ISBN: 978-93-5607-098-1
Learning Web Design - HTML5
A Practical Handbook
By
SHANMUGAPRIYAA S
Title: Learning Web Design - HTML5
Author: Shanmugapriyaa S
Published By: Self-Published
Copyright 2022 Shanmugapriyaa S.
All rights reserved. No portion of this e-book may be reproduced in whole or in part in any form.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Everyone is surfing the web today. Every website or webpage we visit seems to have a similar structure, though they vary by designs, features and in terms of accessibility.
This e-book will elucidate about HTML, which lays the basic structure of todays web. If programming languages are the tools to communicate with systems, then HTML is the communication tool for the web. Whatever we want to see in the web, will be instructed in HTML.
What will you gain on reading and practising this e-book?
Get introduced to the structure of web page
Understand the need of HTML in web design
Learn the HTML elements necessary to build a web page
Implement styles and formatting to web page
Design a web page using semantic elements
Learn to use forms to interact with users
Make use of all media (text, image, audio, video) in the web page
Make the designed web page responsive
You will start from scratch, from knowing the structure of the web page and on completion, you will be able to design a responsive web page using HTML. A website is a collection of web pages. When you know how to design one page, you can automatically develop a website.
This e-book does not limit to the concepts of HTML, but guides you in practising the same in your system. You can consider this as a self-guiding material to make your learning comfortable.
Let us start learning!
Chapter 1: Introduction to Web Page and HTML5
1.1 Structure of a Web Page
Web designing is all about designing web pages. When these web pages are linked to each other and share a common brand or product or purpose, they become a website.
In this section, you will be introduced to how a web page looks. In order to design a web page, we must know how it looks like and what it needs to be created.
Web pages are the ones you see when you browse something on the web, that is something what the browser shows.
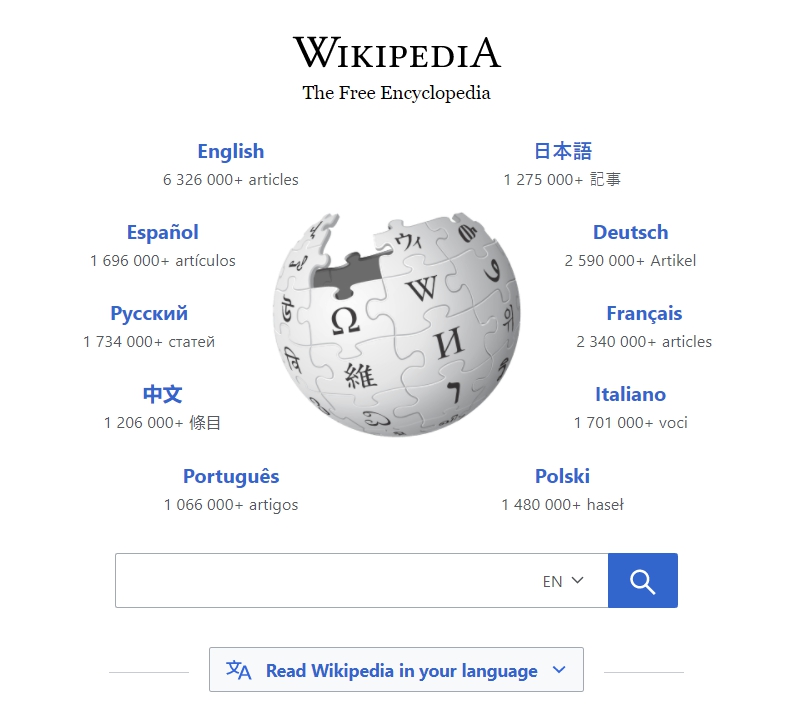
Look at the web page of a sample website: Wikipedia - Home Page
How did this web page come up?
- Open a browser
- Go to https://wikipedia.org/
- Right Click on the page and Choose View Page Source / View Source (Depends on the browser) or Click Ctrl + U
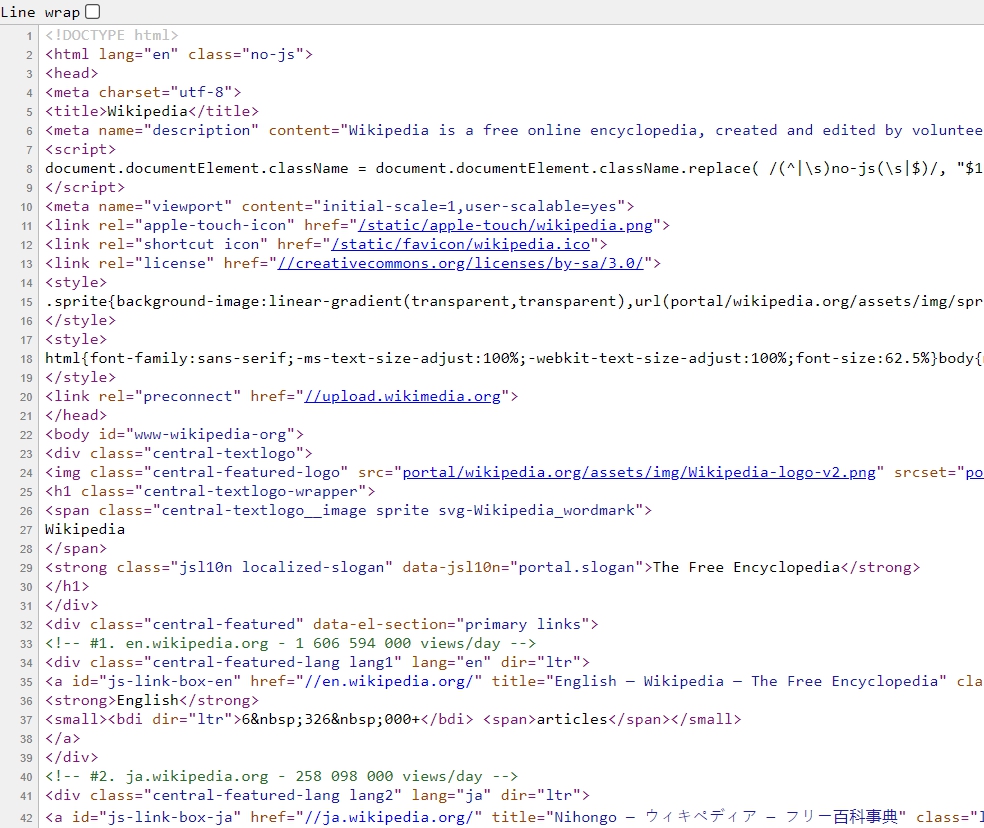
You will see something like this:
This coding is the reason behind the web page look. And we call this coding language as a markup language.
1.2 Introduction to HTML
What is a markup Language?
Markup language is a coding language which annotates a document to represent content.
There are three types of markup languages:
1. Presentational markup
It is used by text processing systems but the coding is usually hidden from users because such markup languages produce WYSIWYG (What you See Is What You Get) output.
2. Procedural markup
The markup language is embedded in text and this in turn provides instructions to programs to process the text.
3. Declarative markup
This markup language is used to provide labels to process specific instructions on how they should be processed.
Languages like HTML, XML fall into this category. They contain meaningful elements called tags that occur between < and >, which mark the start and the end of the specific parts of content respectively.
Thus, HTML is a markup language and HTML5 is the latest standard.
What is HTML?
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language.
Hyper text is a text that has links and references to other content. In general, web pages don't exist individually. They are either preceded by or followed by some text.
Example : Before you landed on Wikipedia home page, you would have opened the browser and searched for the URL in a search engine, or you would have given the URL directly on the address bar of the browser. Starting from there, it's links after links which takes you to the other web pages.
This kind of connecting content via links is generally termed as Hyper text. HTML is a markup language which is used to create hyper text content. And the result of such content is a web page.
A collection of related web pages becomes a website. Process of designing a website involves designing web pages which in turn needs HTML.
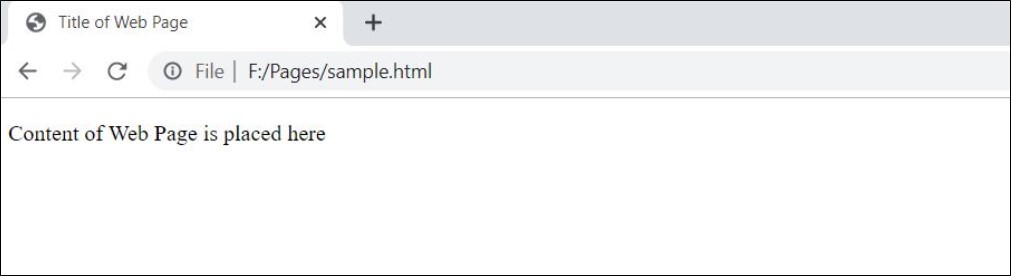
Just have a look at the sample html document:
Content of Web Page is placed here
When you see this document in a browser, the tags are not displayed. But they are used to render the page content as below:
1.3 Importance of HTML5
Modern web pages are coded using HTML5. Still many websites are using HTML 4.01 standard.
HTML Versions:
The first HTML was released in 1991 by Tim Berners Lee. The updated versions are:
HTML 2.0 released in 1995,
HTML 3.2 released in 1997,
HTML 4.01 released in 1999,
XHTML released in 2000.
The latest version is HTML5 released in 2014.
Why HTML 5?
The previous standard version of HTML 5 is HTML 4.01. You need to understand why a new standard of HTML was mandatory for the growing web users.
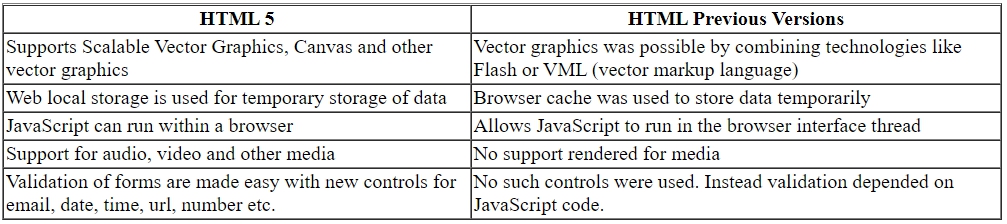
How HTML5 is better than the previous versions?
Advantages for Developers:
1. Error Handling Most browsers have support to parse structurally or syntactically incorrect HTML
2. Improved semantics The code for the layout of the web page is readable and editable with the usage of semantic elements (Explained in Chapter-5: Designing a Web Page)
3. Enhanced support for web application features HTML5 elements provides all functionalities which needed JavaScript or Flash earlier, thus saving time for development. Graphics have become an integral part of HTML5. (Explained in Chapter-7: Graphics and Multimedia in HTML5)
4. Mobile web made easier It makes one design for multiple devices possible. End-users can access web resources at any time in any device. (Explained in Chapter-8: Towards Responsive Web Design)
5. Web local storage to replace cookies Cookies will be expired and cannot store complex data, their capacity is up to 4kb. They slow down the server in transfer of data. But HTML5 provides local storage of web data up to 5MB in the client side permanently until the users themselves erase it. This avoids additional server burden.
Advantages for End-users:
1. Reduces mobile browser crash due to use of new elements of HTML 5
2. Speed loading of content due to responsive feature and also local storage of data