
Recent titles in the Explore Your World! Series

Check out more titles at www.nomadpress.net
Nomad Press
A division of Nomad Communications
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Copyright 2016 by Nomad Press. All rights reserved.
No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without permission in writing from the publisher, except by a reviewer who may quote brief passages in a review or for limited educational use.
The trademark Nomad Press and the Nomad Press logo are trademarks of Nomad Communications, Inc.
Illustrations by Bryan Stone
Educational Consultant, Marla Conn
Questions regarding the ordering of this book should be addressed to
Nomad Press
2456 Christian St.
White River Junction, VT 05001
www.nomadpress.net
CONTENTS
Introduction
What Are Fossils?
Chapter 1
From the Rocks
Chapter 2
Clues to the Past
Chapter 3
Plants and Microbe Fossils
Chapter 4
Animals, Including Humans!
Chapter 5
Plant-Eating Dinosaurs
Chapter 6
Meat-Eating Dinosaurs
Chapter 7
Boom and Bust
Chapter 8
How Paleontologists Work
Interested in primary sources? Look for this icon.
 Use a smartphone or tablet app to scan the QR code and explore more! You can find a list of URLs on the Resources page.
Use a smartphone or tablet app to scan the QR code and explore more! You can find a list of URLs on the Resources page.
If the QR code doesnt work, try searching the Internet with the Keyword Prompts to find other helpful sources.
KEYWORD PROMPTS
fossil discoveries 


INTRODUCTION
WHAT ARE FOSSILS?
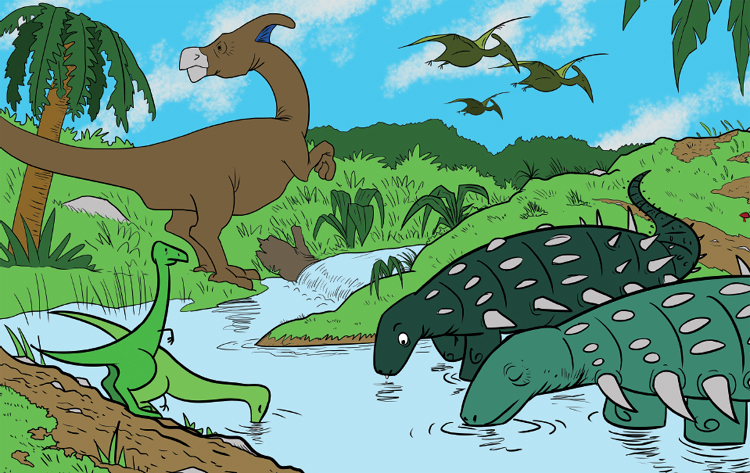
Millions of years ago, huge animals roamed the earth. Some weighed more than 10 times as much as an elephant. Have you heard of these creatures? Theyre dinosaurs! But if dinosaurs lived so long ago, how do we know so much about them?
The answer can be found in what they left behind. A fossil is the remains of an ancient plant or animal that has been preserved in rock. Have you ever found a strange-looking rock that looked like a seashell or had an imprint of a leaf or an animal track? It was probably a fossil.
WORDS TO KNOW
fossil: the remains of any organism, including animals and plants, that have been preserved in rock.
WHAT IS PALEONTOLOGY?
Paleontology is the study of ancient life. Scientists called paleontologists study fossils to find out about plants and animals that lived long ago. Paleontologists want to know what the earths environment was like millions of years ago.
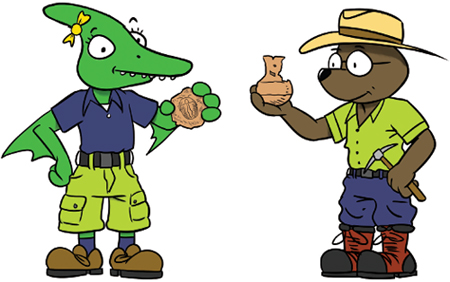
Archaeology is the study of human remains and objects made by humans. Paleontology includes the study of all life, from ferns to dinosaurs to elephants. Paleontologists and archaeologists sometimes work together. For example, a paleontologist might help identify plant fossils at an archaeological site. This can help determine what the early humans who lived there ate.
Paleontology combines geology and biology . A paleontologist must understand organisms , as well as how rocks form and move on the surface of the earth.
WORDS TO KNOW
paleontology: the study of the fossils of plants and animals. A scientist who studies paleontology is a paleontologist.
environment: everything in nature, living and nonliving, including plants, animals, soil, rocks, and water.
archaeology: the study of ancient people through the objects they left behind. A scientist who studies archaeology is a archaeologist.
geology: the study of the earth and its rocks. A scientist who studies geology is a geologist.
biology: the study of living things.
organism: any living thing.
GOOD SCIENCE PRACTICES
Every good scientist keeps a science journal! Choose a notebook to use as your science journal. As you read through this book and do the activities, keep track of your observations in a scientific method worksheet, like the one shown here. Scientists use the scientific method to keep their experiments organized.
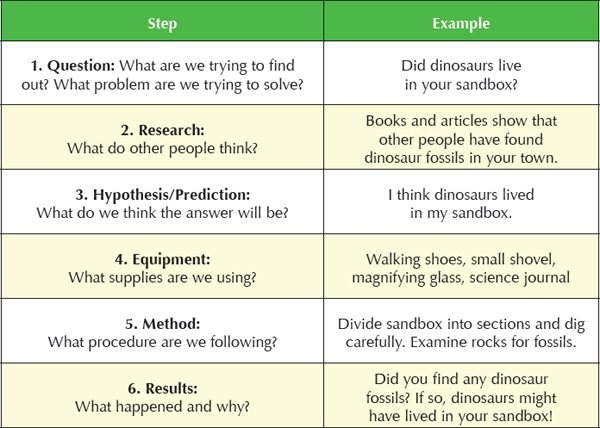
Each chapter of this book begins with a question to help guide your exploration of fossils. Keep the question in your mind as you read the chapter. At the end of each chapter, use your science journal to record your thoughts and answers.
INVESTIGATE!
Why do we use geologic time when we talk about the history of the earth? Why not use human time?
TIMELINE OF THE EARTH
Can you imagine living through a day that isnt divided into hours? How would you know when to eat lunch or when to go to bed? People divide time into different units to help us keep track of time. These units include years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
Geologists divide the entire history of the earth into units, too. They call this history the geologic timescale . The parts of the geologic timescale are based on when different kinds of life developed and on other events in the earths history.
WORDS TO KNOW
geologic timescale: the way the 4.6-billion-year history of the earth is divided up.
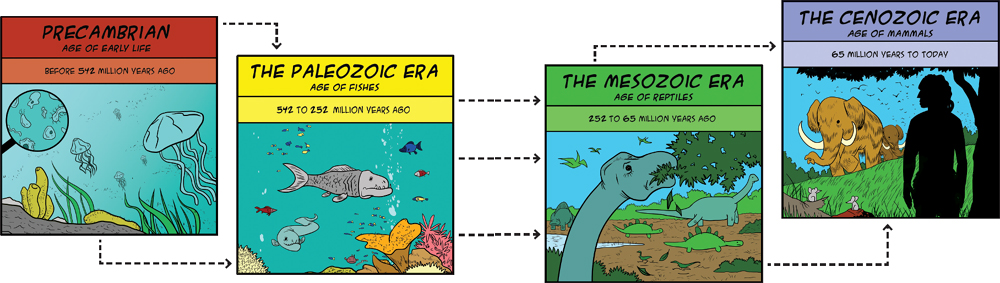
Its a bit like if you divided your own life into units such as babyhood, preschool, and elementary school. The different periods in your life arent all the same length. The different periods in the geologic timescale are all different, too.

The word fossil comes from the Latin word fossilis, which means dug up.
The earth has been around for more than 4 billion years. Thats a lot of time to divide! There are four large periods of time.
 Precambrian is before 542 million years ago.
Precambrian is before 542 million years ago.
 Paleozoic Era is between 542 and 252 million years ago.
Paleozoic Era is between 542 and 252 million years ago.
 Mesozoic Era is between 252 and 65 million years ago.
Mesozoic Era is between 252 and 65 million years ago.
 Cenozoic Era is between now and 65 million years ago.
Cenozoic Era is between now and 65 million years ago.
PRECAMBRIAN: Sometimes called the Age of Early Life, Precambrian was the time before 542 million years ago. The seas contained mats of algae, microorganisms , and simple animals, such as sponges and jellyfish.
THE PALEOZOIC ERA: Sometimes called the Age of Fishes, the Paleozoic Era was between 542 and 252 million years ago. There were lots of fish, corals, and other ocean creatures. Ferns, evergreen forests, insects, and reptiles lived on land. The Paleozoic Era ended with the largest extinction of species in the history of the earth.
Next page















 Use a smartphone or tablet app to scan the QR code and explore more! You can find a list of URLs on the Resources page.
Use a smartphone or tablet app to scan the QR code and explore more! You can find a list of URLs on the Resources page.






 Precambrian is before 542 million years ago.
Precambrian is before 542 million years ago.