DON'T SWEAT THE TEST! Having a problem with math? Nervous about your test? This book introduces all the topics you need to know about pre-algebra and algebra. Learn great testtaking tips for solving multiple choice, short-answer, and show-your-work questions. A great book for students to use on their own, or with parents, teachers, or tutors.
"This book is a must read for anyone who is having trouble with algebra skills. It's a great review for standardized test preparation, too."
Patricia Leonard, MS, Series Math Consultant,
Middle School Math Professional
Need More Practice?
FREE WORKSHEETS AVAILABLE AT ENSLOW.COM
About The Author
AUTHOR REBECCA WINGARD-NELSON has worked in public, private, and home-school mathematics education. She has been involved in various educational math projects, including developing and writing state assessment tests, exit exams, and proficiency tests, as well as writing and editing textbooks and workbooks.

Most of the topics that are found on math tests are taught in the classroom.
Paying attention in class, taking good notes, and keeping up with your homework are the best ways to be prepared for tests. Use test preparation materials, such as flash cards and timed worksheets, to practice your basic math skills. Take practice tests. They show the kinds of items that will be on the actual test. They can show you what areas you understand, and what areas you need more practice in. Relax.
Eat a good meal. Go to bed early enough to get a good nights sleep. Dont cram on new material! Review the material you know is going to be on the test. Get what you need ready. Sharpen your pencils, set out things like erasers, a calculator, and any extra materials, like books, protractors, tissues, or cough drops. Get up early enough to eat breakfast and not have to hurry.
Wear something that is comfortable and makes you feel good. Listen to your favorite music. Get to school and class on time. Stay calm. Stay positive. Before you begin, take a deep breath.
Focus on the test, not the people or things around you. Remind yourself to do your best and not to worry about what you do not know. Work through the entire test, but dont spend too much time on any one problem. Dont rush, but move quickly, first answering all of the questions you can do easily. Go back a second time and answer the questions that take more time. Read each question completely.
Read all the answer choices. Eliminate answers that are obviously wrong. Read word problems carefully, and decide what the problem is asking. Check each answer to make sure it is reasonable. Estimate numbers to see if your answer makes sense. Concentrate on the test.
Stay focused. If your attention starts to wander, take a short break. Breathe. Relax. Refocus. Dont get upset if you cant answer a question.
Mark it, then come back to it later. When you finish, look back over the entire test. Are all of the questions answered? Check as many problems as you can. Look at your calculations and make sure you have the same answer on the blank as you do on your worksheet. Three common types of test problems are covered in this book: Multiple Choice, Show Your Work, and Explain Your Answer. Tips on how to solve each, as well as common errors to avoid, are also presented.
Knowing what to expect on a test and what is expected of you will have you ready to ace every math test you take.
There are different types of numbers that are used to show different values.
Is the number 2 a whole number?
Step 1: Find the definition of a whole number. Whole numbers are the numbers that begin at zero and go up by intervals of one. The lowest whole number is zero. The number 2 is a negative number.
It is less than zero. No, 2 is not a whole number. whole numbers: The numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,...counting numbers: The whole numbers except for 0.natural numbers: Natural numbers are defined in two ways, either the set of whole numbers, or the set of counting numbers.integers: Whole numbers and their opposites.
 Is the number 7 a whole number, counting number, or integer? Explain
Is the number 7 a whole number, counting number, or integer? Explain.
Solution: The only whole number that is not a counting number is zero. Since 7 is not zero, it is a whole number and a counting number. Integers include the set of all whole numbers.
Since 7 is a whole number, it is also an integer. The number 7 is a whole number, a counting number, and an integer.
Some problems ask a question and ask you to explain your answer. Others just ask for an answer. Your score may be based on a correct response as well as how clearly you explain your reasoning.The set of integers includes positive integers, negative integers, and zero. What integer is the opposite of 5? Step 1: Opposite integers are the same distance from zero on the number line, but are on opposite sides. What integer is the opposite of 5? Step 1: Opposite integers are the same distance from zero on the number line, but are on opposite sides.
The integer is five units left of zero. Find the integer that is five units right of zero. 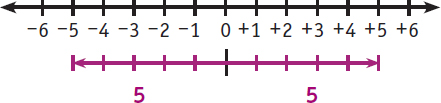 The opposite of 5 is +5. Multiple choice problems give you a list of solutions. Other kinds of problems ask you to provide the solution. Problems that ask you to provide the solution should be answered clearly and in complete sentences.
The opposite of 5 is +5. Multiple choice problems give you a list of solutions. Other kinds of problems ask you to provide the solution. Problems that ask you to provide the solution should be answered clearly and in complete sentences.
 Which number line illustrates the positive integer 4
Which number line illustrates the positive integer 4?

Positive integers are greater than zero.
On a number line, the positive integers are to the right of the zero. Negative integers are to the left of the zero. Since this problem asks for the positive integer, the answer will be to the right of the zero on the number line. The only answer that is to the right of the zero is answer c. Make sure it shows the positive integer 4.
The set of real numbers is made up of two types of numbers: rational numbers and irrational numbers.
Is 0.5 a rational number or an irrational number?
Step 1: Rational numbers can be either positive or negative.
Is 0.5 a rational number or an irrational number?
Step 1: Rational numbers can be either positive or negative.
Look at the number without looking at the sign. 0.5Step 2: Can you write 0.5 as a fraction? Yes. Decimal numbers are written as fractions by writing the decimal part of the number in the numerator and the place value of the last digit in the decimal part as the denominator. The digit 5 is in the tenths place, so use ten as the denominator. Reduce the fraction to lowest terms. 1/2The number 0.5 can be written as the negative fraction 1/2. 1/2 The number 0.5 can be written as the negative fraction 1/2.
Any number that can be written as a fraction is a rational number. 0.5 is a rational number. rational numbers: Numbers that can be written as a ratio, or fraction. For example, 1/4 is a rational number. All integers are rational numbers because they can be written as fractions. 5 = 5/1
















 Most of the topics that are found on math tests are taught in the classroom.
Most of the topics that are found on math tests are taught in the classroom.  Is the number 7 a whole number, counting number, or integer? Explain. Solution: The only whole number that is not a counting number is zero. Since 7 is not zero, it is a whole number and a counting number. Integers include the set of all whole numbers.
Is the number 7 a whole number, counting number, or integer? Explain. Solution: The only whole number that is not a counting number is zero. Since 7 is not zero, it is a whole number and a counting number. Integers include the set of all whole numbers. 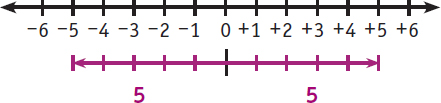 The opposite of 5 is +5. Multiple choice problems give you a list of solutions. Other kinds of problems ask you to provide the solution. Problems that ask you to provide the solution should be answered clearly and in complete sentences.
The opposite of 5 is +5. Multiple choice problems give you a list of solutions. Other kinds of problems ask you to provide the solution. Problems that ask you to provide the solution should be answered clearly and in complete sentences. Which number line illustrates the positive integer 4?
Which number line illustrates the positive integer 4?  Positive integers are greater than zero.
Positive integers are greater than zero.