
THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO MICROSOFT EXCEL VBA FOR BEGINNERS AND SENIORS:
A comprehensive guide to master Microsoft Excel VBA programming techniques, data reporting, business analysis and tips and tricks for effective strategies
BY
MIKE CAGE
name2022
All rights reserved
All rights reserved by author. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior permission of the author.
Although every precaution has been taken to verify the accuracy of the information contained herein, the author and publisher assume no responsibility for any errors or omissions. No liability is assumed for damages that may result from the use of information contained within. First Published in Month 2021 BLUEROSE PUBLISHING
Table Of Contents
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Accesing to the Developer TAB
Enabling VBA
capturing a macro
Viewing macro code
Code analysis
Testing a macro
Editing macro code
Referencing relatives
Saving macros
Trusting macros
Summary
Chapter 2- Writing macros
Looking into the Editor
Visual Basic Editor components
Creating a macro
What if I need to fill the cells up to 100?
Insert Form Button
Adding toolbar buttons
Adding form controls
Recognizing hierarchy
Objects
Collections
Properties
Activity
Identifying a Range
Addressing Cells
Summary
Chapter 3-Storing values
Creating variables
Defining data types
Managing strings
Producing arrays
Describing dimensions
Representing objects
Declaring constants
Summary
Chapter 4- Performing operations
Doing arithmetic
Making comparisons
Assessing logic
Joining strings
Understanding precedence
+ =
4096 / = 2048
Summary
Chapter5- Making statements
Choosing a branch
Branching alternatives
Selecting branches
Performing loops
Looping while true
Breaking from loops
Iterating for each
Including with
Summary
Chapter - Executing procedures
Calling subroutines
Modifying scope
Public variable-name As data-type
Private Sub procedure-name ( )
Passing arguments
Adding modules
Fixing values
Debugging code
Handling errors
Summary
Chapter 7-Employing functions
Defining a function
Calling a function
Scoping a function
Passing array arguments
Stating options
Returning errors
Debugging functions
Describing functions
Summary
Chapter 8- Recognizing events
Creating event-handlers
Opening workbook events
Changing workbook events
Closing workbook events
Spotting worksheet changes
Catching worksheet clicks
Allow editing directly in cells.
Listening for keystrokes
Observing the time
Summary
Chapter -Opening dialogs
Acquiring input
Showing messages
Importing files
Saving files
Producing data forms
Executing Ribbon commands
Summary
Chapter 10-Providing UserForm dialogs
Inserting a UserForm
Adding controls
Comparing control types
Adjusting properties
Naming controls
Displaying forms
Handling form events
Managing lists
Summary
Toolbox.
Chapter11-Developing apps
Ignoring modes
Indicating progress
Controlling MultiPages
Tabbing data pages
Showing chart info
Creating Add-ins
Installing Add-ins
Adding Ribbon buttons
Introduction
If you already know how to use Microsoft Excel but therere a few things you cant do, it is time to learn the strongest functionality it has, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Visual Basic for Applications is a programming language incorporated in Microsoft Excel, Access, PowerPoint and even Word, which let you do all things you already know about them and much more. For example, you want that every time you open a specific Microsoft Word file it writes automatically the current date two lines below where you left last time. Or maybe you want a whole spreadsheet of Excel without formulas on it and still applying them as if they were there. How would you do that? All these things and much more are done with Visual Basic for Applications for Microsoft Office.
Look at the example below:
It looks like a program made for analysis, and it does. Guess what program it is? Probably you are thinking it is not any Microsoft Office
program, but let me tell you that it was made with Microsoft Excel, how would you do something like that without programming? Theres no way!
Youll learn much more than that and will be able to create your own programs using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
If you need a very specific program for your business analysis, something for personal use, or even just for having fun, you need Visual Basic for Applications now!
If youre just starting out with Excel, please refer to our companion book Excel 2016 in easy
Accesing to the Developer TAB
Microsoft Excel doesnt show the Developer TAB by default. It only has File, Home, Insert, etc. But theres no one called Developer. To access to this TAB there are different options, but well show the easiest one.
Right click to the Ribbon (any part inside the red box, except the buttons).
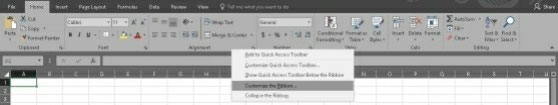
Select Customize the Ribbon
Enable the Developer checkbox and click the OK button.

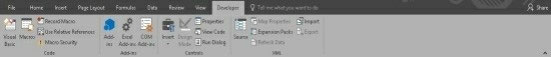
You should see the Developer TAB available now.
Enabling VBA
Before you can get started using the capabilities of VBA, it must first be enabled in your Excel installation:
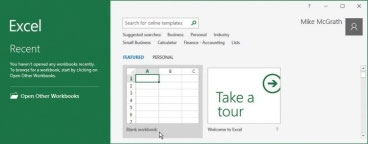
Launch Excel, then choose to open a Blank workbook
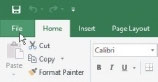
When the workbook opens, choose the File tab on the Excel Ribbon
select the Options item to open the Excel Options dialog box















