Göran Grimvall - Brainteaser Physics
Here you can read online Göran Grimvall - Brainteaser Physics full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2007, publisher: Johns Hopkins University Press, genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.

- Book:Brainteaser Physics
- Author:
- Publisher:Johns Hopkins University Press
- Genre:
- Year:2007
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Brainteaser Physics: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Brainteaser Physics" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Brainteaser Physics — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Brainteaser Physics" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Brainteaser Physics
Brainteaser Physics
Challenging Physics Puzzlers
Gran Grimvall
2007 The Johns Hopkins University Press
All rights reserved. Published 2007
Printed in the United States of America on acid-free paper
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
The Johns Hopkins University Press
2715 North Charles Street
Baltimore, Maryland 21218-4363
www.press.jhu.edu
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Grimvall, Gran.
Brainteaser physics: challenging physics puzzlers / Gran Grimvall.
p. cm.
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN-13: 978-0-8018-8511-2 (acid-free paper)
ISBN-10: 0-8018-8511-6 (acid-free paper)
ISBN-13: 978-0-8018-8512-9 (pbk. : acid-free paper)
ISBN-10: 0-8018-8512-4 (pbk. : acid-free paper)
1. PhysicsMiscellanea. I. Title.
QC75.G75 2007
530dc22 2006025675
A catalog record for this book is available from the British Library.
Solving problems and coping with challenges are human traits. Many of us do these things just for fun. Crosswords and chess problems are found virtually everywhere. Recreational mathematics problems is a genre with a vast literature. Much less common are recreational physics problemsthe theme of this book. Here I present 57 problems. Some of them are well known in the popular scientific literature. Others are classics that have been treated in the pedagogical physics literature. References to such works are given at the end of the book. Most of the problems have appeared in shorter versions in my weekly column, which has been running for more than 27 years in a Swedish journal for engineers. I am presenting them now for the first time for an international audience. I dont claim originality for all those problems, but many of them are given a new twist.
The problems in this book have two sides. One provides a challengejust for fun or recreation. The other is more seriousit shows how physicists think and thus offers training that could also be of professional use. So, the level of discussion in the solutions varies. It can be elementary in the simplest problems, which can be solved without much knowledge of physics. In the more difficult problems, though, a certain background in mathematics is assumed.
The book concludes with some thoughts about how easy it is to make mistakes. Most likely there are several imperfections or outright errors in this book. All comments from readers are welcome. They can be sent to me at the AlbaNova University Center, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden.
For well over a century the popular scientific literature has included braintwisters with solutions that are applications of simple physical ideas. Many of these problems have become classics and have been published over and over again. Some classic problems that require more of mathematics are found in introductory physics textbooks. This chapter contains ten of these hits, roughly in order of increasing difficulty.
A dinghy, with a passenger and an anchor, floats in a small pool. The passenger throws the anchor into the water. Will the water level in the pool increase, decrease, or stay the same?
Ice cubes float in a glass, filled to the brim with water. Will the water spill over when the ice melts?
An aqueduct for boats is like a bridge and canal combined. It rests on supports at its ends. When a barge carrying a tractor is in the middle of the aqueduct, the tractor unfortunately rolls into the water and sinks, while the barge still floats. The mass of the tractor is one ton and the mass of the barge alone is five tons. Is the total force on the supports at the ends of the aqueduct changed? If so, by how much?
A candle, originally 8 cm long, decreases in length by 2 cm/h when it is burning in an ordinary candlestick. Let it now float in water instead (see ). (A small iron nail at the bottom of the candle lowers the center of gravity so that the candle floats with a vertical orientation.) At the start, the top of the candle is 1 cm above the water level. Is the candle extinguished in less than one hour by the water in the glass?
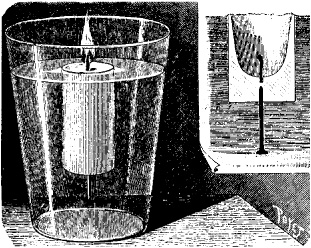
Fig. 1.1. A candle floats in a glass of water. When is it extinguished?
It is raining and you must cross the large parking lot to your car. Because you dont have proper clothes for the rain, and no umbrella, you wonder if its best to walk or to run to your car. If you walk, you will be exposed to the rain much longer, but running into the rain may not be better. What will you do?
You have a set of hardcover books that are all the same size. Put one book at the edge of the table, with a certain overhang. Add more ). What is the minimum number of books needed to make the overhang of the top book clear the edge of the table?
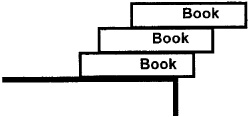
Fig. 1.2. How many books, stacked in a leaning pile, are needed for the top book to clear the edge of the table?
Twelve resistors, all with the resistance 12 , are connected to form the edges of a cube (). What is the largest resistance between any two corners in the cube?
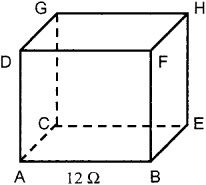
Fig. 1.3. What is the largest resistance between any corners in this cube? Each link has the resistance 12 .
A resistor network has the form of a long ladder (). Each step, and each section of the legs between the steps, is represented by a resistor labeled 1 k. What is the total resistance, as measured between A and B in the figure, if the ladder has seven steps?
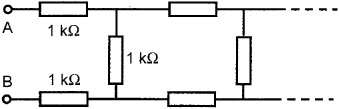
Fig. 1.4. Resistor ladder with two steps. What is the resistance between A and B in a ladder with seven steps?
You have two capacitors with equal capacitance C. One is given the charge Q and the other is uncharged. They are connected as in When the two switches are closed, the charge Q will be equally divided between the capacitors.
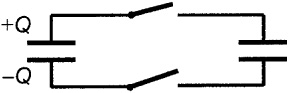
Fig. 1.5. The switches are closed so that a charged capacitor is connected with an uncharged capacitor.
The well-known formula for the energy of a capacitor is
Next pageFont size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Brainteaser Physics»
Look at similar books to Brainteaser Physics. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Brainteaser Physics and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.










