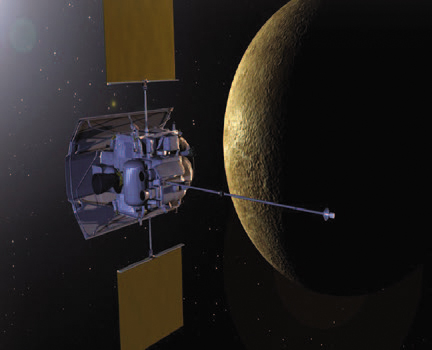
Compared to most planets, Venus is a short hop away from Earth. In 2005, the space probe Venus Express made the journey to Venus in 155 days. It will take you longerto get to Mercury. The Mercury Messenger probe, launched in August 2004, reachedthe planet in January 2008.
See pages to find out which spacecraft have visited Mercury and Venus.
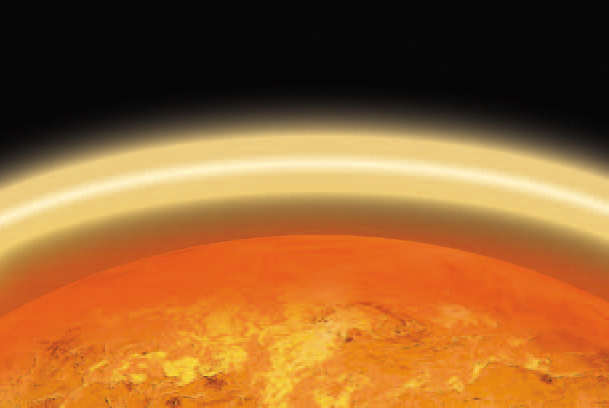
Discover what the atmosphere is like on Venus on pages .
Meet astronaut Paolo Nespoli on page .
EXPLORING MERCURY AND VENUS FROM EARTH
It is not just astronauts who are interested in Mercury and Venus. Humans have beengazing at the planets and trying to uncover their secrets for thousands of years.
EARLY ASTROLOGY
Mercury and Venus can be spotted from Earth in the evening and early morning. Theylook like very large, bright stars. Ancient peoples did not know what planets andstars were, but they began to notice patterns in their movements across the sky.They recorded the patterns and used the data to create calendars and to try to predictthe future. This is known as astrology.
More than 2,500 years ago, the Mayans believed that Venus was as important as theSun. They called the planet Xux Ek , meaning the Great Star, and kept careful recordsof when it appeared in the sky.
NAMING THE PLANETS
Many ancient cultures linked the objects they saw in the sky to religion. Early astronomers were often priests, and the planets were named after gods and goddesses.
The names that we use today come from Roman mythology . Mercury was the Roman messengergod who wore winged sandals so he could speed through the sky. This name suits theplanet Mercury because it also moves quickly across the sky. Sunlight bounces offthick clouds around Venus, making it look like a beautiful shining star. It is namedafter the Roman goddess of love and beauty.
Venus was known as the Morning Star and Evening Star because it looks so bright inthe sky at dawn and dusk. Mercury is much harder to spot.
THE SCIENCE OF ASTRONOMY
Although the movement of planets cannot be used to predict human events, the informationcollected by early astrologers was very useful. Astronomers used it to discover newthings about the planets and Earth itself.
GREEK STAR-GAZING
From around 450 BCE, the ancient Greeks changed how the planets and stars were studied.Many Greek astronomers were mathematicians. They came up with new ideas about whatMercury and Venus were and why they appeared to move through the sky. Some of theirideas were right, but others we now know were wrong.
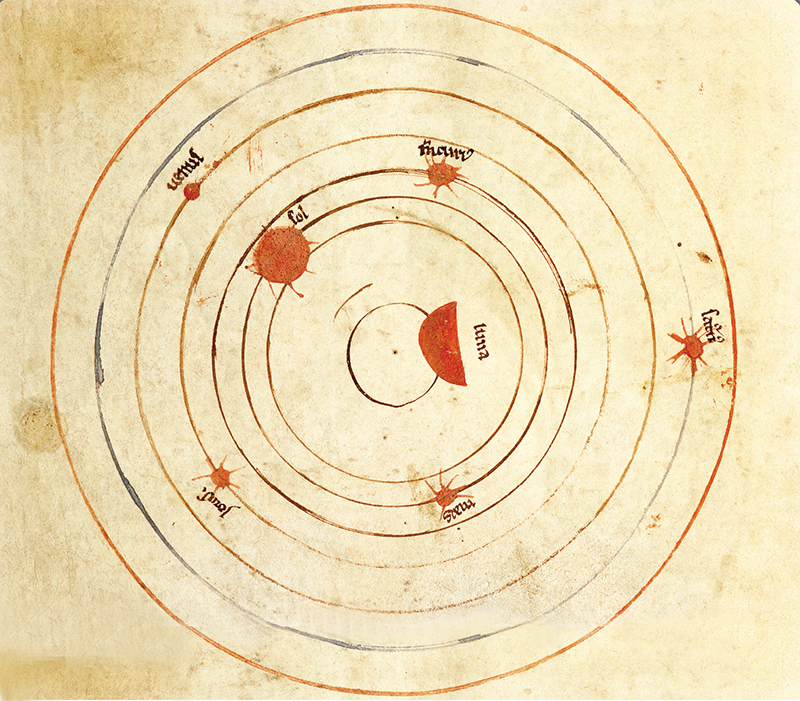
Greek astronomer Ptolemy wrongly thought that the planets, Sun, Moon, and stars traveledaround Earth. This idea lasted for 1,400 years!
ARABIC SCHOLARS
From the 600s CE, Arabic astronomers made many important discoveries. They studiedancient Greek ideas about the solar system. They built huge observatories . The mostfamous Arab astronomer is al-Battani. He made superb instruments to track the movementof planets and figure out their positions.
COPERNICUS AND KEPLER
Al-Battanis work was very helpful to European scientists. In the 1500s, NicolausCopernicus made a huge breakthrough. He suggested that the planets, including Earth,actually traveled around the Sun.
Later, the scientist Johannes Kepler combined Copernicuss ideas with accurate datato explain how the planets move through space. This can be used to predict whereMercury and Venus will be at any timewhich is important information for a modern-dayastronaut trying to get there!
Astrolabes were the laptop computers of the past! They were used to measure the positionof objects in the sky and tell the time of the day or year.
WHOS WHO?
The Greek mathematician Pythagoras (c. 580c.500 BCE) noticed that the Morning Starand Evening Star were actually the same object: Venus. He was also probably the firstto suggest that all planets are spheres (ball-shaped).
A BETTER VIEW OF THE PLANETS
Until the 1600s, astronomers could only see the planets as well as you can see themwith your eyes. When the telescope was invented in 1609, it was suddenly possibleto make planets and stars look much nearer. This allowed scientists to see surprisingnew details.
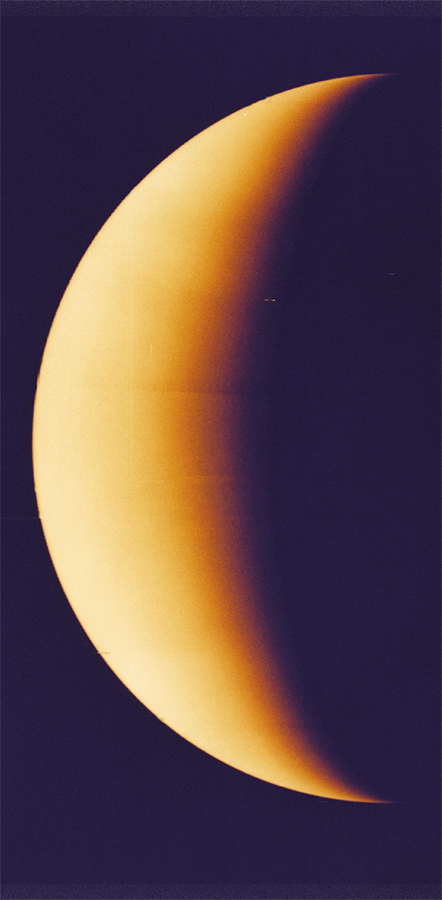
In 1610, Galileo Galilei used telescopes to make an amazing discovery. He saw thatVenus had phases (meaning it appeared to change shape) like the Moon. Galileo knewthat this could only happen if planets orbit the Sun, not Earth. He had proved thatCopernicus was right.
Through his telescopes, Galileo could see different amounts of Venuss sunlit sideat different times. The race was now on to invent better telescopes and make newfindings.
NEW DISCOVERIES
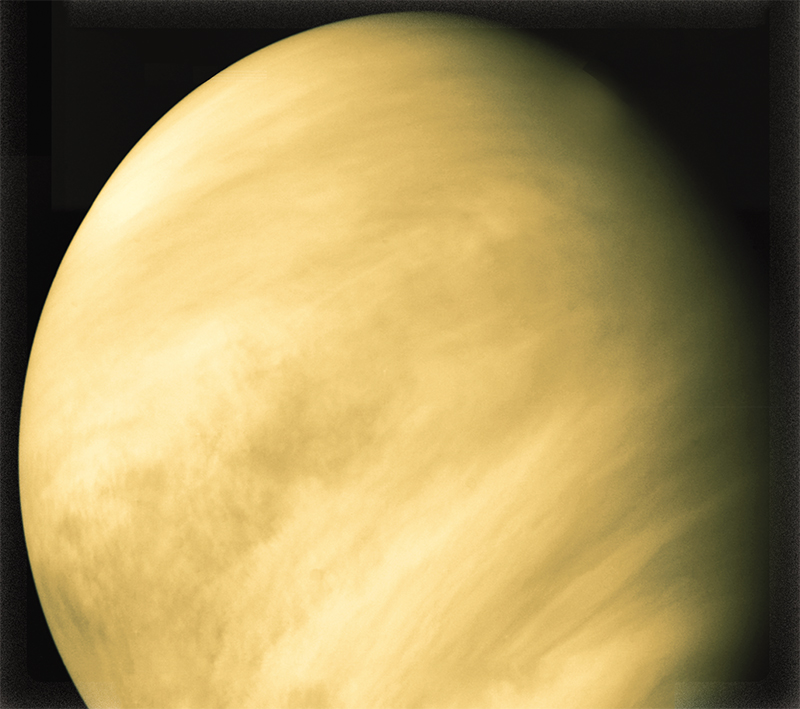
During the 1800s, astronomers developed instruments and techniques that helped themto discover more about planets. From the 1850s, people used cameras to record theimages seen through telescopes, instead of drawing them by hand. Enough detail couldbe seen to create rough maps of Mercurys surface. But even though Venus is closerto Earth than Mercury, the surface of Venus remained a mystery, hidden behind itsthick clouds.