Ian N. Scobie - Diabetes Mellitus
Here you can read online Ian N. Scobie - Diabetes Mellitus full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2012, publisher: Health Press Limited, genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Diabetes Mellitus
- Author:
- Publisher:Health Press Limited
- Genre:
- Year:2012
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Diabetes Mellitus: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Diabetes Mellitus" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
This fully revised fourth edition of Fast Facts: Diabetes Mellitus provides a practical hands-on approach to the causes, clinical manifestations and treatment strategies for type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Mellitus — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Diabetes Mellitus" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:


Ian N Scobie
Consultant Endocrinologist
Medway Maritime Hospital
Gillingham, Kent, and
Honorary Senior Lecturer
Kings College London School of Medicine
London, UK

Katherine Samaras
Associate Professor
The University of New South Wales, and
Senior Staff Specialist, St Vincents Hospital, and
Head, Diabetes and Obesity Clinical Group
Garvan Institute of Medical Research
Darlinghurst, New South Wales, Australia
Declaration of Independence
This book is as balanced and as practical as we can make it.
Ideas for improvement are always welcome: feedback@fastfacts.com

Fast Facts: Diabetes MellitusFirst published 1996; second edition 2001; third edition 2009; reprinted 2010Fourth edition June 2012
Text 2012 Ian N Scobie, Katherine Samaras 2012 in this edition Health Press Limited
Health Press Limited, Elizabeth House, Queen Street, Abingdon, Oxford OX14 3LN, UK Tel: +44 (0)1235 523233 Fax: +44 (0)1235 523238
Book orders can be placed by telephone or via the website. For regional distributors or to order via the website, please go to: fastfacts.com
For telephone orders, please call +44 (0)1752 202301 (UK, Europe and AsiaPacific), 1 800 247 6553 (USA, toll free) or +1 419 281 1802 (Americas).
Fast Facts is a trademark of Health Press Limited.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the express permission of the publisher.
The rights of Ian N Scobie and Katherine Samaras to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted in accordance with the Copyright, Designs & Patents Act 1988 Sections 77 and 78.
The publisher and the authors have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this book, but cannot accept responsibility for any errors or omissions.
For all drugs, please consult the product labeling approved in your country for prescribing information.
Registered names, trademarks, etc. used in this book, even when not marked as such, are not to be considered unprotected by law.
A CIP record for this title is available from the British Library.
ISBN 978-1-908541-23-9
Scobie IN (Ian)Fast Facts: Diabetes Mellitus/Ian N Scobie, Katherine Samaras
Medical illustrations by Dee McLean, London, UK.
Typesetting and page layout by Zed, Oxford, UK.
Converted to eBook by EasyEPUB
National data demonstrate an alarming increase in the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the developed world. The 2011 National Diabetes Fact Sheet in the USA tells us that the prevalence of diabetes is 8.3% in the US population, varying from 7.1% in non-Hispanic whites to 12.6% in non-Hispanic blacks (with even higher rates in Mexican Americans). This equates to 18.8 million people with diabetes (and 7.0 million with undiagnosed diabetes). Data from the UK Quality and Outcomes Framework reveal that 4.26% of the UK population has diabetes, equating to 2.8 million people. The number of people with diabetes worldwide projected for 2025 is more than 300 million.
With increasing urbanization in India there has been an explosive increase in the prevalence of diabetes, which has now reached 8.0%, with 50 million people with type 2 diabetes. In China, diabetes has become a major public health problem, with an estimated prevalence of 9.7%. Although the incidence of new cases of type 1 diabetes is increasing in many countries, the increase in new cases of type 2 diabetes is of near-epidemic proportions. Societal factors seem to be the likely culprits behind this massive increase in diabetes prevalence in both developed and developing countries. Such factors include the adoption of a westernized diet and lifestyle and a decline in physical activity leading to ever-rising rates of obesity. In the developing world, population movements from rural agricultural areas to urban areas are associated with the acquisition of type 2 diabetes.
Cardiovascular disease remains a significant cause of death in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Preventive strategies are needed to minimize cardiovascular risk and improve outcome. However, these should not be at the expense of the pursuit of good blood glucose control, as this closely correlates with the development of those specific microvascular complications of diabetes that so clearly define this ubiquitous condition.
In parallel with the increase in diabetes prevalence, diabetes research continues to flourish; from basic science through to randomized prospective clinical trials, there is a great endeavor to determine the exact pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and other forms of diabetes and their complications, and to understand how best to prevent and treat them. One particular feature has been the recent advent of new pharmaceutical products to treat type 2 diabetes, albeit associated with problems along the way. Research continues into the development of a possible vaccine to prevent type 1 diabetes.
The aim of this fourth edition of Fast Facts: Diabetes Mellitus is to provide readers with an up-to-date picture of our understanding of diabetes mellitus and its various causes, its clinical manifestations and the treatment strategies that can be used to reduce the burden of its metabolic consequences.
The prevalence of diabetes around the world is increasing rapidly (see the .
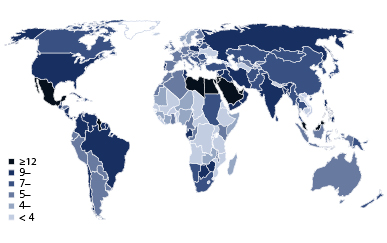
Figure 1.1 Comparative prevalence of diabetes: the scale shows the percentage of the adult population affected by diabetes. IDF Diabetes Atlas, fifth edition. International Diabetes Federation, 2011.
It is clear some nations have substantially higher rates of diabetes. Data from 2011 in the Diabetes Atlas of the IDF show the highest national prevalence of diabetes in adults from Kiribati, the Marshall islands, Nauru, Lebanon and other Middle Eastern nations ().
| Country | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| Kiribati | 25.7 |
| Marshall islands | 22.2 |
| Kuwait | 21.1 |
| Nauru | 20.7 |
| Lebanon | 20.2 |
| Qatar | 20.2 |
| Saudi Arabia | 20.0 |
| Bahrain | 19.9 |
| Tuvalu | 19.5 |
| United Arab Emirates | 19.2 |
| Data from IDF Diabetes Atlas, fifth edition. International Diabetes Federation, 2011. |
Diabetes caused 4.6 million deaths globally in 2011 approximately 6% of the total world mortality. Even more people have died from cardiovascular disease, the risk of which is increased by diabetes-related comorbidities such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension and renal disease. Data for deaths attributable to diabetes according to world regions are shown in .
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Diabetes Mellitus»
Look at similar books to Diabetes Mellitus. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Diabetes Mellitus and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.