A LONG WAY HOME
A LONG WAY HOME
Migrant Worker Worlds 18002014
Edited by Peter Delius, Laura Phillips and
Fiona Rankin-Smith

Published in South Africa by:
Wits University Press
1 Jan Smuts Avenue
Johannesburg, 2001
www.witspress.co.za
Published edition Wits University Press 2014
Compilation Edition editors 2014
Chapter Individual contributors 2014
Text editors Peter Delius and Laura Phillips 2014
Image editor Fiona Rankin-Smith 2014
First published 2014
ISBN: 978-1-86814-767-0 (print)
ISBN: 978-1-86814-768-7 (digital)
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the written permission of the publisher, except in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright Act, Act 98 of 1978.
All images remain the property of the copyright holders. The publishers gratefully acknowledge the publishers, institutions and individuals referenced in captions for the use of images. Every effort has been made to locate the original copyright holders of the images reproduced here; please contact Wits University Press at the address above in the case of any omissions or errors.
Cover artwork Tito Zungu, decorated envelope, pen on paper, date unrecorded, 8.9 15 cm, Standard Bank African Art Collection (Wits Art Museum)
Copy edited by Alison Lockhart
Proofread by Inga Norenius and Julie Miller
Indexed by Clifford Perusset
Cover design by Emmaneel Vorster
Book design and layout by Oliver Barstow
Printed and bound by Paarl Media, Paarl
Acknowledgements
This book and its accompanying exhibition were made possible only with the help and support of a large group of people. In particular, we would like to extend thanks to those who commented on drafts and gave advice on the manuscript, including Harriet Perlman, William Beinart, Deborah James, Luli Callinicos and Saul Dubow.
We would also like to thank the Wits Art Museum (WAM) gallery staff and Gail Behrmann, Isabella Kentridge and Sarah Delius for their help in collecting and compiling images for use in the book. Thanks too to Oliver Barstow of Fourthwall Books for his layout expertise.
We are most grateful for the sponsorship from Hollard, Standard Bank and Lauren Gore, whose contributions helped make this publication possible.

INTRODUCTION
Highlighting Migrant Humanity
Peter Delius and Laura Phillips
In the twentieth century, South Africa became internationally infamous for a pervasive system of racial discrimination. Less widely acknowledged is how fundamental migrant labour was to the making of modern South African society. Nowhere else in the world have urbanisation and industrialisation been as comprehensively based on migrant labour as in South Africa. Migrancy and institutionalised racism fed off each other and shaped the lives and deaths of millions of people. And, as the tragic events at Marikana have underscored, it is a system that haunts South Africas present as well as its past.
The main aim of this book is to portray migrant experience, agency and humanity in thought, action and expression dimensions that are often neglected in overviews of the migrant labour system. It can be read on its own, but it was conceived during the planning of an art exhibition on migrant life entitled Ngezinyawo Migrant Journeys, which opened at the Wits Arts Museum in April 2014. It is our hope that this book, together with the images, artefacts and soundtracks in the exhibition, will provide an enriched perspective on the history of migrant labour.
Migrants have often been presented as victims tossed to and fro on currents entirely out of their control. In this view, they have no agency and certainly no part in shaping the development and the form of the system. While there is no doubting the asymmetries of power in the making of an economy based on migrant labour, there is a considerable body of research from recent decades that has qualified this account, showing how migrant struggles and choices helped to shape the system. What has also emerged much more clearly is how migrants found ways to assert and express their humanity. They crafted rich forms of art, dress, dance, music and song. They created a myriad of social forms from burial societies to mine marriages to sustain them in desolate and often dangerous environments. They conjured forms of masculinity that enabled them to conceive of their lives as the heroic struggles of warriors in a peculiar form of purgatory. As the twentieth century progressed and growing numbers of women travelled to town, their presence created new economic and social practices and added vivid strands to the tapestry of city life.
A view from above
A focus on migrant experience and agency needs to be located in a wider understanding of the migrant labour system. At the outset, it is worth recalling that migrant labour in southern Africa, despite its highly coercive character, was not a uniquely or even supremely harsh form of labour mobilisation:
Many labour systems around the world were more draconian, coercive and brutal than South Africas. Plantation slavery in the New World and Soviet forced labour in the Siberian gold mines made the harsh conditions in the South African mines pale by comparison. But most of these systems never aspired to be voluntary labour systems operating under the norms of modern industrial capitalism.
Neither was southern Africa unusual in the importance of migrant labour in the early phases of industrialisation. But it differed from many other societies in that it increased in importance over time, and was entrenched through an insidious system of pass controls and removals from urban areas.
There are few commentators today who would dispute that migrant labour has been a deeply destructive part of our history. Many accounts of the systems evolution emphasise the extent to which it was created and shaped by capital and the state. These explanations focus on the last decades of the nineteenth century, as an increasingly pervasive participation in migrant labour was entrenched by colonial conquest, the loss of vast swathes of land, the imposition of taxes, draconian pass laws and centralised recruiting. By the early twentieth century, the system provided cheap labour on a large scale to the mines, factories and some farms. In the ensuing decades, workers wages stagnated, while rural economic resources, which had helped to prop up their families, were placed under mounting strain. Some of the more fertile rural areas were able to sustain significant levels of food production, but in most regions, very limited returns from farming and an expanding need for cash ensured that men (and increasingly women) had no option but to find employment on the mines and farms and in the cities.
Table 0.1 Contract labour migration to South African mines
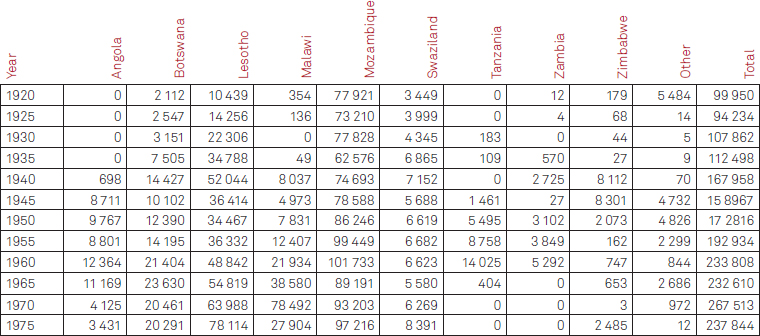
Source: J Crush, V Williams and S Peberdy, Migration in Southern Africa. A paper prepared for the Policy Analysis and Research Programme of the Global Commission on International Migration, September 2005, p. 3
Workers, far from their homes and families, were penned for achingly long periods of time in soulless, single-sex compounds, where they were subject to a tribalised and authoritarian system of administration. These prison-like structures were also designed to minimise workers contact with trade unions and political organisations. The impediments to worker organisation, collective consciousness and action under these conditions are a much more credible explanation for a low-wage economy than continuing access to rural resources of the families of migrant workers.
Next page












