
The crew of the Endurance
Top row: Holness and Bakewell. Second row: McNish, James, Wild, Worsley, Stephenson
(above Worsley), Hudson, How, Green. Third row: Cheetham, Crean, Hussey, Greenstreet, Shackleton,
Sir Daniel Gooch (who sailed as far as South Georgia as a dog minder), Rickinson, Hurley.
Front row: Clark, Wordie, Macklin, Marston, McIlroy.
Also by Caroline Alexander
One Dry Season
The Way to Xanadu
Battle's End
Mrs. Chippy's Last Expedition
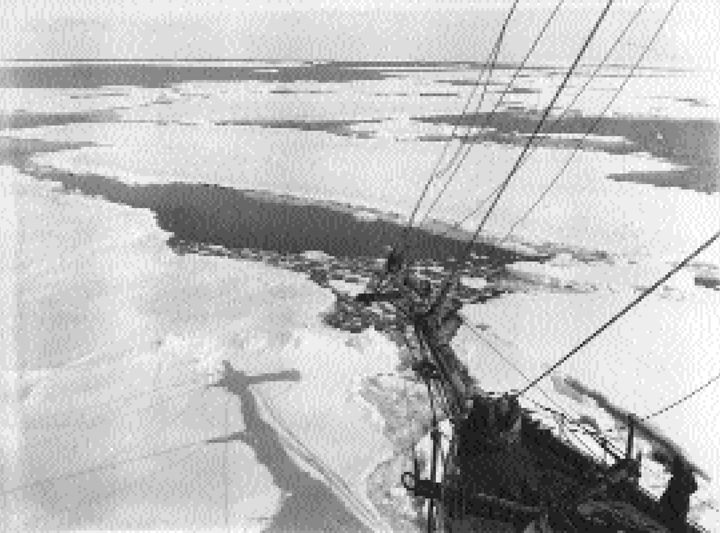

Cutting through the pack ice

TO MRS. CHIPPY
Who pioneered the way

Blackborow with Mrs. Chippy

Never for me the lowered banner, never the last endeavour.
SIR ERNEST SHACKLETON
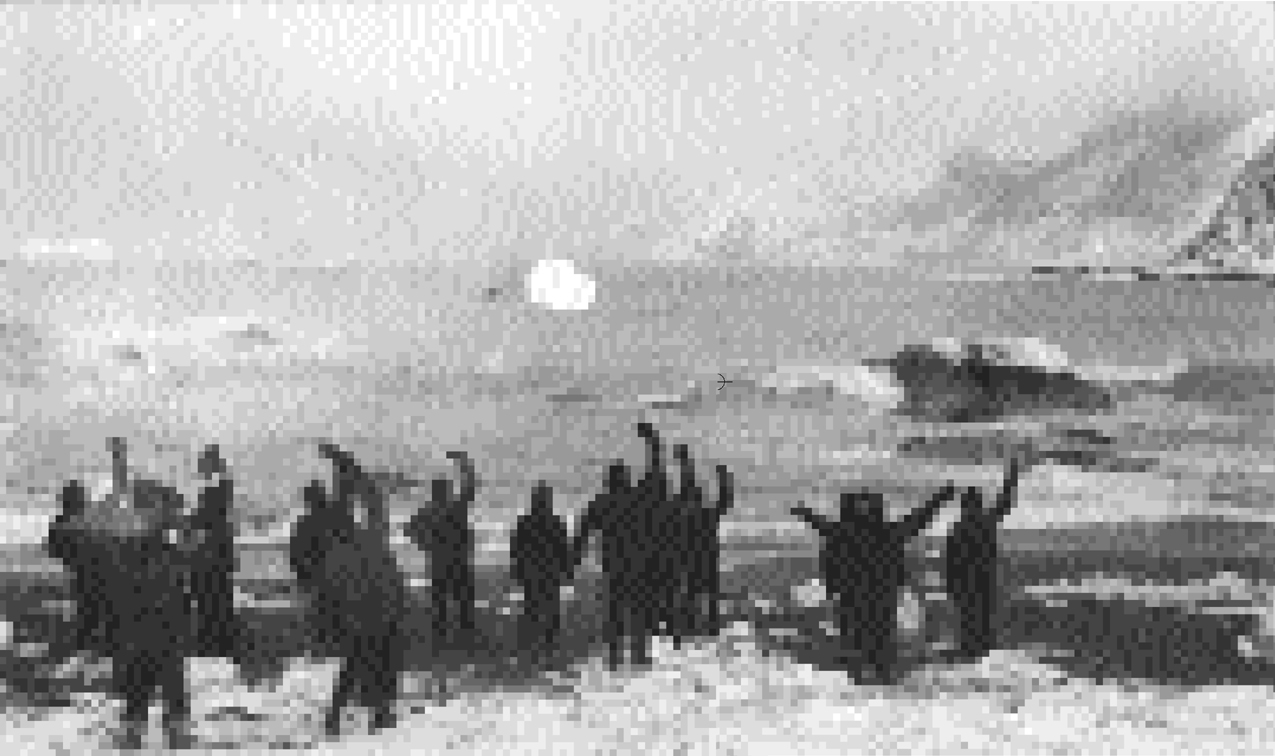
The Rescue

Sir Ernest Shackleton
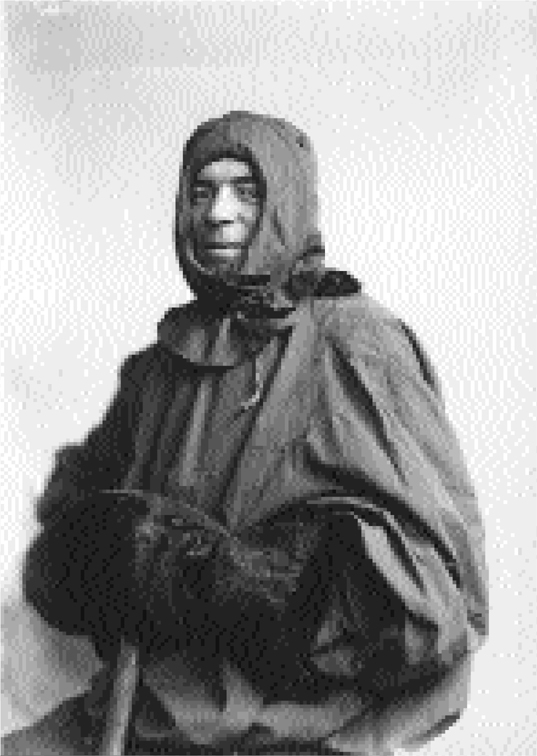

Frank Hurley
The expedition's gifted and gritty photographer poses for a studio shot in his Burberry helmet and tunic.
The Heroic Age
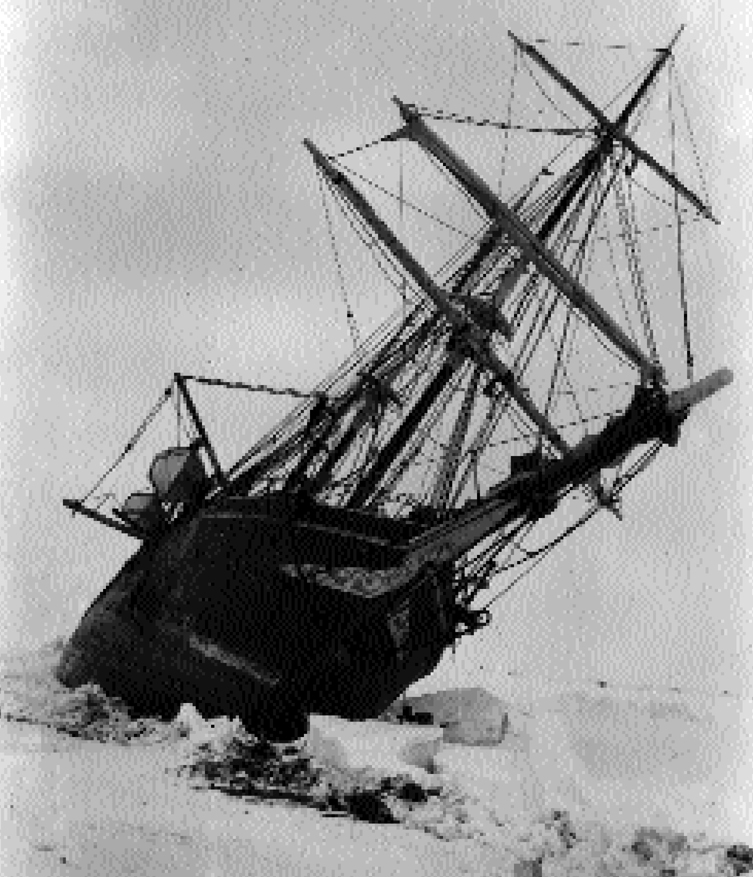
T he captain of the ship, Frank Worsley, would remember the day vividly ever afterward. It was July, midwinter in Antarctica, and the darkness of the long polar night had been upon them for many weeks. The temperature was 30 Fahrenheit, and around the ship, extending to the horizon in all directions, was a sea of ice, white and mysterious under the clear, hard stars. From time to time, the shriek of the wind outside broke all conversation. Away in the distance, the ice would groan, and Worsley and his two companions would listen to its ominous voice as it travelled to them across the frozen miles. Sometimes, the little ship would quiver and groan in response, her wooden timbers straining as the pressure from millions of tons of ice, set in motion by some faraway disturbance, at last reached her resting place and nipped at her resilient sides. One of the three men spoke.
She's pretty near her end. The ship can't live in this, Skipper. You had better make up your mind that it is only a matter of time. It may be a few months, and it may be only a question of weeks, or even days but what the ice gets, the ice keeps.
The year was 1915. The speaker was Sir Ernest Shackleton, one of the most renowned polar explorers of his day, and the third man was Frank Wild, his second-in-command. Their ship, Endurance, was trapped at latitude 74 south, deep in the frozen waters of Antarctica's Weddell Sea. Shackleton had been intent on an ambitious mission: He and his men had travelled to the south to claim one of the last remaining prizes in exploration, the crossing on foot of the Antarctic continent.
Since December 1914, the Endurance had battled unusually heavy ice conditions, travelling more than 1,000 miles from the remote whaling stations on the island of South Georgia, at the gateway to the Antarctic Circle. One hundred miles short of her intended harbor, new ice conditions brought the Endurance to a halt. A northeast gale blowing on and off for six straight days compressed the pack against the Antarctic ice shelf, trapping the ship fast within it. Days later, the temperature plummeted to 9, as good as cementing the loose pack for the winter. Meanwhile, the leisurely, unrelenting northerly drift of the Weddell Sea carried the Endurance within the pack farther and farther from the land it had come so close to reaching.
When Shackleton embarked upon his Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, he was already a national hero with two polar expeditions behind him, including one that had taken him to within 100 miles of the South Pole, the farthest south anyone had travelled at that time. Yet for all the heroism of these earlier efforts, neither had accomplished what it had set out to do. By the time Shackleton headed south again in 1914, the prize of the South Pole, which he had twice sought, had been claimed by others. Undaunted, he had turned his sights upon a last great venturethe crossing of the Antarctic continent from the Weddell to the Ross Sea. The preparations for the Endurance expedition had been all-consuming; not the least of Shackleton's tasks had been raising the funds to make it possible. He was forty years of age, and he had summoned all his experience as explorer and organizer to bear on this ambitious undertaking. Shackleton could not yet know it, but the trans-Antarctic expedition would amount to another unsuccessful venture. Yet ultimately it would be for this, the failed Endurance expedition, that he would be most remembered.
Antarctic exploration of the early twentieth century was unlike exploration of anywhere else on earth. No dangerous beasts or savage natives barred the pioneering explorer's way. Here, with wind speeds up to nearly 200 miles an hour and temperatures as extreme as 100 Fahrenheit, the essential competitions were pure and uncomplicated, being between man and the unfettered force of raw Nature, and man and the limits of his own endurance. Antarctica was also unique in being a place that was genuinely discovered by its explorers. No indigenous peoples had been living there all along, and the men who set foot on the continent during this age could authentically claim to have been where no member of humankind had ever cast a shadow.
Beginning in 1914 and ending in 1917, straddling the First World War, the Endurance expedition is often said to have been the last in the Heroic Age of polar exploration. The significance and ambition of Shackleton's proposed trans-Antarctic crossing is best appreciated within a context of the ordeals of heroismand egotismthat had played out before. Indeed, Shackleton's greatness as a leader on the Endurance owes much to the sometimes insane suffering of his earlier Antarctic experiences.
The Heroic Age began when the ship Discovery, under the command of Captain Robert Falcon Scott, set out for Antarctica's McMurdo Sound in August 1901. Despite public talk of scientific advancement, the real objective of this first inland expedition, as of subsequent ones, was to reach the as yet unclaimed South Pole and win it for Britain. Scott chose two men to accompany him on this first bid for the poleDr. Edward Wilson, a physician, zoologist, and close friend; and Lieutenant Ernest Shackleton, a twenty-eight-year-old merchant service officer, whose commissions had taken him to Africa and the East. On November 2, the three men set out with nineteen sledging dogs and five loaded sledges. They faced an unspeakably daunting challenge, a round-trip journey of more than 1,600 miles, hard sledging all the way, through an entirely unknown and uncharted environment.






















