deformity Etiology Leg deformity
Introduction
Lower limb deformities can consist of any combination of length inequality, angular deformity, and/or asymmetric girth. While the list of possible etiologies is quite extensive, categorizing them can help simplify diagnosis and treatment. Many investigators have broadly classified lower limb deformity into congenital and acquired, with some including a developmental group. This chapter focuses on the etiologies that are most clinically relevant to the orthopedic surgeons.
We have divided the causes of pediatric lower limb deformities into four broad categories: namely underlying conditions, congenital, developmental, and acquired deformities from sequelae of disease or complications (Table ). Most of these disorders are discussed in greater details in the subsequent chapters.
Table 1.1
General categorization of the types of lower limb deformities in children based on etiology
Underlying conditions | Metabolic: rickets, renal osteodystrophy |
Genetic disorders: osteogenesis imperfecta, neurofibromatosis |
Neuromuscular: cerebral palsy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth arthrogryposis |
Skeletal dysplasias |
Benign tumors: fibrous dysplasia, Olliers, multiple hereditary exostoses |
Malignant tumors |
Inflammation: rheumatoid arthridities, hemophilic arthropathy |
Vascular anomalies |
Congenital | Congenital femoral deficiency (proximal focal femoral deficiency) |
Congenital fibular deficiency (fibular hemimelia) |
Congenital tibial deficiency (tibial hemimelia) |
Tibial dysplasia: congenital pseudarthrosis, posteromedial bowing |
Hemihypertrophy |
Amniotic band syndrome |
Congenital knee dislocation |
Developmental | Genu varum |
Blounts disease |
Genu valgum |
Acquired: sequelae and complications | Residual hip deformity: developmental dysplasia of the hip, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, Legg-Calve-Perthes, avascular necrosis |
Posttraumatic: Cozen fracture |
Post-infectious |
Iatrogenic |
Underlying Generalized Conditions
Metabolic Disorders
Certain metabolic disorders and endocrinopathies can affect the maturation of growth plate chondrocytes by the alteration of normal regulatory signals or by disturbance of the functional matrix components necessary for new bone formation. Some endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism and growth hormone deficiency [] can mechanically weaken the physis, predisposing to pathologic conditions such as slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE). These same disorders can render the chondrocytes more susceptible to compressive forces, leading to angular deformities.
Rickets
Rickets is a clinical manifestation of defective mineralization of the long bone physes due to inadequate levels of calcium or phosphate in children. Osteomalacia, the defective mineralization of osteoid at cortical and trabecular surfaces, is seen in both children and adults. There are many different forms of rickets that result in very similar radiographic and clinical manifestations (Table ).
Table 1.2
Rickets and related disorders
Type | Cause |
|---|
Nutritional | Vitamin D deficiency |
Dietary calcium deficiency |
Combination of both |
Gastrointestinal | Poor absorption due to disease (gluten sensitivity, Crohns/ulcerative colitis, short gut) |
End-organ insensitivity | Insensitivity to vitamin D3 |
Vitamin D dependent | 1 alpha hydroxylase deficiency |
X-linked hypophosphatemia | PHEX gene defect, wasting of phosphate in kidney |
Renal tubule abnormality | Kidneys waste many molecules, particularly phosphate |
Hypophosphatasia | Alkaline phosphatase deficiency (gene mutation on chromosome 1) |
Renal osteodystrophy | Renal failure |
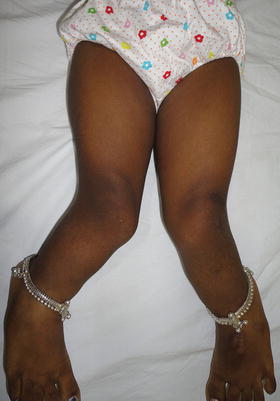
Fig. 1.1
Genu valgum in a 7-year old-female. The etiology was nutritional rickets. Image courtesy Dr. Hitesh Shah
Renal Osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy is the combination of rickets and hyperparathyroidism that occurs secondary to end-stage renal disease. The findings of rickets are explained by the failing kidney being unable to produce a sufficient amount of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Additionally, the dysfunction of the tubular system decreases clearance of phosphate and causes secondary hyperparathyroidism, which manifests as brown tumors and subperiosteal erosions [].
The deformity that results from these metabolic disorders depends on the stage along the physiologic varus/valgus spectrum that the child is at the age of onset of the disorder. The onset of nutritional rickets and inherited disorders is generally seen during infancy and therefore they produce genu varum. On the other hand, renal osteodystrophy usually causes genu valgum because acquired renal failure occurs later when children are more likely in the physiologic valgus age group [].
Genetic Disorders
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta is caused by genetic mutations that affect the quantity or quality of collagen produced. Many distinct mutations have been identified and can thus create a wide spectrum of phenotypic manifestations. Those who are more severely affected have extensive bony fragility that leads to numerous fractures, short stature, and angular deformities of the long bones and the spine [].
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatoses (NF) are a group of genetic multisystem disorders involving products of all three germ lines: neuroectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The most common and orthopedically relevant form is neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) previously known as von Recklinghausen disease, which involves predominantly peripheral nervous system although it involves cells of mesodermal origin as well.