Mobile communications industry has been developing at an amazing speed, and at present it has become one of the important pillar industries in the global economic development. There is no doubt that mobile communications technology is changing peoples life and work, and will continue to have an important impact on social development [].
Therefore, 5G is facing both opportunities and challenges. For users, 5Gs vision is information comes as you wish, and everything is in touch []. With the popularity of wearable devices, the types and number of mobile terminals will experience explosive growth. Predictably, in the future, demand for virtual reality and augmented reality experience, demand for cloudization of massive office data, wireless control of industrial manufacturing or production processes, remote medical surgery, automation in a smart grid, transportation safety and other aspects, not only require 5G network data transmission rate to reach a very high level, but also require real-time experience with almost zero latency. In addition, cost reduction and energy saving should also be considered.
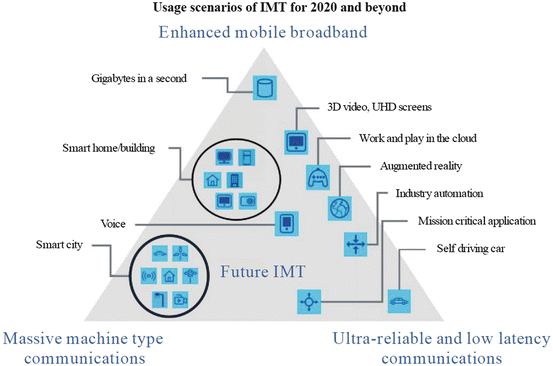
Fig. 1.1
Usage scenarios of IMT for 2020 and beyond
1.1.1 5G Application Types
The birth of 5G largely benefited from the large scale growth of the mobile Internet and the Internet of Things (IoT), and the application of 5G also mainly lies in the development of these two networks []. In recent years, mobile Internet, as the carrier of main businesses of mobile data communications, has greatly promoted the development of various fields of information service. Various service providers made full use of the advantages of their resources and services and developed numerous refreshing applications, reaching an effect of flowers blooming together in market. By 2020, users will see more convenient functions realized via mobile Internet, and demand for virtual reality and augmented reality in game experience will be met. With the further development of mobile Internet, information transmission rate will grow by thousands of times.
IoT is an ideal example of the full application of new generation technology. In all walks of life, human beings are able to manage production and live in a more precise and dynamic manner via IoT, achieving an intelligent state and improving resource utilization and productivity level [].
1.1.2 5G Application Scenarios and Requirements Indicators
Application scenarios of 5G are related to every aspect in peoples daily life, work, entertainment and transportation, and wireless communications will show different characteristics in all kinds of different scenarios. For example, the crowed or dense mobile devices areas such as residential areas, stadiums and marketplaces, wireless communications will have the characteristics of high traffic volume density and high number of connections, while on transport tools such as subway and high-speed railways, the high mobility feature of wireless communications will be prominent. At present, the Fourth Generation mobile communications system (4G) is not able to satisfy the requirements of some special scenarios featuring high traffic volume density, high number of connections and high mobility [].
In crowded scenarios such as stadiums which need ultrahigh traffic volume density and ultrahigh connection density, we need the wireless communications transmission rate as high as that of the optical fiber so that it can carry the businesses like photo transmission, video transmission, live broadcast and other services. In high-speed mobility scenarios, e.g., High-Speed Rail (HSR), the traffic volume density and connection are relatively lower than those of stadiums. Since HSRs speed is usually above 200 km/h, it has high requirements for the wireless communication systems to support high-speed mobility.
Although its very convenient for us to access the Internet now, half of our world is still beyond the coverage of Internet after several decades when mobile terminals came into being. With the development and change of Internet, the denotation of Internet is expanded accordingly and more and more devices are connected with each other. Cisco System forecasts that by the year of 2019, the whole world will have 11.5 billion devices to be connected [], including some hard-to-connect devices which are under water or beyond the coverage of satellite, so it becomes more and more important to meet the requirements for wide coverage in future.
It is predicted that in a long period in the future, mobile data traffic will continue to show explosive growth []: from 2010 to 2020, global mobile data traffic growth will increase by more than 200 times while from 2010 to 2030, more than 20,000 times. Meanwhile, the growth of Chinese mobile data traffic is higher than the global average level. It is predicted that from 2010 to 2020, it will grow by more than 300 times, while from 2010 to 2030, more than 40,000 times.
Therefore, based on the requirements above, 5Gs overall goals are: much faster, more efficient, and more intelligent. Specific 5G performance requirements are shown in Table ].
Table 1.1
5G performance requirements
| Value |
|---|
Peak data rate | >10 Gbps |
User experienced data rate | >0. 1 Gbps |
Connection density | Million connections/square kilometers |
Service density | 10 Gbps/square kilometers |
End-to-end latency | Millisecond order |
To satisfy users experience in multiple dimensions, combination of different technologies is needed to reach the 5G performance requirements in the above table. For example, ultra-dense wireless communications technology can make contributions to improving performance indicators of user experienced data rate, connection density and service density through increasing the base station deployment density. Massive antenna technology can effectively improve the spectrum utilization efficiency through increasing antennas number and it has an important significance in improving peak data rate, user experienced data rate, connection density and service density. Millimeter wave communications technology can increase usable spectrum in a large scale, which is good for improving performance indicators of peak data rate, user experienced data rate and service density.