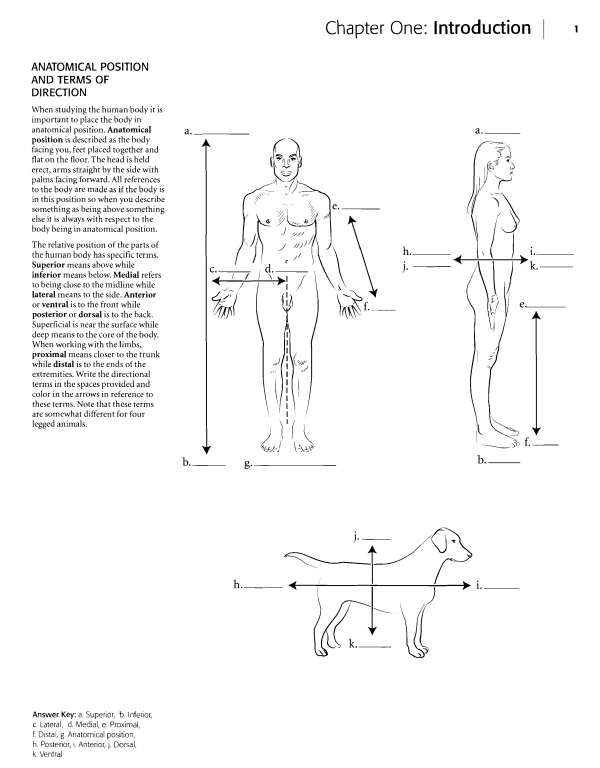
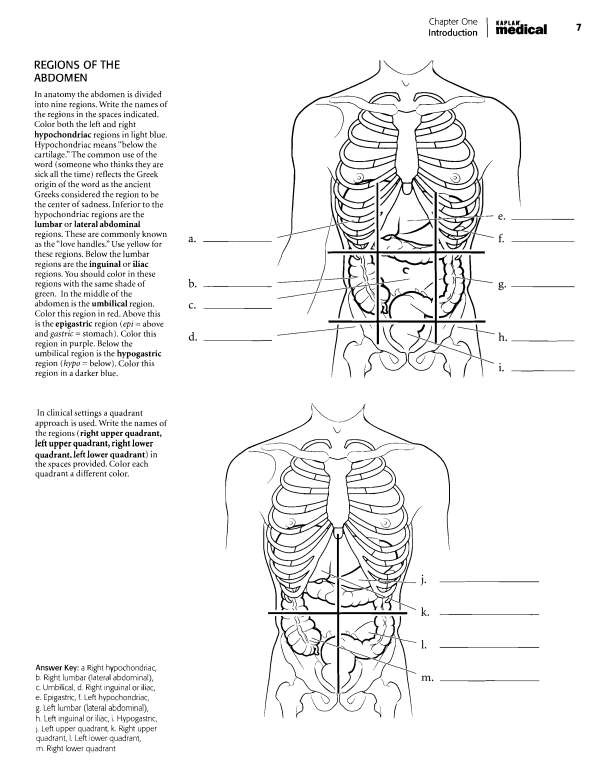
chapter One Introduction KAPLAN... ,-, medical ^' BODY REGIONS (POSTERIOR) For the posterior view of the body fill in the terms and color the regions of the body. The anatomical names are given first with the common names in parentheses. cephalic (head) nuchal (neck) scapular (shoulder blade) vertebral (backbone) lumbar (love handles) brachial (arm) olecranon (elbow) antebrachial (forearm) gluteal (buttocks) femoral (thigh) popliteal (back of knee) sural (calf) calcaneal (heel) Answer Key: a.Cephalic (head), b. Nuchal (neck), c Scapular (shoulder blade), d. Brachial (arm), e.
Vertebral (backbone), f. Olecranon (elbow), g. Lumbar (love handles), h. Antebrachial (forearm), i. Gluteal (buttocks), j. Femoral (thigh), k.
Popliteal (back of knee), I. Sural (calf), m. Calcaneal (heel) 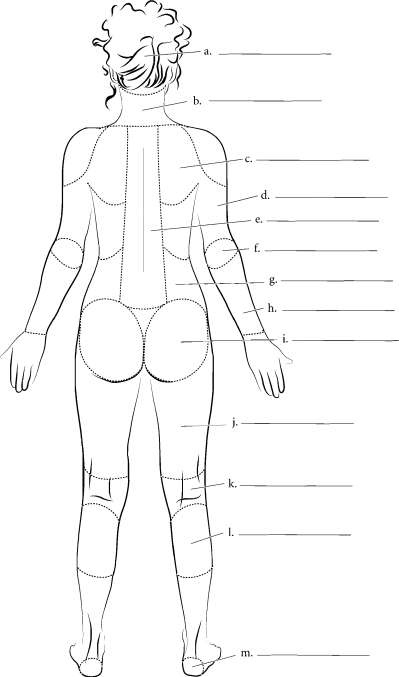 Chapter One Introduction medical '^ BODY CAVITIES The organs of the body are frequently found in body cavities. The body is divided into two main cavities, the dorsal body cavity and the ventral body cavity. The dorsal body cavity consists of the cranial cavity, vifhich houses the brain and the spinal canal, vi^hich surrounds the spinal cord. The ventral body cavity contains the upper thoracic cavity, vi^hich is subdivided into the pleural cavities, housing the lungs, and the mediastinum.
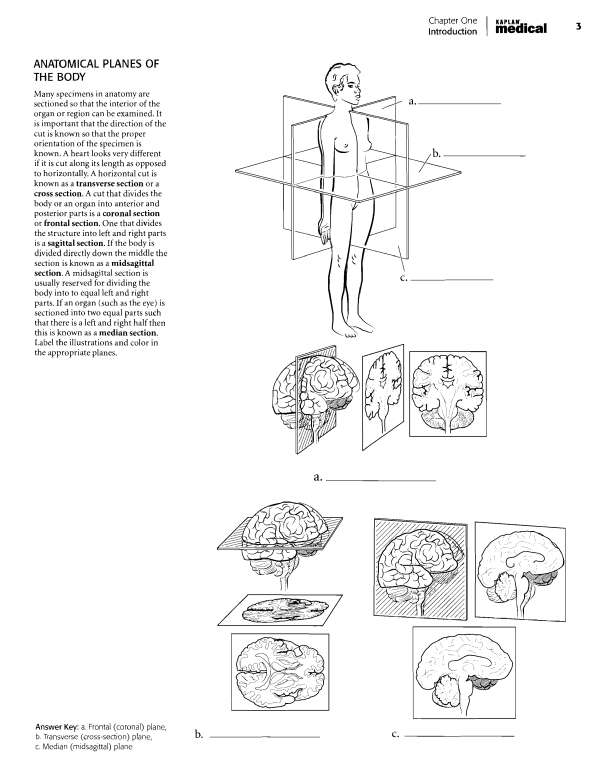
Chapter One Introduction medical '^ BODY CAVITIES The organs of the body are frequently found in body cavities. The body is divided into two main cavities, the dorsal body cavity and the ventral body cavity. The dorsal body cavity consists of the cranial cavity, vifhich houses the brain and the spinal canal, vi^hich surrounds the spinal cord. The ventral body cavity contains the upper thoracic cavity, vi^hich is subdivided into the pleural cavities, housing the lungs, and the mediastinum.
The mediastinum contains the heart in the pericardial cavity, the major vessels near the heart, nerves, and the esophagus. Below the thoracic cavity is the abdominopelvic cavity, which contains the upper abdominal cavity, housing the digestive organs, and the inferior pelvic cavity, which holds the uterus and rectum in females or just the rectum in males. Label the specific and major cavities of the body and color them with different colors. 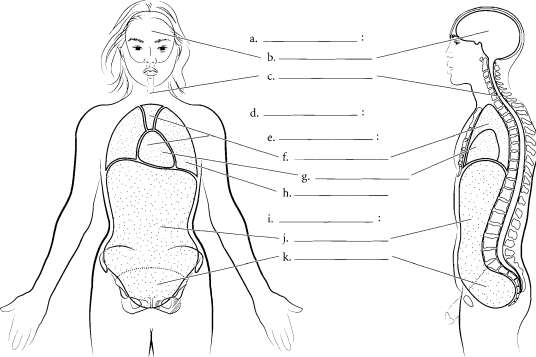 Answer Key: a. Dorsal body cavity, b. Cranial cavity, c.
Answer Key: a. Dorsal body cavity, b. Cranial cavity, c.
Spinal canal, d. Ventral body cavity, e. Thoracic cavity, f. Mediastinum, g. Pericardial cavity, h. Pleural cavity, I.
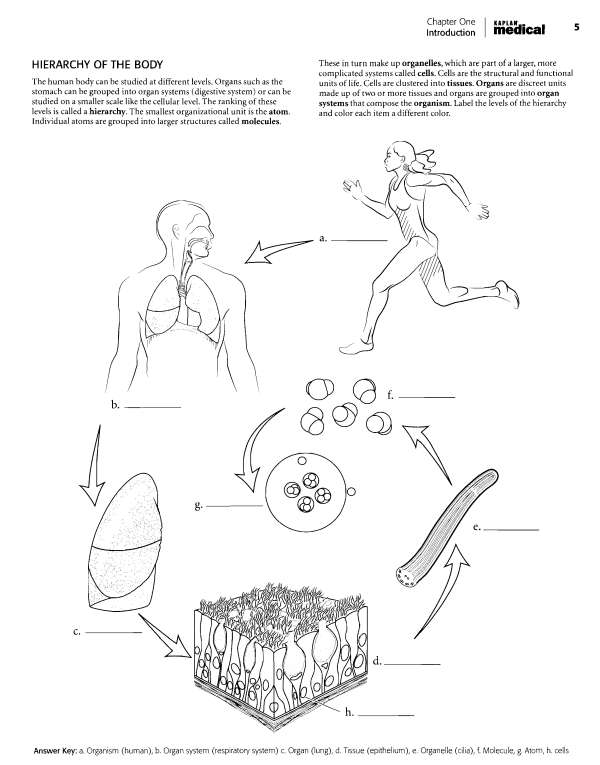
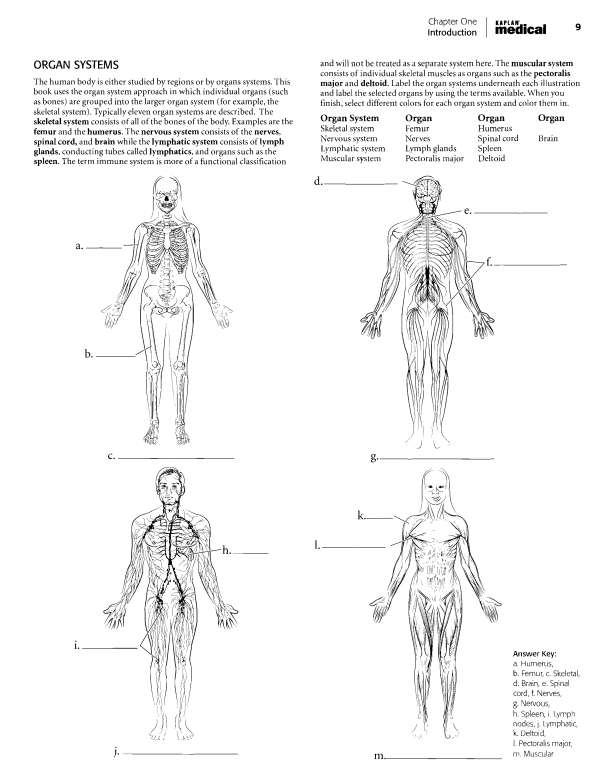
Abdominopelvic cavity, j. Abdominal cavity, k. Pelvic cavity Chapter Two: Cells, Tissues, and Integument | 21 OVERVIEW OF CELL AND CELL MEMBRANE Cells consist of an enclosing plasma membrane, an inner cytoplasm with numerous organelles, and other cellular structures. The fluid portion of the cell is called the cytosol. Color the cytosol in last after you color the rest of the cellular structures. One of the major structures in the cell is the nucleus.
It is the genetic center of the cell and consists of fluid karyoplasm, chromatin (containing DNA), and the nucleolus. Color these features and label them on the illustration. The cytoskeleton consists of microtubules, intermediate filaments and microfilaments. It is involved in maintaining cell shape, fixing organelles, and directing some cellular activity. Label the organelles of the cell and use a different color for each one. The mitochondria are the energy-producing structures of the cell while the Golgi apparatus assembles complex biomolecules and transports them out of the cell.
Proteins are made in the cell by ribosomes. If the ribosomes are found by themselves in the cytoplasm, they are called free ribosomes. If they are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, they are called bound ribosomes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum manufactures lipids and helps in breaking down toxic materials in the cell. Other structures in the cell are vesicles (sacs that hold liquids). Phagocytic vesicles ingest material into the cell.
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes while peroxisomes degrade hydrogen peroxide in the cell. After you label and color the organelles make sure to go back and shade in the cytosol. Centrioles are microtubules grouped together and are involved in cell division. 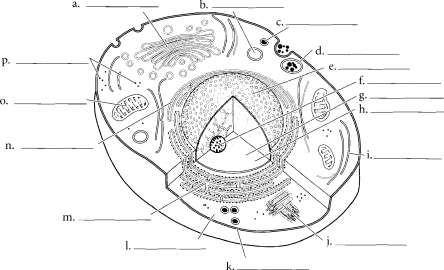 The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bUayer. Color the phosphate molecules on the outside and inside of the membrane one color and the lipid layer another color. Cholesterol molecules occur in the membrane and, depending on their concentration, can make the membrane stiff or more fluid.
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bUayer. Color the phosphate molecules on the outside and inside of the membrane one color and the lipid layer another color. Cholesterol molecules occur in the membrane and, depending on their concentration, can make the membrane stiff or more fluid.
Proteins that are found on the outside of the membrane are called peripheral proteins while proteins that pass through the membrane are called integral proteins. Frequently these make up gates or channels that allow material to pass through the membrane. Attached to proteins on the cell membrane are carbohydrate chains. These provide cellular identity. Label and color the cell membrane structures. 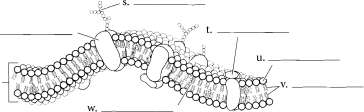 Answer Key: a.
Answer Key: a.
Coigi apparatus, b. Lysosome, c. Peroxisome, d. Phagocytic vesicle, e. Nucleus, f. Nucleolus, g.
Chromatin, h. Karyoplasm, i. Cytoskeletori, J. Ceritrioles, k. Plasma membrarie, I. Cytoplasm, m.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum, n. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum, o. Mitochondrion, p. Free ribosomes, q. Phospholipid bilayer, r. Integral protein, s.
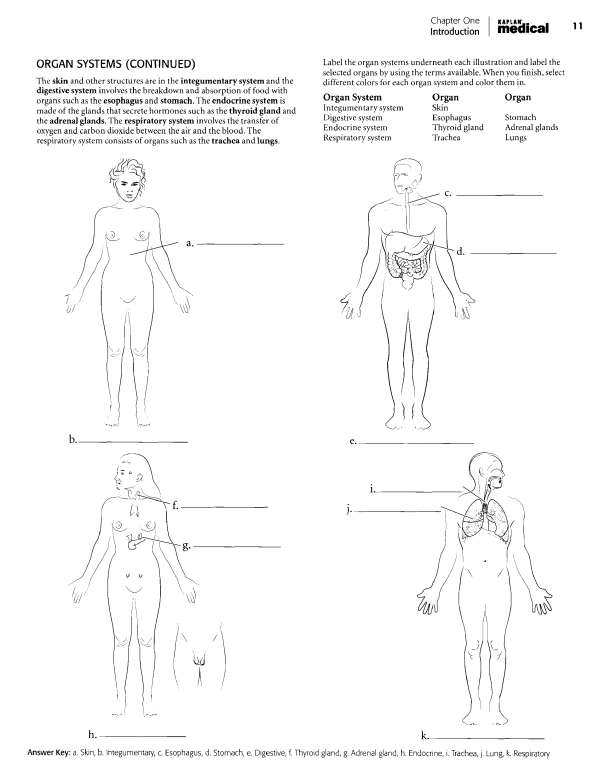
Carbohydrate chain, t. Peripheral protein, u. Phosphate molecule, v. Lipid layer, w. Cholesterol molecule Chapter Two Cells, Tissues, and Integument KHPLAN' , . medical ^^ SIMPLE EPITHELIA There are four types of tissues in humans and these make up all of the organs and binding material in the body.
Epithelial tissue makes up linings of the body. In many cases, where there is exposure (outside, such as the skin, or inside, such as in blood vessels), epithelium is the tissue found. It is named according to its layers (typically simple or stratified) and the shape of cells (such as cuboidal). Simple squamous epithelium is a single layer of flattened cells. Simple cuboidal epithelium is also a single layer of cells but the cells are in the shape of cubes. Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of long columnar cells.
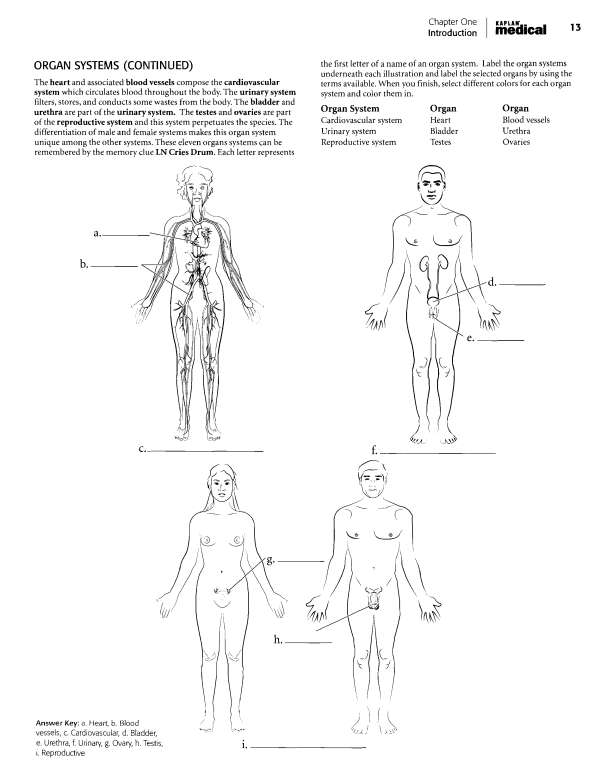
Label and color these epithelial types and pay attention to the basement membrane, the noncellular layer that attaches the epithelium to lower layers. It should be colored red. Color the nuclei in purple, the cytoplasm blue, and label the cells. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is in a single layer of cells but it looks stratified on first appearance. Not all of the cells reach the surface of the tissue. All of the cells reach the basement membrane.
Label and color the nuclei, basement membrane, cell membrane and the cilia in this tissue. Top view . '/':_: ;. Side view 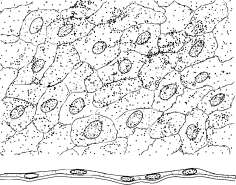












 Chapter One Introduction medical '^ BODY CAVITIES The organs of the body are frequently found in body cavities. The body is divided into two main cavities, the dorsal body cavity and the ventral body cavity. The dorsal body cavity consists of the cranial cavity, vifhich houses the brain and the spinal canal, vi^hich surrounds the spinal cord. The ventral body cavity contains the upper thoracic cavity, vi^hich is subdivided into the pleural cavities, housing the lungs, and the mediastinum.
Chapter One Introduction medical '^ BODY CAVITIES The organs of the body are frequently found in body cavities. The body is divided into two main cavities, the dorsal body cavity and the ventral body cavity. The dorsal body cavity consists of the cranial cavity, vifhich houses the brain and the spinal canal, vi^hich surrounds the spinal cord. The ventral body cavity contains the upper thoracic cavity, vi^hich is subdivided into the pleural cavities, housing the lungs, and the mediastinum. Answer Key: a. Dorsal body cavity, b. Cranial cavity, c.
Answer Key: a. Dorsal body cavity, b. Cranial cavity, c. The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bUayer. Color the phosphate molecules on the outside and inside of the membrane one color and the lipid layer another color. Cholesterol molecules occur in the membrane and, depending on their concentration, can make the membrane stiff or more fluid.
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bUayer. Color the phosphate molecules on the outside and inside of the membrane one color and the lipid layer another color. Cholesterol molecules occur in the membrane and, depending on their concentration, can make the membrane stiff or more fluid. Answer Key: a.
Answer Key: a.