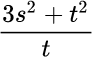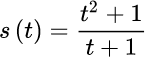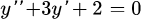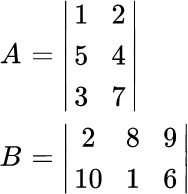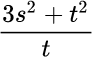Contents
Landmarks
Page List
Our objective in writing FE Mechanical Exams: TwoPractice Exams was to create a book that (1) provides exam-likepractice for the NCEES FE Mechanical exam and (2) familiarizes youwith the NCEES FE Reference Handbook (Handbook), the only reference you are allowedto use during the exam. We believe this book accomplishes both objectives.
After we published FE Civil Exams: 5 Practice Exams, we determined that a similar book was needed to help readers preparingfor the NCEEES FE Mechanical Engineering (ME) examination. For thisnew book, we have created 220 questions covering two full-length practiceexams. The questions have the same difficulty and format as the FEMechanical Engineering exam. The FE Mechanical Engineering exam hasevolved in its format and content, so weve included alternativeitem type (AIT) problems in the book. Each exam has 110 problems.
In order to better simulate the exam experience, the questionsare limited to the 14 knowledge areas and their subknowledge areaslisted by NCEES in its specifications for the exam. The number ofquestions in each knowledge area follows the average weight that NCEEShas given to the knowledge/subknowledge area in its exam specifications.The equations used in the solutions have the same notations as givenin the Handbook. Detailed tables in the introductoryportion of this book will help you learn where to look in the Handbook to find the data and equations youll needduring the exam.
This book represents a great deal of effort from a great manypeople. We would like to acknowledge the team at PPI, including
Editorial: Bilal Baqai, Susan Bedell, Scott Marley, Pooja Thakur,Grace Wong, Michael Wordelman
Art and Cover Design: TomBergstrom
Production: Sean Woznicki, Richard Iriye, Beth Christmas,Kim Wimpsett, Kim Burton-Weisman
Project Management: JeriJump
Content and Product: Anna Howland; Joseph Konczynski,PE; Nicole Evans
Publishing Systems: Sam Webster
Wed also like to thank our technical reviewers and calculationcheckers: S. Sandler, PE; Lise Palmer, PE
We hope thisbook helps you with your exam preparation. Thoughwe made every effort to ensure the technical accuracy of our problems,any mistakes you find are ours alone. Please submit suspected errorsusing PPIs errata reporting website, ppi2pass.com/errata.
MohammadIqbal, D.Sc.,PE, SE, Esq.
Ali A. Iqbal, PE
Use this book to practicesolving problems by using the NCEES FE Reference Handbook as your sole reference. The Handbook is theonly reference you may use during theNCEES FE Mechanical exam.
You should be familiar withthe Handbook before you begin to take the practiceexams in this book. Know whichexam knowledge areas cover which particular mechanical engineeringconcepts and formulas. Then use the review materials of your choiceto study those concepts and formulas.
Attempt to solveeach problem on your own, using only the Handbook as a reference. If you are unsure where to beginon any particular problem, use the tables found in the NCEES Handbook Sections by Problem Number sectionof this book to find the sections in the Handbook that each problem references. If you are still unable to solve theproblem, review the first few lines of the solution, and see if youcan do the rest on your own. If you cannot solve several similar problems,go back and review your study materials, and then retry the problems.Once you feel comfortable solving problems within a given exam, moveon to the next exam in the book.
Give yourself plenty of time to study and test yourself; beginat least three months before the exam. The time required to studywill vary based on how long you have been out of school and whetheryour knowledge is general or specialized. Create a study schedulefor yourself and stick to it. If you give yourself adequate time tostudy, if you study hard, and if you work the problems until you aresure you understand how to navigate the Handbook quickly and efficiently, you will give yourself the best possiblechance to pass the NCEES FE Mechanical exam.
.
For a geothermal project, thetemperature increases from 20C at the surface of the earth to90C at a depth of 2 km below the ground. Assuming a linear temperaturegradient, the underground temperature at 3800 m below the ground surfaceis most nearly
(A)
113C
(B)
133C
.
A particlemoves along a lineso that its position at time t is
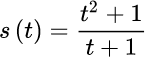
The velocity at t =2.5 s is most nearly
(A)
0.78
(B)
0.84
.
A differential equationis given.
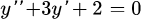
Its general solution is
(A)
y = C1e2x + C2ex
(B)
y = C1e2x +C2ex
(C)
y = C1ei2x + C2eix
(D)
y = ex (3 cos x + 2 sin x)
.
Two matrices are given.
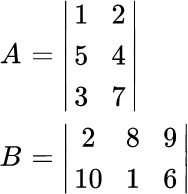
Matrices A and B aremultiplied to obtain a product matrix C. Whichstatement about the matrix multiplication is true?
(A)
The product matrix C will havetwo rows and three columns.
(B)
The productmatrix C will havethree rows and two columns.
(C)
The product matrix C will have three rowsand three columns.
(D)
The multiplicationis not possible since the matrices A and B do not have the same numberof rows and columns.
.
Consider the equation x7 100 = 0. The zerothroot equals 2. Using Newtons method of root extraction, whatis most nearly the value of x after the seconditeration?
(A)
0.1429
(B)
1.9307
.
Consider the followingprogramsegment.
| 10 | INPUT A |
| 20 | B= 1 |
| 30 | ITER=1 |
| 40 | ITER=ITER + 1 |
| 50 | C=0.5*(B+A/B) |
| 60 | B=C |
| 70 | GOTO 40 |
| 80 | END |
What is the programing error in thealgorithm?
(A)
division by zero
(B)
endless loop
(C)
missing print statement
(D)
both endless loop and missing print statement
.
What is the differential z/s for z = xy where x = s2 + t2 and y = s/t?
(A)