Peter Hessler - The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution
Here you can read online Peter Hessler - The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2019, publisher: Penguin Press, genre: Detective and thriller. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution
- Author:
- Publisher:Penguin Press
- Genre:
- Year:2019
- Rating:3 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
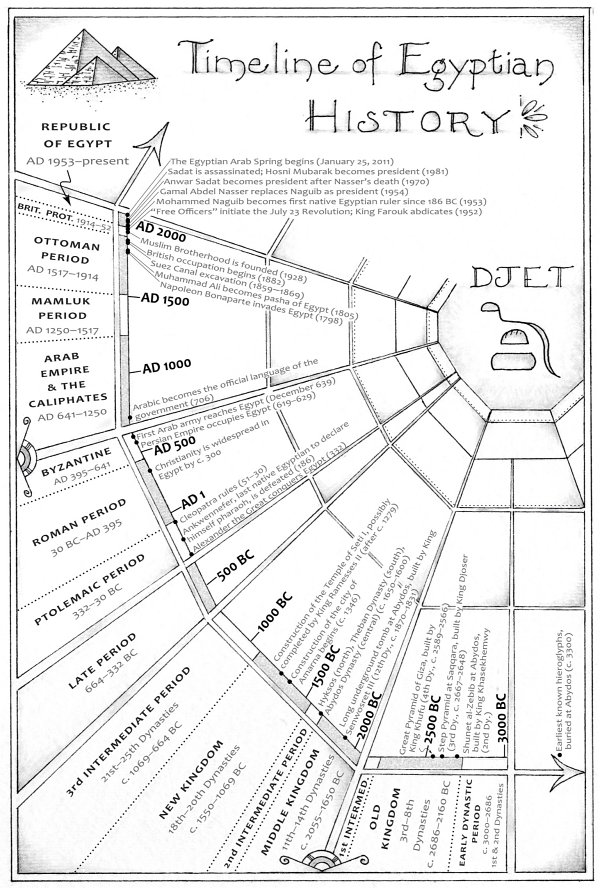
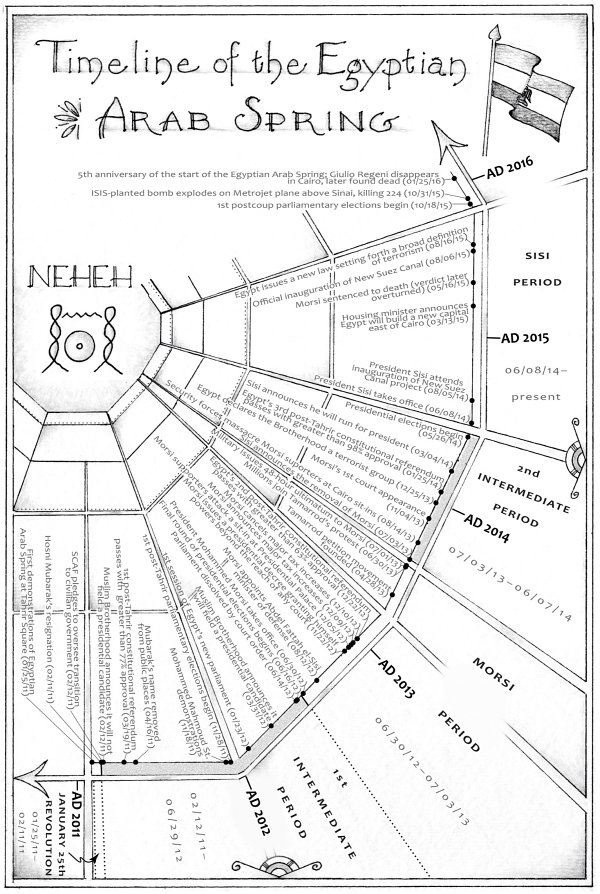
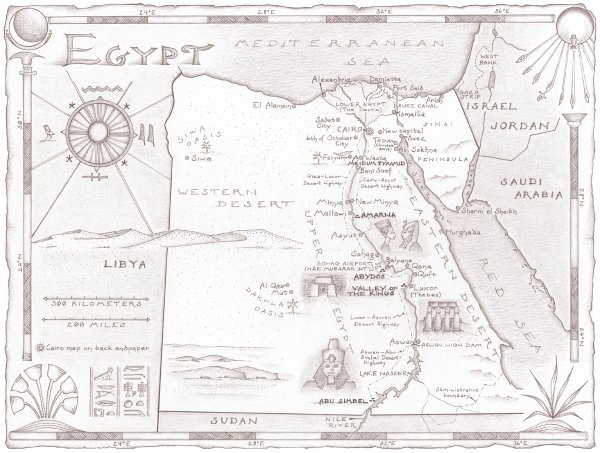
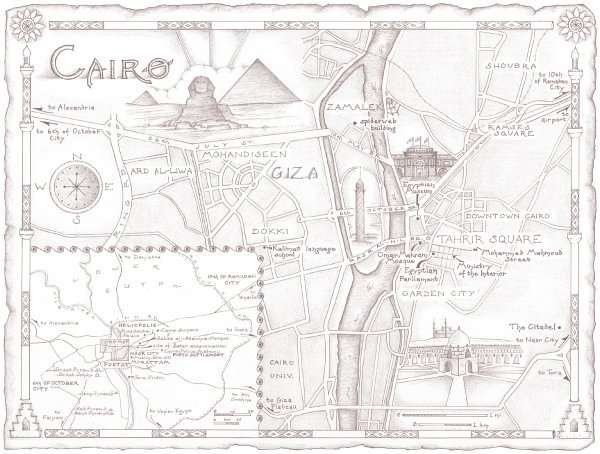
Drawn by a fascination with Egypts rich history and culture, Peter Hessler moved with his wife and twin daughters to Cairo in 2011. He wanted to learn Arabic, explore Cairos neighborhoods, and visit the legendary archaeological digs of Upper Egypt. After his years of covering China forThe New Yorker, friends warned him Egypt would be a much quieter place. But not long before he arrived, the Egyptian Arab Spring had begun, and now the country was in chaos.
In the midst of the revolution, Hessler often traveled to digs at Amarna and Abydos, where locals live beside the tombs of kings and courtiers, a landscape that they call simplyal-Madfunathe Buried. He and his wife set out to master Arabic, striking up a friendship with their instructor, a cynical political sophisticate. They also befriended Peters translator, a gay man struggling to find happiness in Egypts homophobic culture. A different kind of friendship was formed with the neighborhood garbage collector, an illiterate but highly perceptive man named Sayyid, whose access to the trash of Cairo would be its own kind of archaeological excavation. Hessler also met a family of Chinese small-business owners in the lingerie trade; their view of the country proved a bracing counterpoint to the Wests conventional wisdom.
Through the lives of these and other ordinary people in a time of tragedy and heartache, and through connections between contemporary Egypt and its ancient past, Hessler creates an astonishing portrait of a country and its people. What emerges is a book of uncompromising intelligence and humanity--the story of a land in which a weak state has collapsed but its underlying society remains in many ways painfully the same. A worthy successor to works like Rebecca WestsBlack Lamb and Grey Falconand Bruce ChatwinsThe Songlines,The Buriedbids fair to be recognized as one of the great books of our time.
Peter Hessler: author's other books
Who wrote The Buried: An Archaeology of the Egyptian Revolution? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.