Glossary
the way in which an animals color or shape matches its surroundings and makes it difficult to spotchanges in Earths weather, including changes in temperature, wind patterns, and rainfallto do with a tree that produces hard, dry fruit called conesto do with a tree or bush that loses its leaves every yearlong period with little or no rain, leading to a shortage of watersomeone who studies how plants and living creatures relate to each other and their environmentgases that are sent out into the airchange from a liquid to a gasdevelop over time into forms that are better adapted to survive changes in the environmentland or soil where plants grow wellleaves of a tree or plantarea of dry, falling air that causes dry weather, except for occasional thunderstormsstrong wind that blows high in the atmosphere and has an effect on the weatherdistance of a place north or south of the Equator, measured in degreesvery small gray or yellow plant that spreads over the surface of rocks, walls, and trees and does not have any flowerssmall green or yellow plant without flowerssubstance that is vital for a plant or animal to live and growkind of farming that does not use artificial (unnatural) chemicals on the cropschemical used for killing pests especially insectsliquid in a plant or tree that carries food to all its partsway of doing things that does not destroy natural resourcestrees that are grown to be used in building or for making thingsa funnel cloud descending from storm clouds, with violent winds whirling around in a circle.area between the Tropic of Cancer north of the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn, south of the Equator
Read More
BOOKS
- Gardner, Robert. Temperate Forest Experiments: 8 Science Experiments in One Hour or Less. Berkeley Heights, N.J.: Enslow Elementary, 2015.
- Heos, Bridget. Do You Really Want to Visit a Temperate Forest? Mankato, Minn.: Amicus Illustrated, 2015.
- Johansson, Philip. The Temperate Forest: Discover This Wooded Biome. Berkeley Heights, N.J.: Enslow Elementary, 2015.
PLACES TO VISIT
Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks, California
https://www.nps.gov/seki/index.htm
See dramatic mountains and canyons and the worlds largest trees.
Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming (with parts in Idaho and Montana)
https://www.nps.gov/yell/index.htm
See hundreds of animal species, including wolves, bison, bears, and antelope.
Yosemite National Park, California
https://www.nps.gov/yose/index.htm
Explore waterfalls, meadows, deep valleys, and giant sequoias.
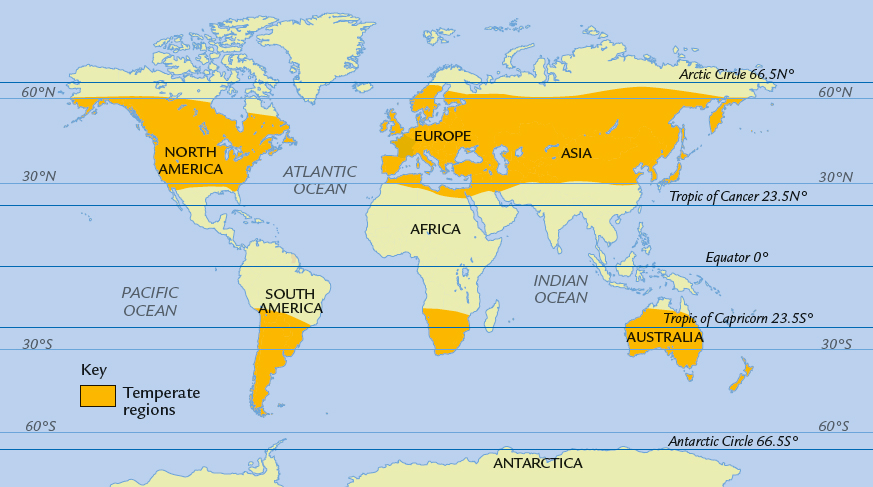
Where are the Temperate Climate Zones?
Its the middle of summer. In the Mediterranean, its hot and sunny. In Seattle, Washington, its mild and rainy. Welcome to temperate climates the most varied climates in the world.
This map shows the temperate climate zones of the world.
MARITIME AND CONTINENTAL, COOL AND WARM
The temperate climates are found between the and the polar regions. There are two main types of temperate climates: maritime and continental. The maritime climate is influenced by ocean winds and currents. The places with a maritime climate are usually on the western edges of continents and are between 30 and 60 north and south of the Equator. Examples of areas with a maritime climate include western Europe and western North America. Inland areas between the tropics and the polar regions have a continental climate, as do areas between 30 and 60 north of the Equator, in central and eastern North America and Asia.
Temperate continental climates can be divided into warm and cool continental climates. Maritime climates can also be divided into warm and cool maritime climates. A warm maritime, or Mediterranean, climate is found in parts of Spain, Italy, Greece, and Turkey. The southeastern tip of Australia, coastal Norway, and parts of Iceland have a cool maritime, or Marine West Coast, climate.
DID YOU KNOW?
In temperate climates, it is generally warm in summer and cool in winter. But it is unusual to experience the scorching temperatures of the tropics or the bitter cold of the polar regions.
In the United States, there is a cool continental climate east of the Rockies and north into Canada, from around 40 north. South of around 40 north, theres a warm continental climate. A large strip across central China has a cool continental climate. Eastern China has a warm continental climate.
The comfortable temperatures in the temperate climates have allowed a wide variety of plants and animals to develop. Resources from the land, forests, and seas are plentiful. Theyre such popular places to live and visit that these regions are under great pressure from people, industry, and agriculture.
Cape Town, South Africa, is an example of an area with a warm maritime climate. These occur along west coasts of continents, generally south of 40 in the northern hemisphere and north of 40 in the southern hemisphere.
What are Temperate Climates Like?
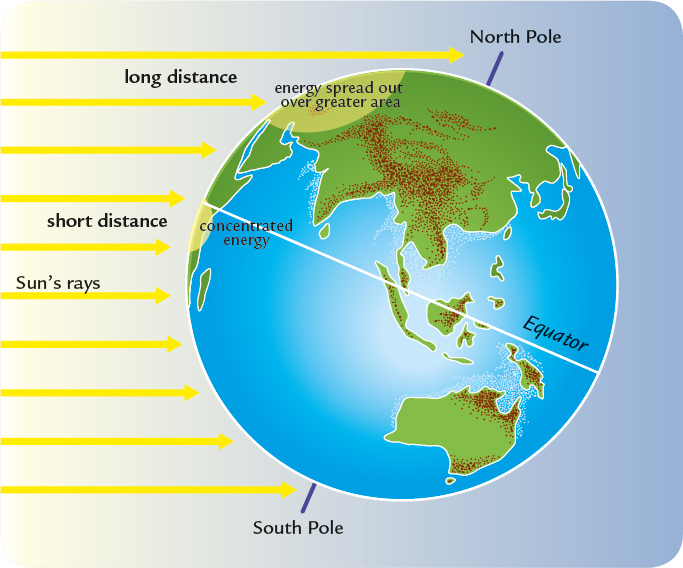
Temperate climates are cooler than tropical climates. In the temperate zones, the Suns rays are spread out and strike over a wide area.
Cool maritime zones have four seasons. Yet even in summer, there might be rain, fog, and low temperatures. Summers do tend to be drier than other times of year though. Warm maritime regions are a bit different. Here, there are two seasons: hot, dry summers and cool, rainy winters. Inland, the ocean does not moderate the temperature as it does at the coast (see .
This diagram shows how the Suns rays are more spread out in the temperate zones than in the tropics.
DID YOU KNOW?
The tilt of Earths axis creates the seasons. When the southern hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, the region has summer. The northern hemisphere tilts away from the Sun, and its winter. Earth turns on its axis and six months later, its the opposite. The northern hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, and people in that half of the world enjoy summer.
COOL MARITIME CLIMATE: WET AND WINDY
In regions with a cool maritime climate, there is more rain near the coast than inland. Thats because these zones are on the west of temperate continents, and winds in temperate zones generally come from the west, bringing rain. On the plus side, the temperatures are milder, so its not so chilly in winter. The ocean heats up and cools down more slowly than the land. This makes the temperatures on the land at the coast less extreme than the temperatures inland. The water remains cold in summer, keeping the coasts cool, and stays warm into winter, making the land warmer.
Cornwall is on the southwest coast of the United Kingdom. The west coast has more rain than the east coast.