Published by Black Inc.,
an imprint of Schwartz Books Pty Ltd
Level 1, 221 Drummond Street
Carlton VIC 3053, Australia
www.blackincbooks.com
Copyright John Martinkus 2020
John Martinkus asserts his right to be known as the author of this work.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without the prior consent of the publishers.
9781760642426 (paperback)
9781743821350 (ebook)
Cover design by Akiko Chan
Text design and typesetting by Akiko Chan
Map by John Waddingham
All images supplied
Cover image NurPhoto / Getty Images
To all the West Papuans, dead and alive, who have dedicated their lives to justice since the illegal Indonesian takeover of 1961.
To the activists, journalists, health workers, priests and nuns who have given so much to help the people of this tormented land, and still do.
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
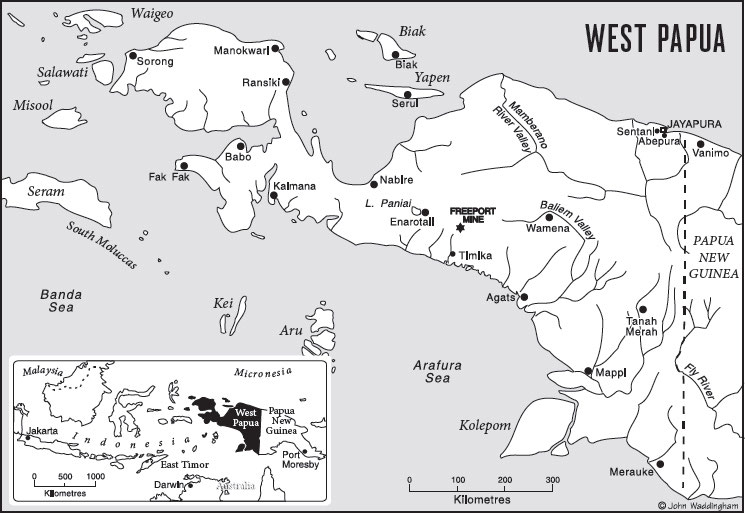
It was a kind of obsession for the men who had had their first taste of conquering and combat in what was then Dutch New Guinea. They jumped in from aircraft or arrived by landing craft at remote locations to, as they saw it, remove the last vestiges of Dutch colonialism from their domain. They were tough men in unmapped jungle with little idea what they would face: hostile natives, difficult terrain, a lack of supplies. And so, when those 1200 or so Indonesian paratroopers leapt into West Papua in 1961 and 62, they were easily defeated. The Dutch marines rounded them up, with the help of the spear tips and arrows of the local population. One Dutch marine spoke of feeling sick as he watched two ragged Indonesian soldiers be dragged out of the jungle, shot dead on a bridge and their bodies dumped in the river. He saw prisoners delivered to the Papuan auxiliaries. The Papuans saw no point in keeping the prisoners, and besides, it kept the other ones quiet. Starving, sick and with the arses literally rotting out of their fatigues, the Indonesians were paraded in front of the newsreel cameras of the day.
It was a diplomatic fluke and not a military victory that won Indonesia the territory of Dutch New Guinea. But those junior officers who survived their own failed attack later became generals, obsessed with an idea that would justify their suffering and eulogise the dead superiors and comrades of their youth: building the road. The Trans-Papua Highway, which would finally fulfil the Sukarno-era boast of a unified Indonesian nation. From Sabang to Merauke, the president would chant to cheering rallies, referring to the easternmost island off the tip of Aceh and the southernmost town in West Papua, the latter barely a days ride in a tinnie with an outboard to Australia across the Torres Strait. The Trans-Papua Highway would traverse some of the most remote and inhospitable terrain in Asia. An area with mountains so high that it has one of the few equatorial glaciers in the world. A place where people are dying to this day, fighting and fleeing Indonesian military operations.
The plan evolved in the minds of the generals and their civil servants. They would push out from Sorong on the birds head, an important port on the tip of West Papua. They would work down from the next regional town, Manokwari, and out from the capital, Jayapura, both on the north coast. Then, in a pincer movement, they would link and push through to the highlands, through Nduga province to the capital of the isolated Baliem Valley, Wamena. Wamena had only had its first European visitor in 1904; it wasnt until 1920 and 1938 that other expeditions came through.
The Dani and Nduga people who inhabit this part of the West Papuan highlands are different. They are physically tougher, due to their environment of high-altitude jungle and mountains, and they are culturally different as well: centuries of limited contact with the coastal tribes, and internecine fighting and almost ceremonial wars with each other, have bred a very robust people. They refuse to admit their region is part of Indonesia and will not speak Bahasa. They are not people likely to back down. But the generals, with their dream of the road, did not care for the wishes of the Nduga and the Dani. In the words of Indonesian defence minister Ryamizard Ryacudu (a former general with a history of human rights abuses), they would crush them. And now we are witnessing from a distance, due to restrictions put in place by the generals what crushing means.
THE END OF THE ROAD
This is a story that covers many years and many trips I made to far-flung parts of Indonesia, mostly in search of conflicts to report on. I wanted to go where no Western journalists were allowed. I started in the mid-1990s in East Timor, now the independent country of Timor Leste, travelling as a tourist because journalists were banned. I hung out there, despite regular casual death threats and constant surveillance. Eventually I got up into the mountains with the pro-independence guerrillas. I hiked quietly with them in the jungle and slept in a tarpaulin-covered hole with branches over the top, hiding from the Indonesian troops who came so close we could hear their boots breaking twigs in the scrub. That band of men were mostly killed or captured the following year, after they attacked and killed thirty Indonesian police in an ambush near their hideout. Their commander, David Alex, was taken alive but never seen again.
I returned to East Timor again and again and, following the fall of the dictator Suharto in May 1998, I was able to stay there permanently and obtain a journalist visa. I covered the rise of the student opposition, reporting on the marches and protests and the inevitable backlash by the Indonesian military and the militias they used as a screen to hide their killing. Weeks that turned into months were spent covering massacres and killings across the provinces. Counting bodies, getting numbers of the dead. Basic reporting, really, but always in the face of threats from the Indonesian military, the police, their intelligence operatives and their militias, as they maintained the fiction that they were simply trying to keep the peace between two warring Timorese sides: the pro-independence movement and the Timorese militia, whom they were arming, organising, paying and driving around, and sometimes impersonating, to massacre their fellow citizens. For the record, Australia went along with this fiction until the final days, when the Timorese voted overwhelmingly for independence and the Indonesian state turned on both the East Timorese killing those they deemed pro-independence, burning and depopulating their towns and villages and the foreign community, forcing them to evacuate so they could finish their job without foreign witnesses. It is a modus operandi the Indonesian military used again in Aceh in 2003 and, at the time of writing, is using in West Papua.