Springer Science+Business Media New York 2016
Isabelle Mus-Veteau (ed.) Heterologous Expression of Membrane Proteins Methods in Molecular Biology 1432 10.1007/978-1-4939-3637-3_1
1. Cell-Free Production of Membrane Proteins in Escherichia coli Lysates for Functional and Structural Studies
Ralf-Bernhardt Rues 1, Erik Henrich 1, Coilin Boland 2, Martin Caffrey 2 and Frank Bernhard 1
(1)
Centre for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance, Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Goethe-University of Frankfurt/Main, Max-von-Laue-Str. 9, 60438 Frankfurt/Main, Germany
(2)
Membrane Structural and Functional Biology Group, School of Medicine and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Abstract
The complexity of membrane protein synthesis is largely reduced in cell-free systems and it results into high success rates of target expression. Protocols for the preparation of bacterial lysates have been optimized in order to ensure reliable efficiencies in membrane protein production that are even sufficient for structural applications. The open accessibility of the semisynthetic cell-free expression reactions allows to adjust membrane protein solubilization conditions according to the optimal folding requirements of individual targets. Two basic strategies will be exemplified. The post-translational solubilization of membrane proteins in detergent micelles is most straightforward for crystallization approaches. The co-translational integration of membrane proteins into preformed nanodiscs will enable their functional characterization in a variety of natural lipid environments.
Key words
G-protein-coupled receptors Nanodiscs Synthetic biology Membranes Membrane protein crystallization Lipid screening
Introduction
Cell-free (CF) expression in lysates of certain Escherichia coli strains has become a standard tool for the preparative-scale production of a wide variety of membrane proteins [). In the detergent-based D-CF or membrane-based L-CF modes, the membrane proteins will be co-translationally solubilized by supplied detergents or membranes, respectively. The selected expression modes can have strong impact on efficiencies, costs, and final sample quality and should be carefully and extensively screened before preparative-scale production is approached.
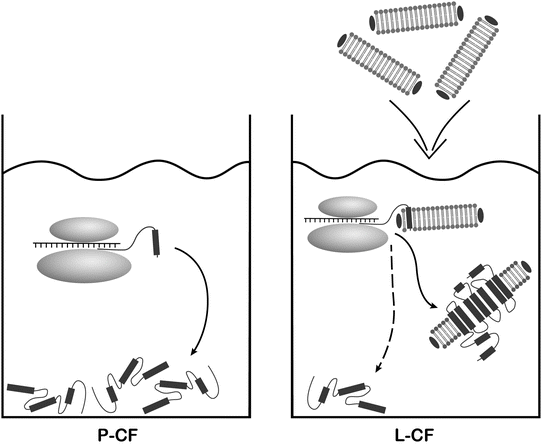
Fig. 1
CF expression modes exemplified in the protocols. DgkA is synthesized in the P-CF mode as initial precipitate and post-translationally solubilized in detergent for its subsequent crystallization. The ETB receptor is synthesized in the L-CF mode and co-translationally inserted into supplied NDs
The structural as well as the functional characterization of membrane proteins synthesized in all three CF modes has already been accomplished []. The development of customized reaction protocols and screening of additives are mostly indispensable for obtaining suitable and efficient CF production protocols. However, based on the currently accumulated knowledge, some preliminary guidelines start to appear that could help to focus on the screening of the most promising reaction compounds and expression conditions. In this chapter, we present most recent optimizations in protocol and reaction design that streamline membrane protein expression projects and reduce costs as well as workload. We further highlight new technical details that could be valuable upon establishing CF expression technologies.
CF expression in E. coli lysates is excellent for prokaryotic as well as for eukaryotic membrane proteins. We describe applications of CF-synthesized membrane protein samples from two core expression modes in the most efficient continuous-exchange cell-free (CECF) configuration []. This production strategy is in particular suitable for critical membrane proteins that are sensitive against contact with detergents. Both described protocols might serve as guidelines for similar work with related proteins.
Materials
All stock solutions should be prepared with ultrapure water and stored at 20 C if not otherwise stated.
2.1 General Materials
Fermenter for bacterial cultures, e.g., 510 L volume.
French Press.
Photometer.
Standard centrifuges and set of rotors.
Thermo shaker for incubation.
Chromatographic system (e.g., kta purifier, GE Healthcare).
Q-Sepharose column (GE Healthcare).
Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) material or column (Cube Biotech).
Sonicator.
Centriprep filter devices, 10 kDa MWCO (Millipore).
Mini-extruder (Avanti Polar Lipids).
2.2 E. coli Lysate Preparation
E. coli strains A19, BL21, or C43.
2 TPG medium: 10 g/L yeast extract, 16 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L NaCl, 100 mM glucose, 22 mM KH2PO4, 40 mM K2HPO4.
Antifoam (Sigma).
40 LY-A/B buffer: 400 mM Tris-acetate pH 8.2, 560 mM Mg(OAc)2, 2.4 M KCl.
1 LY-A buffer (washing buffer) diluted from the 40 LY-A/B stock, supplemented with 6 mM -mercaptoethanol.
1 LY-B buffer (lysis buffer) diluted from the 40 LY-A/B stock, supplemented with 1 mM DTT and 1 mM phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride (PMSF).
40 LY-C buffer: 400 mM Tris-acetate pH 8.2, 560 mM Mg(OAc)2, 2.4 M KOAc.
1 LY-C + DTT buffer (dialysis buffer): Diluted from the 40 LY-C stock, supplemented with 0.5 mM DTT.
5 M NaCl.
2.3 T7-RNA Polymerase Preparation
E. coli BL21 (DE3) Star pAR1219 [].
LB medium: 10 g/L peptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 5 g/L NaCl.
1 M isopropyl--D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG).
30% (w/v) streptomycin sulfate in H2O.
Buffer-T7RNAP-A (equilibration buffer): 30 mM TrisHCl pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM -mercaptoethanol, 5% glycerol.
Buffer-T7RNAP-B (dialysis buffer): 10 mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4 pH 8.0, 10 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 5% glycerol.
Resuspension buffer: 30 mM TrisHCl, pH 8.0, 10 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, and 10 mM -mercaptoethanol.
2.4 DNA Template Preparation
Specific primers designed for the target DNA.
Vent polymerase (New England Biolabs).
PCR purification kit (Qiagen).
Restriction enzymes and ligase for template preparation.
Plasmid DNA purification kit (Machery-Nagel/Qiagen).
Agarose (Rotigarose, Roth).
2.5 CECF Expression Reactions
MD100 dialysis cartridges as reaction mix containers (Scienova).
96-Deep-well microplates as feeding mix containers (Ritter riplate PP, 2 mL).
Dialysis tubes, 1214 kDa MWCO (Spectrum).
Slide-A-Lyzer devices, 10 kDa MWCO (Thermo Scientific).
Optional: High-yield E. coli lysates including T7RNAP (Cube Biotech) as controls.
Stock solutions required for CECF reactions are listed in Table .
Table 1
Reagent example for CECF expression reaction with 1 mL RM and 14 mL FM