 Please visit our website, www.garethstevens.com. For a free color catalog of all our high-quality books, call toll free 1-800-542-2595 or fax 1-877-542-2596. Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Richards, Jon. | Simkins, Ed. Title: Materials / Jon Richards and Ed Simkins. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index.
Please visit our website, www.garethstevens.com. For a free color catalog of all our high-quality books, call toll free 1-800-542-2595 or fax 1-877-542-2596. Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Richards, Jon. | Simkins, Ed. Title: Materials / Jon Richards and Ed Simkins. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index.
Identifiers: ISBN 9781538242834 (pbk.) | ISBN 9781538242858 (library bound) | ISBN 9781538242841 (6 pack) Subjects: LCSH: Materials--Juvenile literature. | Materials science--Juvenile literature. | Information visualization--Juvenile literature. Classification: LCC TA403.2 R47 2020 | DDC 620--dc23 Published in 2020 by Gareth Stevens Publishing 111 East 14th Street, Suite 349 New York, NY 10003 Copyright 2020 Wayland, a division of Hachette Childrens Group All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without permission from the publisher, except by a reviewer. Printed in the United States of America CPSIA compliance information: Batch #CS19GS: For further information contact Gareth Stevens, New York, New York at 1-800-542-2595.
CONTENTS ATOMS AND MOLECULES Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. Atoms combine to make everything in the universe, including your body and enormous, blazing stars. 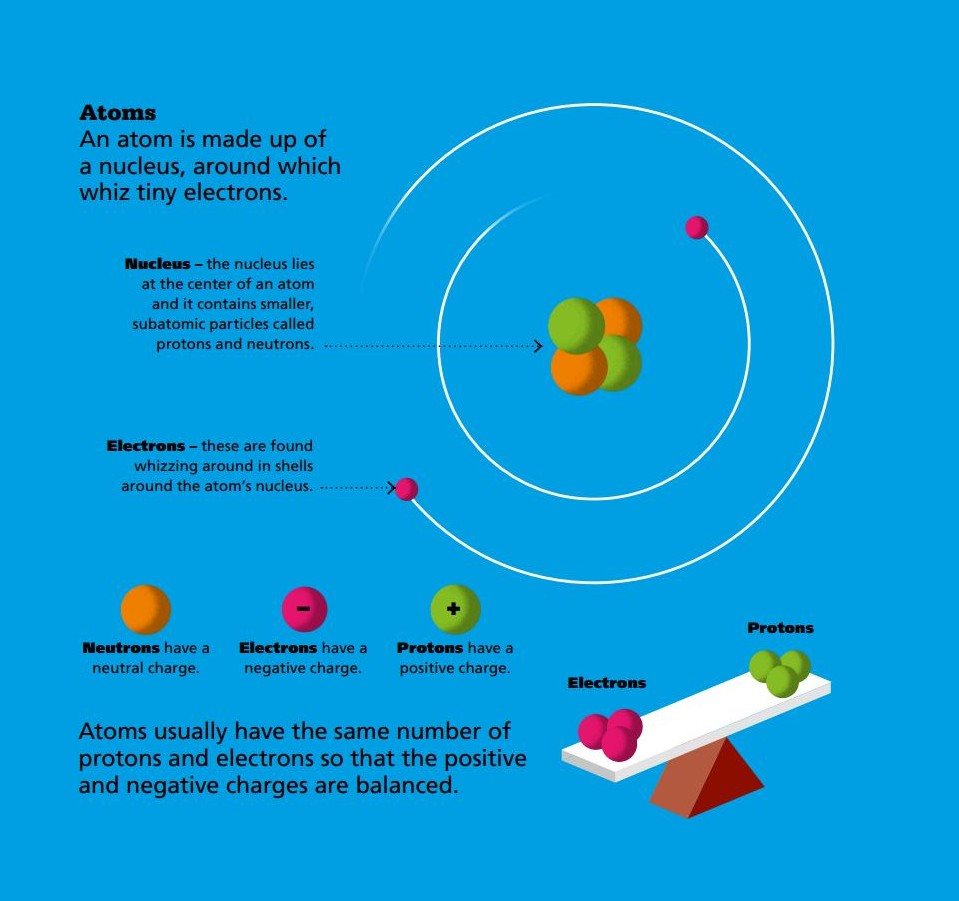
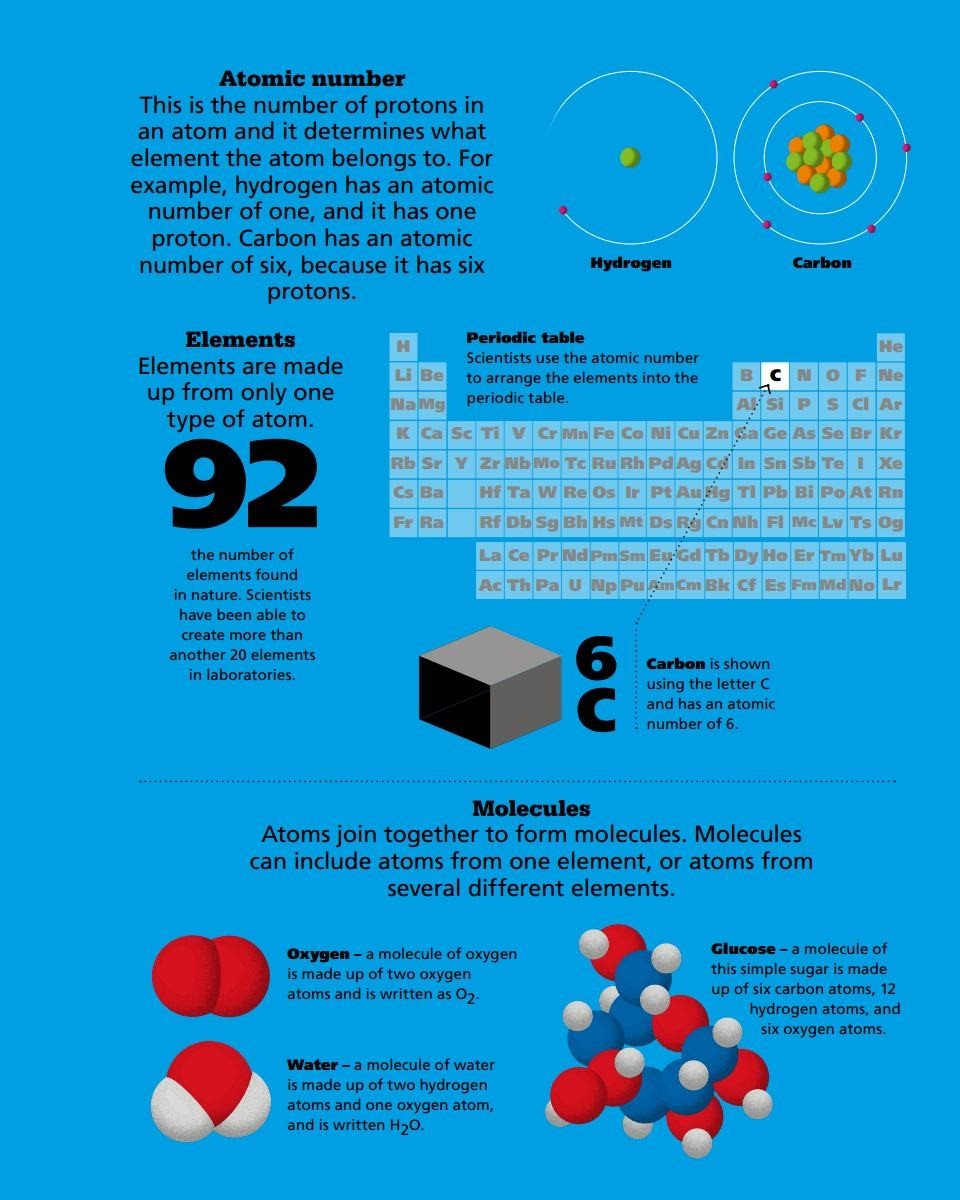 SOLIDS Matter and materials come in different forms, or states. Something that is solid has a fixed shape, it cannot flow, and it cannot be compressed, or squashed.
SOLIDS Matter and materials come in different forms, or states. Something that is solid has a fixed shape, it cannot flow, and it cannot be compressed, or squashed. 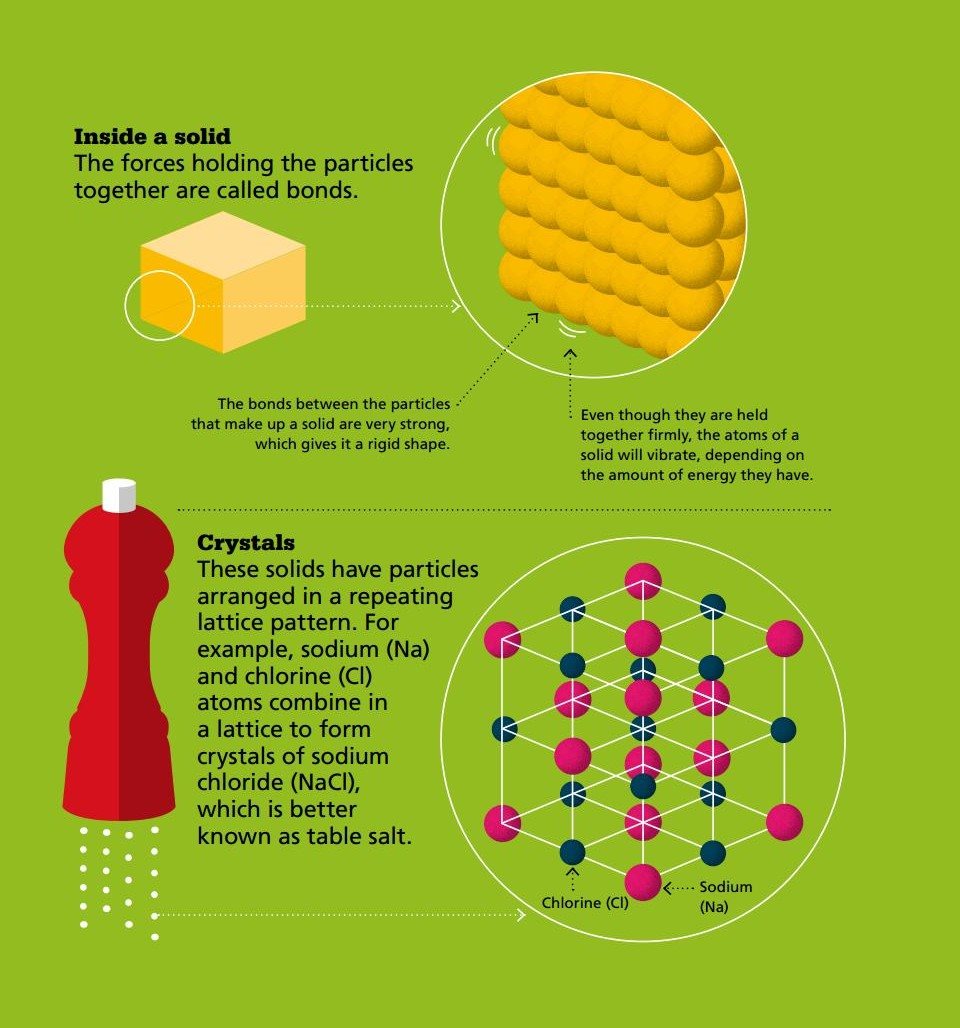
 CARBON This amazing element appears in a wide range of different forms.
CARBON This amazing element appears in a wide range of different forms. 
 LIQUIDS Liquids can flow and will take on the shape of anything they are poured into, but they will have a fixed volume and cannot be compressed.
LIQUIDS Liquids can flow and will take on the shape of anything they are poured into, but they will have a fixed volume and cannot be compressed. 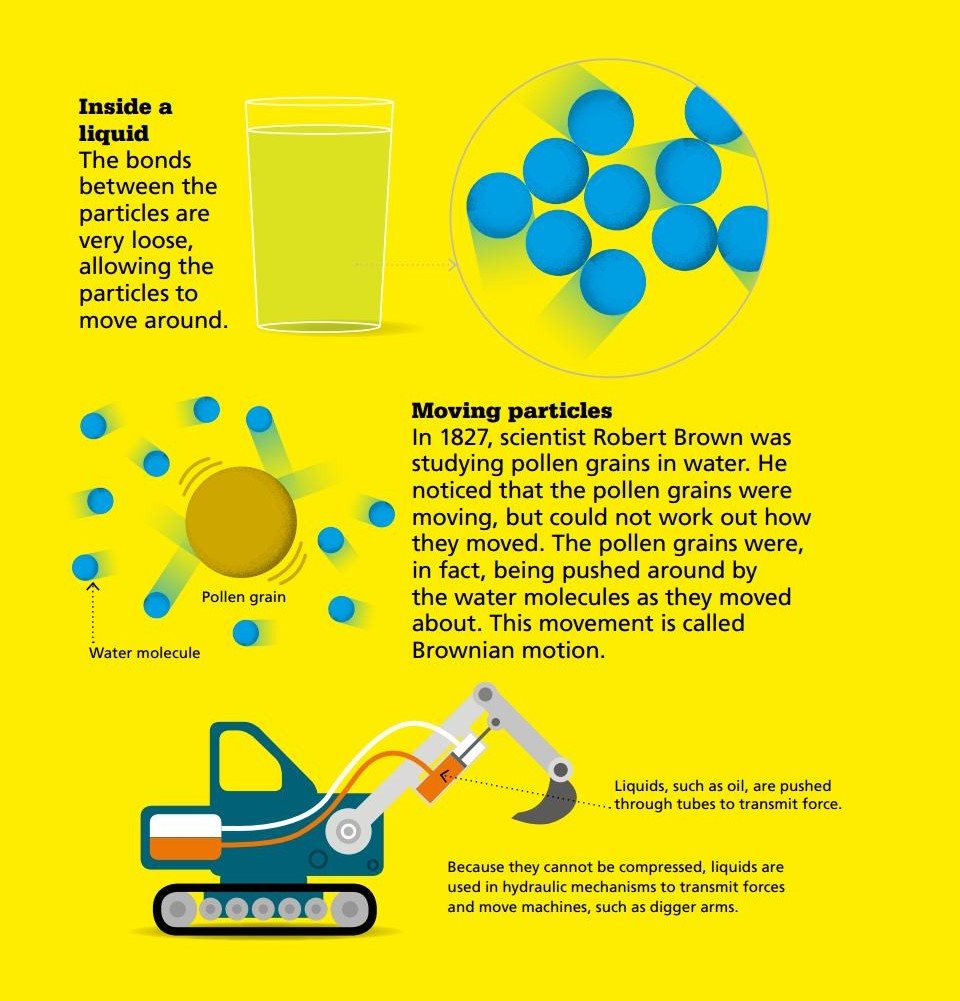
 WATER Water is the most common liquid on the planet and is the only substance that naturally exists in solid, liquid, and gas states on Earth.
WATER Water is the most common liquid on the planet and is the only substance that naturally exists in solid, liquid, and gas states on Earth. 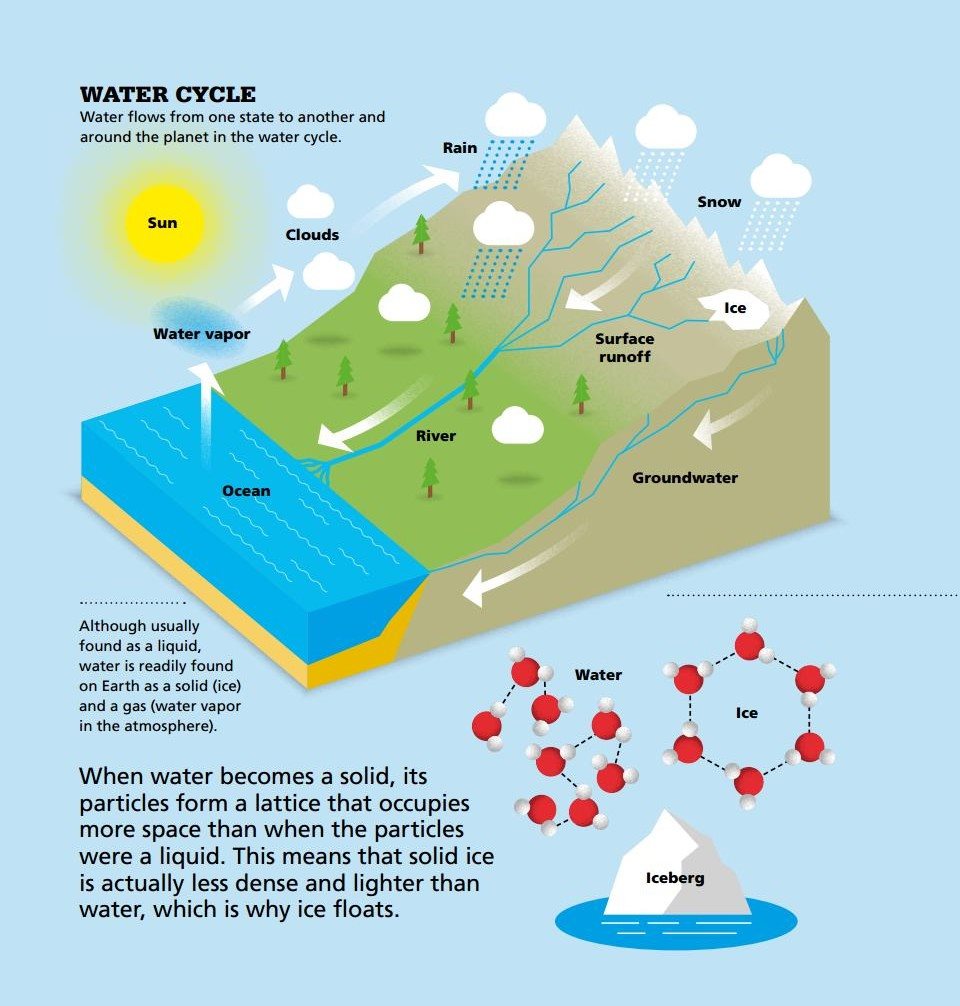
 GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space.
GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space. 
 GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space.
GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space.
As gases expand, the particles that make them up get farther and farther apart. 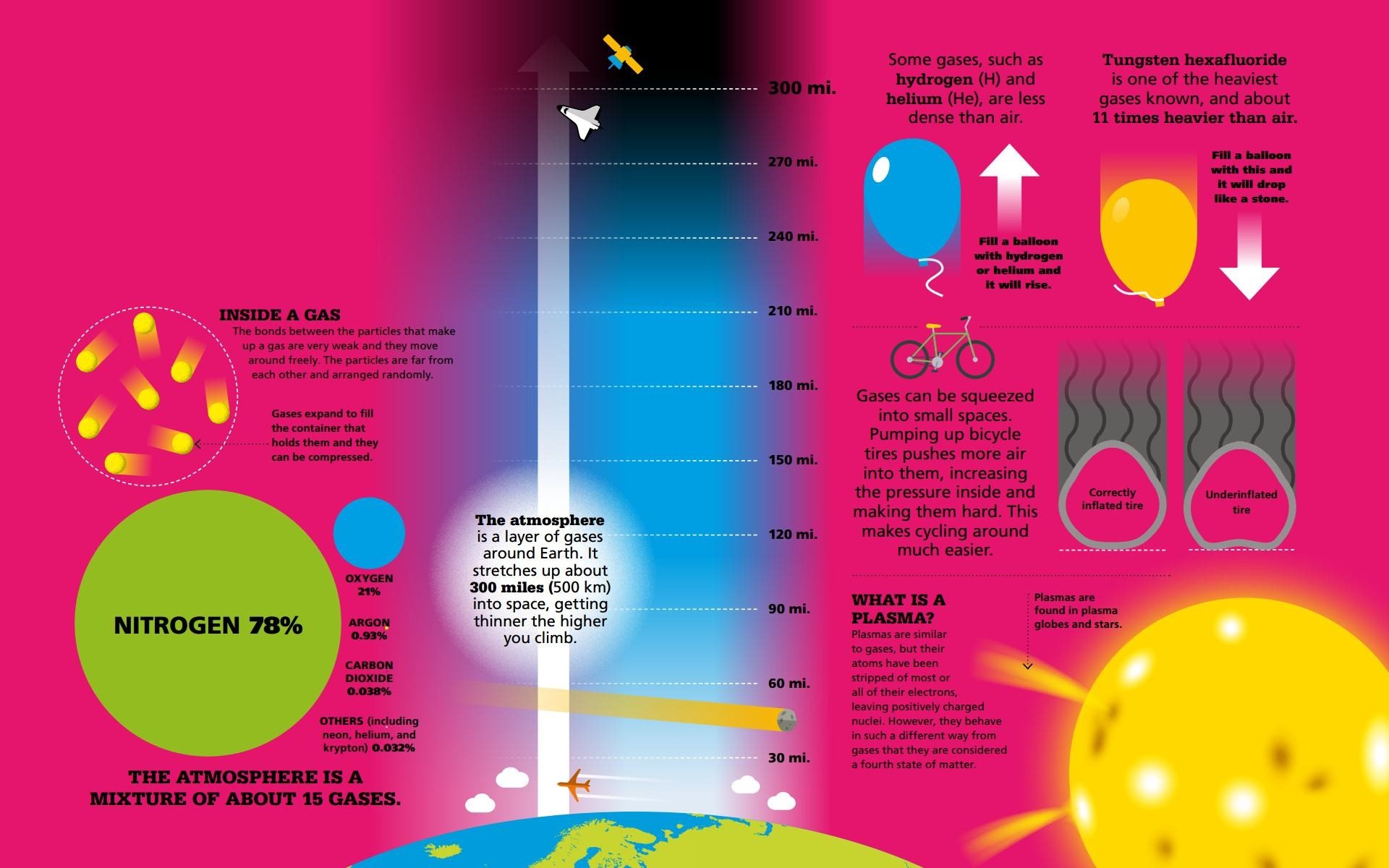 HYDROGEN Hydrogen (H) is a colorless, odorless gas, but its amazing properties make it one of the most important elements in the universe.
HYDROGEN Hydrogen (H) is a colorless, odorless gas, but its amazing properties make it one of the most important elements in the universe. 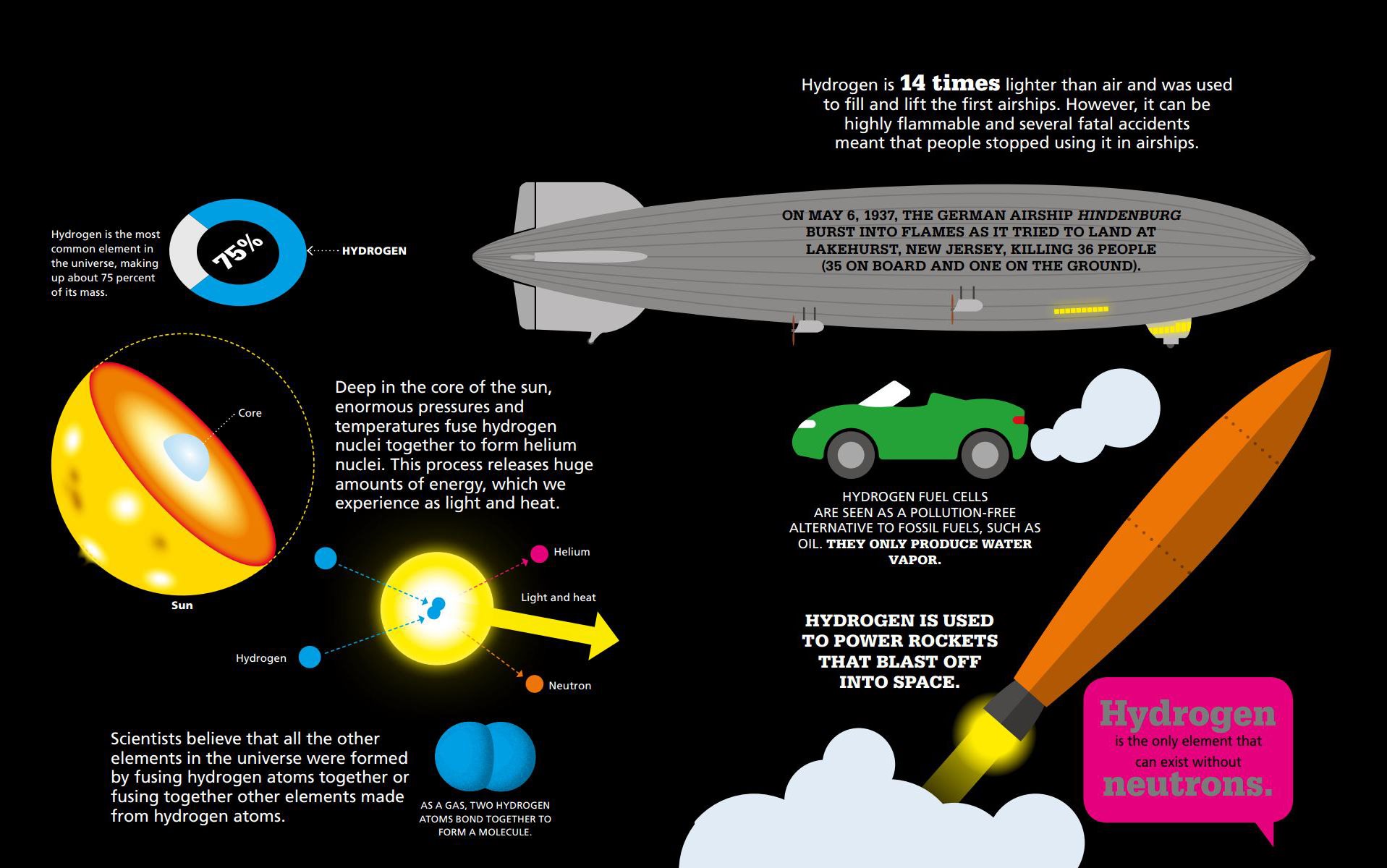 MELTING AND FREEZING Moving from one state to another requires a change in temperature. Changing from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while changing from a liquid to a solid is called freezing.
MELTING AND FREEZING Moving from one state to another requires a change in temperature. Changing from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while changing from a liquid to a solid is called freezing. 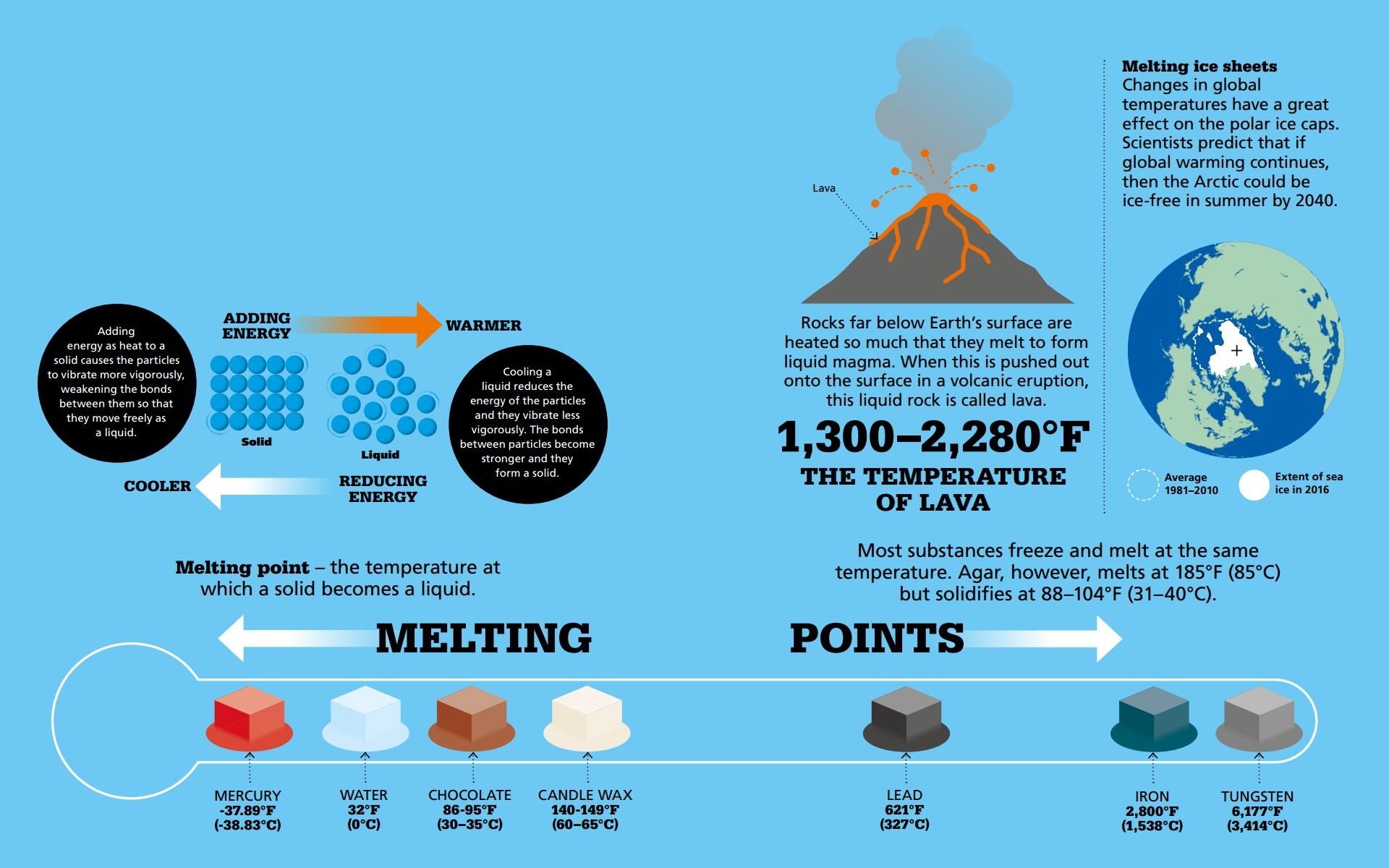 BOILING AND CONDENSING Changing from a liquid to a gas is called boiling, while changing from a gas to a liquid is called condensing.
BOILING AND CONDENSING Changing from a liquid to a gas is called boiling, while changing from a gas to a liquid is called condensing. 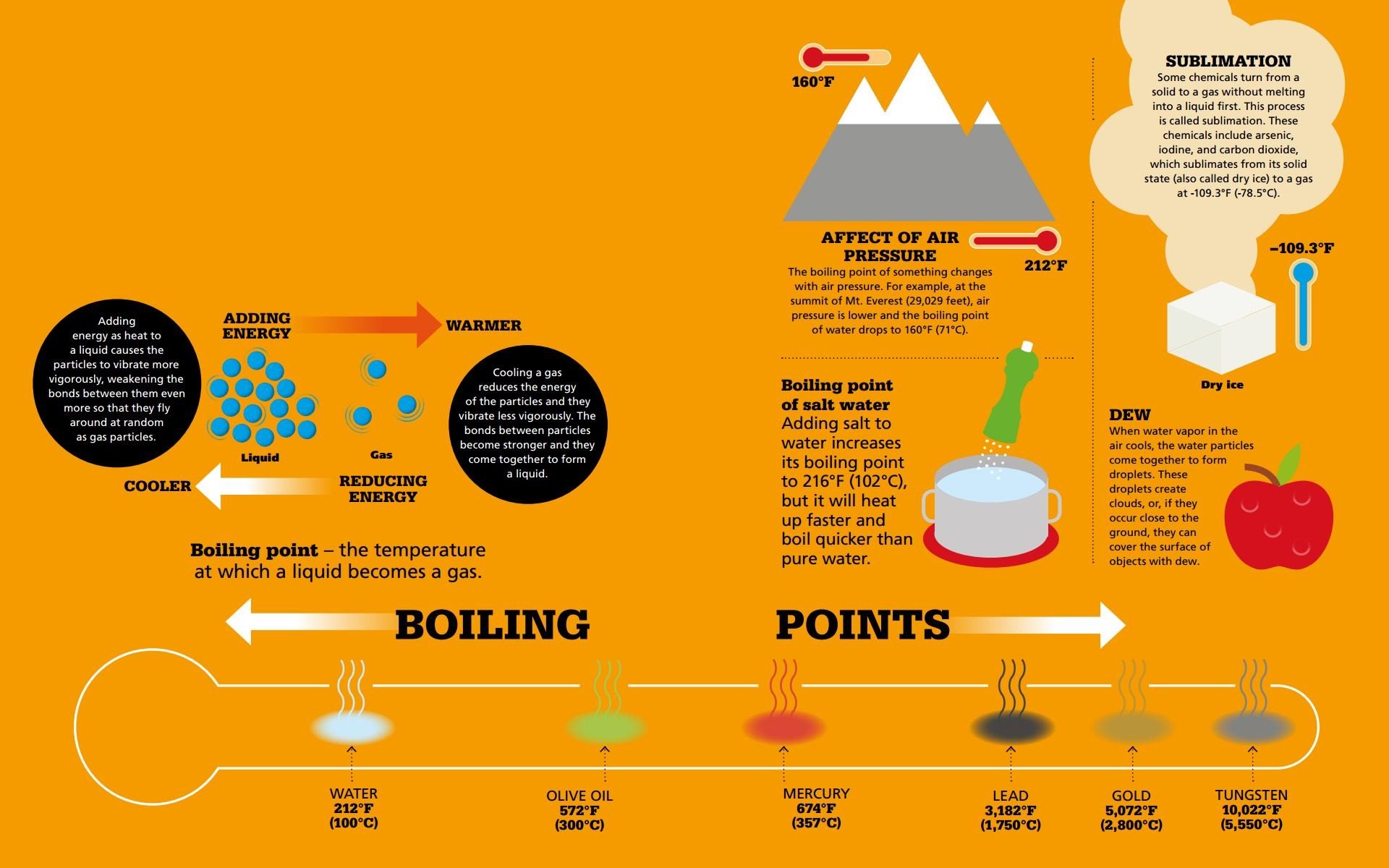 HARD AND SOFT Different materials have different properties.
HARD AND SOFT Different materials have different properties.
They may not look and feel the same, and could be suitable for various roles. One of the properties scientists use to define materials is how hard or soft they are.  PLASTIC AND ELASTIC Materials can be classified on how they react when a force is applied to them will they bend and stretch and then return to their original size, or will they take on their new shape permanently?
PLASTIC AND ELASTIC Materials can be classified on how they react when a force is applied to them will they bend and stretch and then return to their original size, or will they take on their new shape permanently? 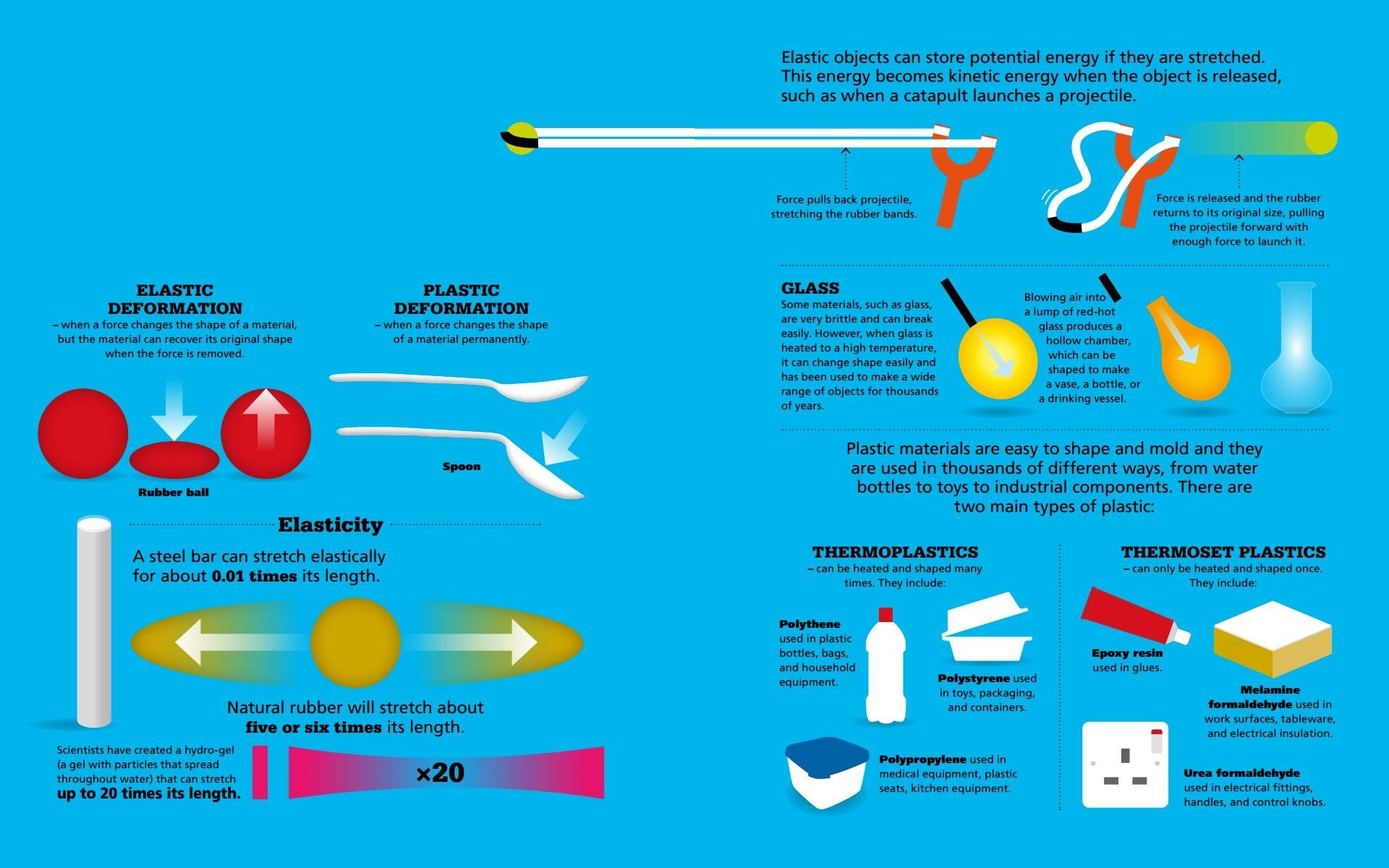 ACIDS AND BASES Liquids can be classified on their acidity, or how they react to other substances. The level of acidity includes acids at one end of the scale and bases and alkalis at the other. While these substances can be very dangerous if they are strong, they have many important everyday uses and some play a vital role in keeping us alive.
ACIDS AND BASES Liquids can be classified on their acidity, or how they react to other substances. The level of acidity includes acids at one end of the scale and bases and alkalis at the other. While these substances can be very dangerous if they are strong, they have many important everyday uses and some play a vital role in keeping us alive. 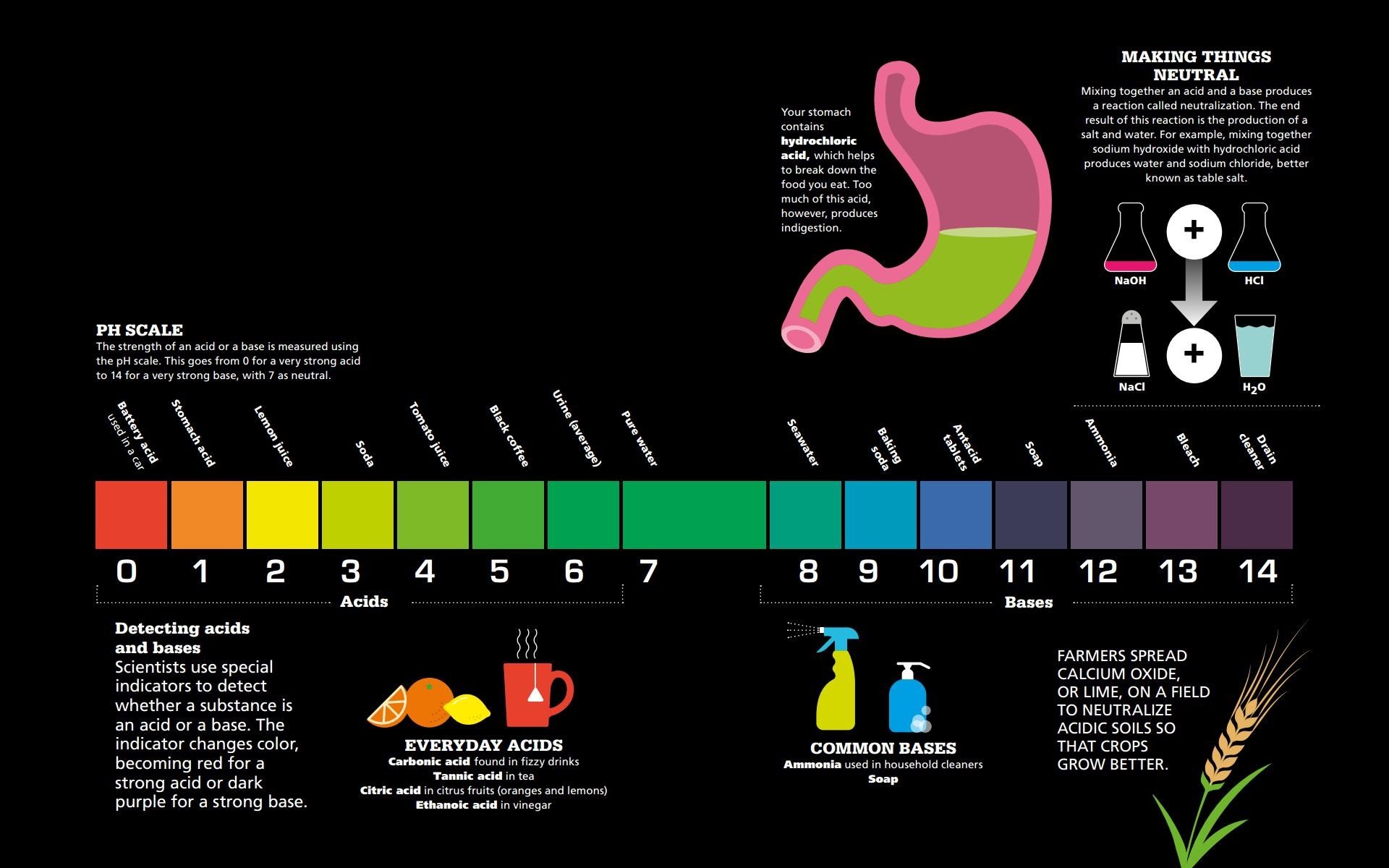 MIXTURES AND COMPOSITES Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are mixed together without reacting with each other.
MIXTURES AND COMPOSITES Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are mixed together without reacting with each other.
Substances are also combined to form new and very useful materials. 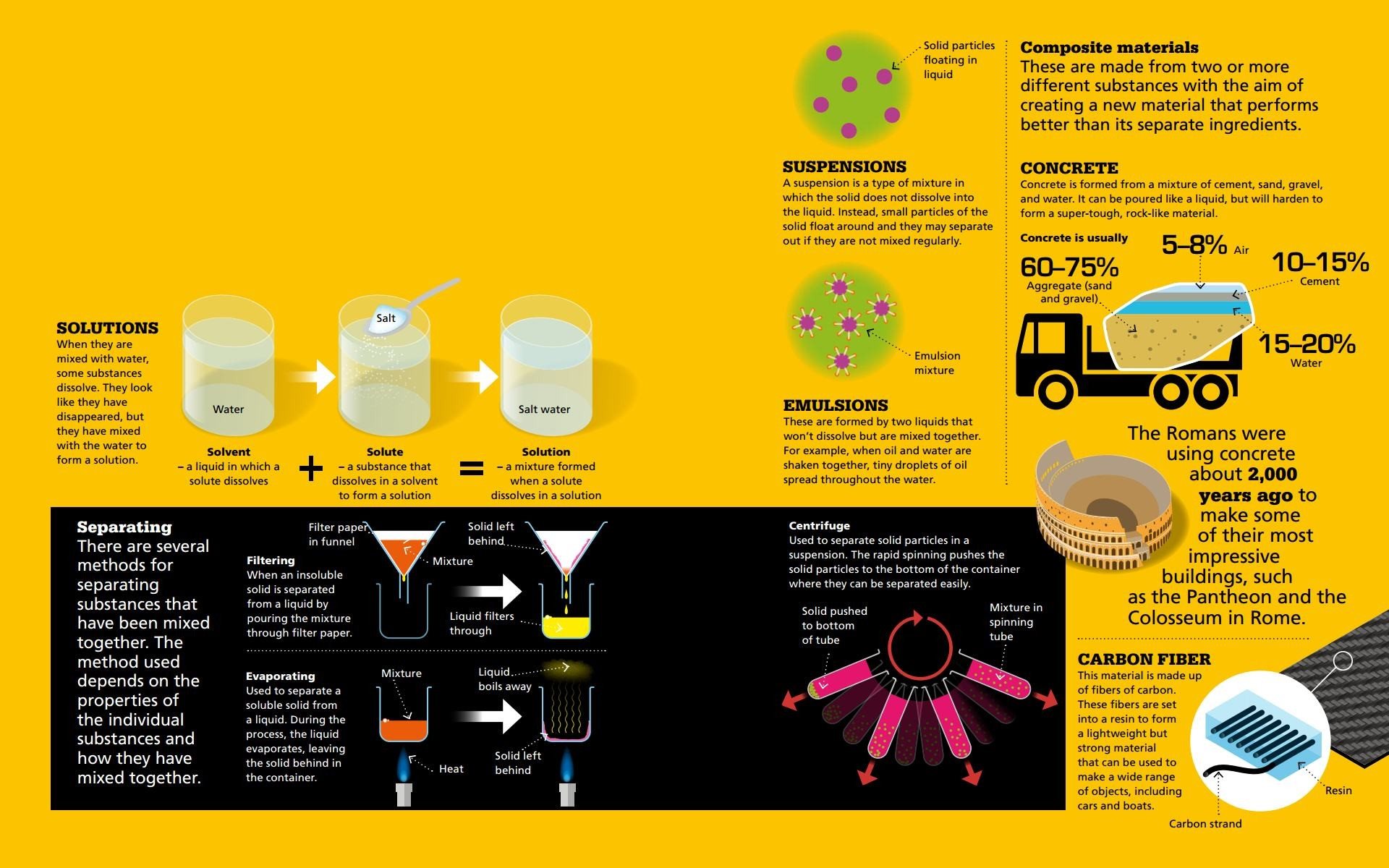 GLOSSARY acid A highly reactive liquid that can dissolve some substances. alloy A mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal with another element, such as carbon. atom A basic building block of matter, made of electrons, protons, and neutrons. base A substance that reacts with an acid to produce water and a salt. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid.
GLOSSARY acid A highly reactive liquid that can dissolve some substances. alloy A mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal with another element, such as carbon. atom A basic building block of matter, made of electrons, protons, and neutrons. base A substance that reacts with an acid to produce water and a salt. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid.
Clay and sand are examples of ceramics. compress To squeeze something into a smaller space. Gases can be compressed, while solids and liquids cannot. condense To change state from a gas to a liquid. crystal A solid made of atoms or molecules arranged in a regular pattern. electron A negatively charged subatomic particle. element A form of matter containing just one kind of atom. fossil fuel A fuel, such as coal, oil, and gas, that is found in the earth. fossil fuel A fuel, such as coal, oil, and gas, that is found in the earth.
Next page










 Please visit our website, www.garethstevens.com. For a free color catalog of all our high-quality books, call toll free 1-800-542-2595 or fax 1-877-542-2596. Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Richards, Jon. | Simkins, Ed. Title: Materials / Jon Richards and Ed Simkins. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index.
Please visit our website, www.garethstevens.com. For a free color catalog of all our high-quality books, call toll free 1-800-542-2595 or fax 1-877-542-2596. Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Richards, Jon. | Simkins, Ed. Title: Materials / Jon Richards and Ed Simkins. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index. | Series: Science in infographics | Includes glossary and index.
 SOLIDS Matter and materials come in different forms, or states. Something that is solid has a fixed shape, it cannot flow, and it cannot be compressed, or squashed.
SOLIDS Matter and materials come in different forms, or states. Something that is solid has a fixed shape, it cannot flow, and it cannot be compressed, or squashed. 
 CARBON This amazing element appears in a wide range of different forms.
CARBON This amazing element appears in a wide range of different forms. 
 LIQUIDS Liquids can flow and will take on the shape of anything they are poured into, but they will have a fixed volume and cannot be compressed.
LIQUIDS Liquids can flow and will take on the shape of anything they are poured into, but they will have a fixed volume and cannot be compressed. 
 WATER Water is the most common liquid on the planet and is the only substance that naturally exists in solid, liquid, and gas states on Earth.
WATER Water is the most common liquid on the planet and is the only substance that naturally exists in solid, liquid, and gas states on Earth. 
 GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space.
GASES AND PLASMAS Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a set volume and can expand to fill any space.  HYDROGEN Hydrogen (H) is a colorless, odorless gas, but its amazing properties make it one of the most important elements in the universe.
HYDROGEN Hydrogen (H) is a colorless, odorless gas, but its amazing properties make it one of the most important elements in the universe.  MELTING AND FREEZING Moving from one state to another requires a change in temperature. Changing from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while changing from a liquid to a solid is called freezing.
MELTING AND FREEZING Moving from one state to another requires a change in temperature. Changing from a solid to a liquid is called melting, while changing from a liquid to a solid is called freezing.  BOILING AND CONDENSING Changing from a liquid to a gas is called boiling, while changing from a gas to a liquid is called condensing.
BOILING AND CONDENSING Changing from a liquid to a gas is called boiling, while changing from a gas to a liquid is called condensing.  HARD AND SOFT Different materials have different properties.
HARD AND SOFT Different materials have different properties. PLASTIC AND ELASTIC Materials can be classified on how they react when a force is applied to them will they bend and stretch and then return to their original size, or will they take on their new shape permanently?
PLASTIC AND ELASTIC Materials can be classified on how they react when a force is applied to them will they bend and stretch and then return to their original size, or will they take on their new shape permanently?  ACIDS AND BASES Liquids can be classified on their acidity, or how they react to other substances. The level of acidity includes acids at one end of the scale and bases and alkalis at the other. While these substances can be very dangerous if they are strong, they have many important everyday uses and some play a vital role in keeping us alive.
ACIDS AND BASES Liquids can be classified on their acidity, or how they react to other substances. The level of acidity includes acids at one end of the scale and bases and alkalis at the other. While these substances can be very dangerous if they are strong, they have many important everyday uses and some play a vital role in keeping us alive.  MIXTURES AND COMPOSITES Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are mixed together without reacting with each other.
MIXTURES AND COMPOSITES Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are mixed together without reacting with each other. GLOSSARY acid A highly reactive liquid that can dissolve some substances. alloy A mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal with another element, such as carbon. atom A basic building block of matter, made of electrons, protons, and neutrons. base A substance that reacts with an acid to produce water and a salt. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid.
GLOSSARY acid A highly reactive liquid that can dissolve some substances. alloy A mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal with another element, such as carbon. atom A basic building block of matter, made of electrons, protons, and neutrons. base A substance that reacts with an acid to produce water and a salt. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid. ceramic A nonmetallic solid that does not conduct electricity and is not easily dissolved by acid.