height above sea levelanimal that can live on land and in waterlayer of gases that surrounds Earthtiny forms of life in the air, water, and soil, and in dead creatures and plants, that are often a cause of diseasecutting down or burning the trees in an areaarea where a river splits into smaller branches before entering the seawhen food is changed into substances the plant or animal can uselong period with little or no rain, leading to a shortage of waterplant that grows on another plantchange of water from a liquid into a gasgood for growing cropssubstance that farmers add to soil to make plants grow betterfuel such as coal or oil, which was formed over millions of years from the remains of animals or plantsincrease in the overall temperature of Earths atmospherewhen gases that warm Earth, such as carbon dioxide and methane, are released into the atmosphere (HEP)using the power of moving water to make electricity (person)one of the original peoples of a landtropical tree that grows in mud or at the edge of rivers and has roots that are above groundperson or animal that moves to another part of the country or another land this is called migrationwind that brings heavy rain and storms to tropical areasmoving from place to place in search of grazing landsubstance that is vital for a plant or animal to live and growillegally hunting animals on someone elses landflat, open area of land that is covered with grass but has few treesway of doing things that does not destroy natural resourceslevel at and below which water is found in the ground
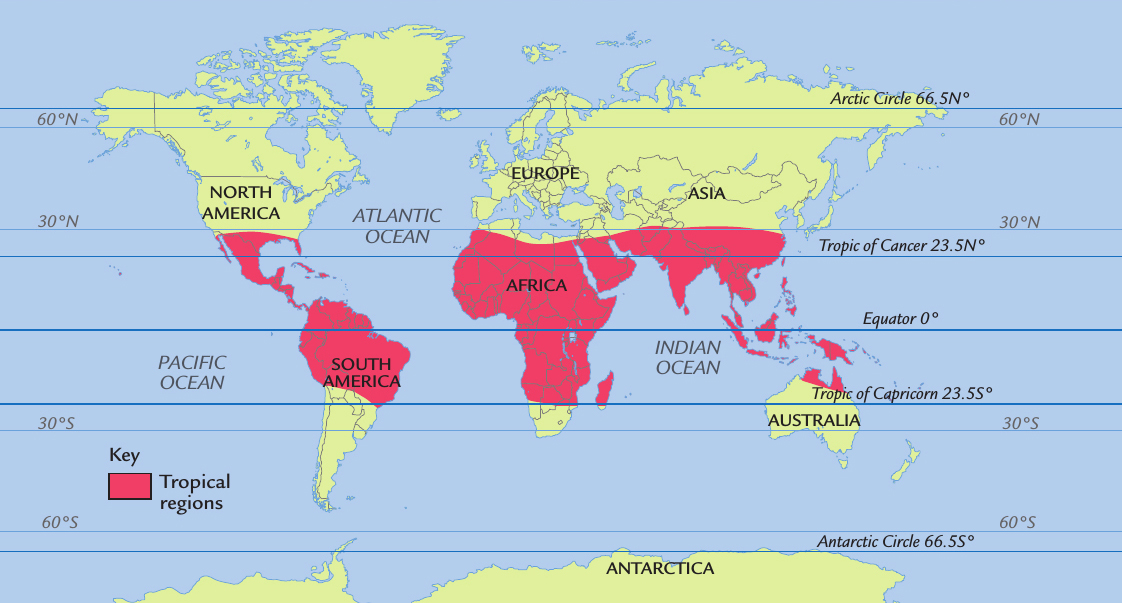
The tropical regions form a band around the Equator, between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. South and Central America have enormous rain forests. In Asia, the rain forests reach from India in the west to Borneo in the east. Australia has dense rain forests too.
But tropical climates arent all the same. Some are hotter and damper than others. Close to the Equator, the climate gets wetter. The driest parts are the tropical deserts at the northern and southern edges of the tropics.
This map shows the tropical zones that lie around the Equator.
AMAZING FACT:
The Amazon rain forest in South America is the largest in the world. Its twice the size of India.
LOW LATITUDES
The Sun is always strong and sometimes shines directly on these regions. There are tall tropical trees, amazing plants that people live deep in the remote rain forest in addition to loggers, ranchers, and miners.
The Amazon rain forest spans nine countries in South America.
DID YOU KNOW?
At the Equator, day and night are of almost equal length all the year round. The Sun rises at about 6 a.m. and sets at roughly 6 p.m. every day.
What are Tropical Climates Like?
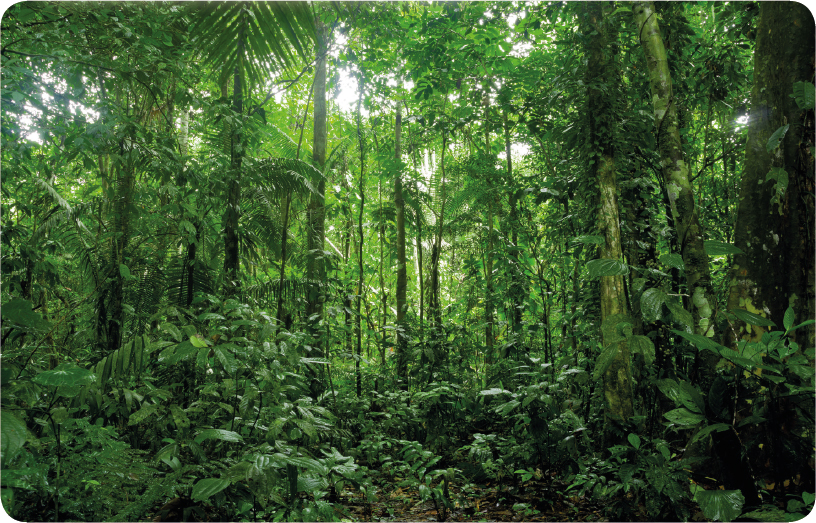
TROPICAL RAIN FORESTS
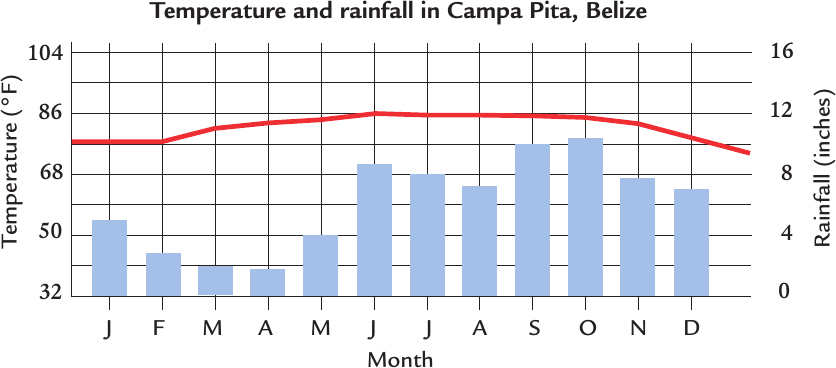
It never gets very cold in the tropical rain forests, even at night. The temperature is usually between 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) and 90F (32C), but it can get up to 100F (38C). Thats pretty hot and steamy! The winds bring moisture to the land. Close to the Equator, the tropical rain forest regions are the wettest on the planet. They have 400 inches (1,000 centimeters) of rainfall a year more than eight times as much as New York City. It rains all year round. Thats why the rain forests are so dense and lush. Thunderstorms might be an occasional, exciting event for many people, but in the rain forests they happen nearly every day.
This graph shows the temperature and rainfall in Belize, Central America.
TROPICAL MONSOONS
Some areas of the tropics, such as southern Asia or West Africa, have a tropical climate. Heavy rains fall in these regions during the monsoon season, which lasts up to three months in the summer. There may be violent thunderstorms here too. People in the tropics regularly have to cope with heavy rain, strong winds, flooding, and mudslides.
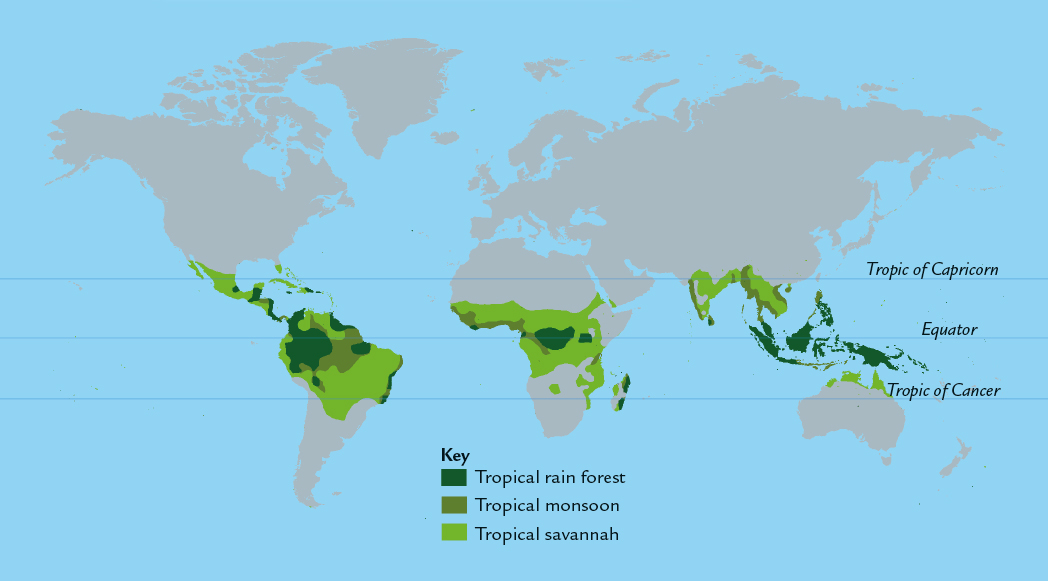
This map shows where the three kinds of tropical climates occur: tropical rain forest, tropical monsoon, and tropical savannah.
AMAZING FACT:
Sub-Saharan Africa covers over 9 million square miles (almost 24 million square kilometers). More than half of this area is tropical savannah.
TROPICAL SAVANNAH
The tropical lies farther away from the Equator. The tropical savannah has three seasons: cool and dry; hot and dry; and hot and wet. Its usually warm, but the temperature varies during the year. The wet season here is shorter than in areas with a monsoon climate and theres less rain although there are still heavy downpours.
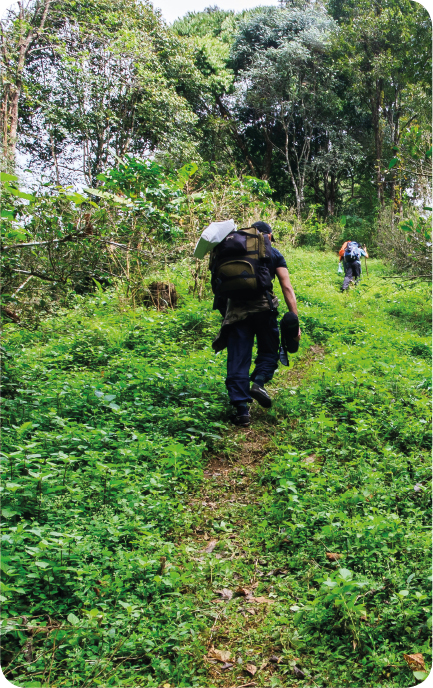
A CHILLY CLIMB
Tropical regions are not hot everywhere. , but as the land rises above about 3,000 feet (900 m), these are replaced by montane (mountain) forests. As in the cooler climates, these forests have deciduous trees, which lose their leaves in winter. On the mountain peaks, there is even snow.
A traveler walks up a steep trail in the mountain forest of Khun Jae National Park, Thailand.
DID YOU KNOW?
Winds influence the climate. Trade winds blow from the north or south toward the Equator. These warm breezes blow nearly all the time. In the Northern Hemisphere they blow from the northeast, and in the Southern Hemisphere, from the southeast. The trade winds meet in the tropics. As they rise, they cool, creating clouds and heavy rainfall. They bring thunderstorms and warm, damp weather.
The altitude affects rainfall too. As moist air rises over a mountain, it cools. Clouds form and it rains. By the time the air reaches the other side of the mountain, it has lost its moisture. Little rain falls this side is in what is called a rain shadow.