Explaining 6G Spectrum THz, mmWave, Sub 6, and Low-Band
Xianzhong Xie1 School of Optoelectronic Engineering Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing, P.R. China
2 Mikatel International Inc., Quebec, Canada
3 cole de Technologie Suprieure, Universit du Quebec, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Abstract
This chapter aims to provide readers with a general vision of 6G. Firstly, we give a simple overview of various aspects related to 6G, including inevitability of 6G research, international organizations for standardization, and also 6G research progress of some countries/regions. Then, 6G spectrum compositions are discussed in detail with emphasis on SUB-6, mmWAVE, and Terahertz (THz).
Keywords: 6G, Frequency spectrum.
THE SIXTH GENERATION MOBILE COMMUNICATION (6G)
The development of mobile/wireless communication has gone through the process of 1G/2G/3G/4G, and it has entered a critical stage of 5G commercial development. From the historical perspective of industrial development, the mobile communication system has been updated every ten years. The increasing demand for user communication and the innovation of communication technology is the driving force for the development of mobile communication []. Researchers now start to focus on the sixth-generation mobile communication (6G) networks. Some countries and organizations have already initiated the exploration of 6G technology with the launch of 5G commercial deployment in major countries around the world.
The Inevitability Of 6g Research
The 10-year Cycled Rule
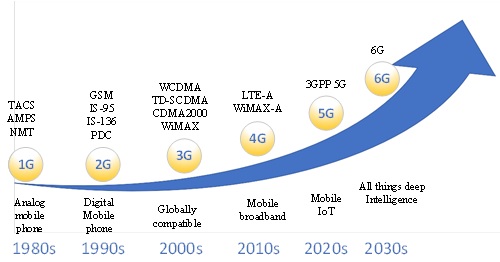
Since the introduction of the first generation (1G) mobile communication system in 1982, a new generation of wireless mobile communication systems has been updated approximately every 10 years, as shown in Fig. (]. In other words, when the previous generation enters the commercial period, the next generation begins conceptual and technical research. 5G research started 10 years ago, and now 6G research is in line with the development law of mobile communication systems. It may take about ten years for 6G to arrive, but research on 6G cannot be delayed. Mobile communications will stride towards the 6G era.
Fig. (1)) The evolution of mobile communication systems.
Catfish Effect
The catfish effect means that it also activates the survival ability of the small fish when the catfish disturbs the living environment of the small fish. It is to adopt a means or measures to stimulate some enterprises to become active and invest in the market to actively participate in the competition, which will activate enterprises in the same industry in the market. 5G is different from previous generations of mobile communication systems mainly aimed at IoT/vertical industry application scenarios. Many vertical industry members will definitely participate in the 5G ecosystem with the large-scale deployment of 5G networks. The in-depth participation of emerging companies (especially internet companies born with innovative thinking) in the future will have a huge impact on the traditional communications industry and even a revolutionary impact compared with the status quo dominated by traditional operators, which is called catfish effect.
The Explosive Potential of IoT Business Models
IoT is the inevitability of the internet from top to bottom in the industry. It is an extension from the inside out, with the cloud platform as the center. Just as the emergence of smartphones stimulated 3G applications and triggered the demand for large-scale deployment of 4G, it is believed that certain IoT business models will also stimulate the 5G industry to burst at a certain point in the 5G era, which will stimulate the future needs of 6G networks. To accommodate the stringent requirements of their prospective applications, we need to have enough imagination. We must prepare in advance for the possible future network and lay a good technical foundation []. Based on the above analysis, we can draw the conclusion that now is the right time to start the research on the next generation wireless mobile communication system.
The 5G Performance Would Limit New IoT Applications
Despite the strong belief that 5G will support the basic MTC and URLLC related IoT applications, it is arguable whether the capabilities of 5G systems will succeed in keeping pace with the rapid proliferation of ultimately new IoT applications []. The unprecedented requirements imposed by these services will push the performance of 5G systems to its limits within 10 years of its launch. Moreover, these services have urged that 6G should be capable of unleashing the full potentials of abundant autonomous services comprising past as well as emerging trends.
International Organization for Standardization
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
According to the ITU work plan, the RA-19 meeting in 2019 will not establish a new IMT technical research resolution. It indicates that the research cycle from 2019 to 2023 is still mainly for 5G and B5G technology research, but the 6G vision and technology trend research will be carried out from 2020 to 2023. The mainstream companies in the industry generally believe that it is more appropriate to establish the next generation IMT technology research and naming resolution at the RA-23 meeting in 2023. ITU-T SG13 (International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Study Group 13) established the ITU-T Focus Group Technologies for Network 2030 (FG NET-2030) at its meeting in July 2018. The FG NET-2030 intends to define the requirements of networks of the year 2030 and beyond []. 6G research work was carried out at ITU-R WP5D (the 34th International Telecommunication Union Radio Communication Sector 5D Working Group meeting) held in February 2020, which includes the formulation of a 6G research timetable, future technology trend research reports, and the writing of future technology vision proposals.
The Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
3GPP is the main promoter and integrator of communication system technical specifications managing the standardization work such as the introduction of communication system requirements, system architecture design, security, and network management. 3GPP has completed the development of the first version of the 5G international standard Release 15 (R15) focusing on supporting enhanced mobile broadband scenarios and ultra-high reliability and low-latency scenarios in June 2018. The development of a complete 5G international standard Release 16 (R16) will be completed in Autumn 2020, which will fully support the three application scenarios determined by the ITU. Also, 3GPP is promoting 6G research and standardization activities. 3GPP Release 17 (R17) has started to investigate advanced features that would shape the evolution toward 6G [], and substantive 6G international standardization is expected to start in 2025.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
To better summarize and sort out the related technologies of next-generation networks, IEEE launched the IEEE 5G Initiative in December 2016 and renamed it IEEE Future Networks in August 2018 to enable 5G and the future network. IEEE is also developing corresponding 5G standards, which are expected to be submitted to ITU for approval in 2020. At present, IEEE has carried out some 6Gtechnical seminars. The 6G wireless summit will be held by IEEE in March every year, and the first 6G wireless summit was initiated by IEEE in the Netherlands on March 25, 2019. The industry and academia were invited to publish the latest insights on 6G. The theoretical and practical challenges that need to be addressed to realize the 6G vision are discussed. The global 6G research vision, requirements and potential approaches were published in 6G White Papers at the end of June 2020.